Each processor, P0 and P1, has twelve DIMM slots (D0-D11), six on each processor
side. Each DIMM slot supports a single memory channel, for total of twelve DDR5
memory channels per processor (0-11).
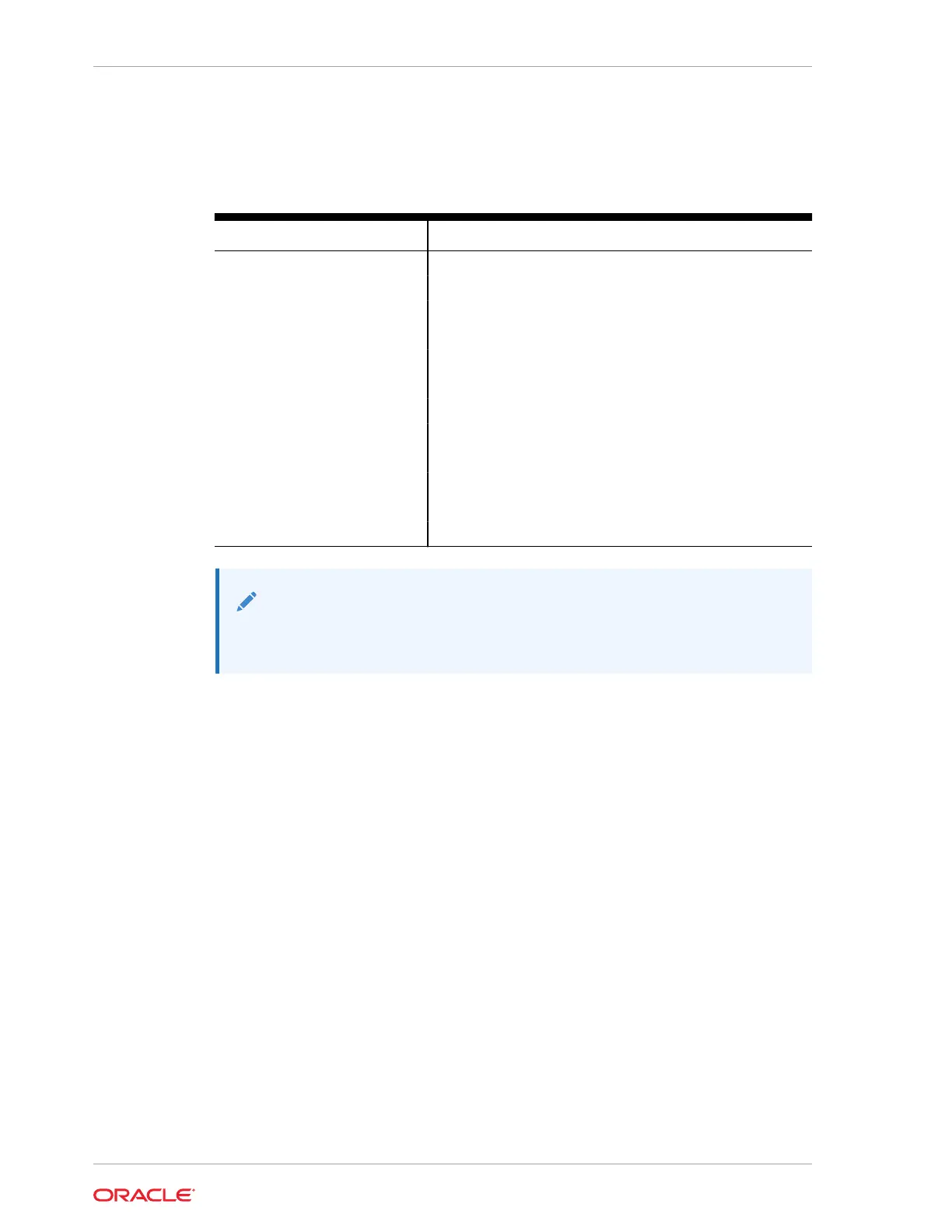
Table 4-1 Memory Channels and DIMM Slots for P0 and P1
Memory Channel DIMM Slot
0 D3
1 D1
2 D0
3 D5
4 D4
5 D2
6 D8
7 D10
8 D11
9 D6
10 D7
11 D9
Note:
In single-processor systems, the DIMM slots associated with processor 1
(P1) are nonfunctional and should not be populated with DIMMs.
DIMM Population Scenarios
There are two scenarios in which you are required to populate DIMMs:
• A DIMM fails and needs to be replaced.
In this scenario, you can use the Fault Remind button to determine the failed
DIMM, and then remove the failed DIMM and replace it. To ensure that system
performance is maintained, you must replace the failed DIMM with a DIMM of the
same size (in gigabytes) and type (quad-rank or dual-rank). In this scenario, do not
change the DIMM configuration.
• You purchased new DIMMs and want to use them to upgrade the server memory.
In this scenario, you must adhere to the DIMM population rules and follow the
recommended DIMM population order for optimal system performance.
DIMM Population Rules
The population rules for adding DIMMs to the server are as follows:
• The server supports:
– Up to 24 DDR5 DIMMs, 12 per processor socket.
– 64 GB dual-rank (DR) Registered DIMMs (RDIMMS).
Chapter 4
Servicing DIMMs (CRU)
4-10

 Loading...
Loading...









