EGM-5 Operation Manual V. 1.04 124 support@ppsystems.com
Appendix 1. Soil CO
2
Efflux and Net Canopy CO
2
Flux
The SRC-2 Soil Respiration Chamber can be used with the EGM-5 Portable CO
2
Gas Analyzer for
closed system measurement of soil CO
2
efflux. The CPY-5 Canopy Assimilation Chamber can also be
used with the EGM-5 for closed system measurement of net canopy CO
2
flux.
Theory
The respiration (or assimilation) is measured by placing a closed chamber on the soil and measuring the
rate of increase of the CO
2.
concentration inside the chamber.
(1.1) Then, assuming a well-mixed and sealed system:
=
()
×
Where:
= respiration/assimilation rate (CO
2
flux in moles or grams of CO
2
unit area
-1
unit time
-1
)
= is the CO
2
concentration at = 0
= is the concentration at a time
later
= is the area of soil exposed
= the total system volume
It has been suggested that to make accurate measurements of the respiration it is essential to start with a CO
2
concentration in the chamber below ambient and measure until the concentration is above ambient, presumably
with the intention of getting some compensation for leakage. However, this leakage can only take place at ground
level, where the CO
2
concentration is unknown and most certainly will not be what we would consider as ambient.
Over the short period of measurement and with the relatively small CO
2
concentrations in the chamber
compared with the soil concentrations, we would expect the assimilation to be a constant flux, giving a
constant rate of change in the chamber CO
2
concentration.
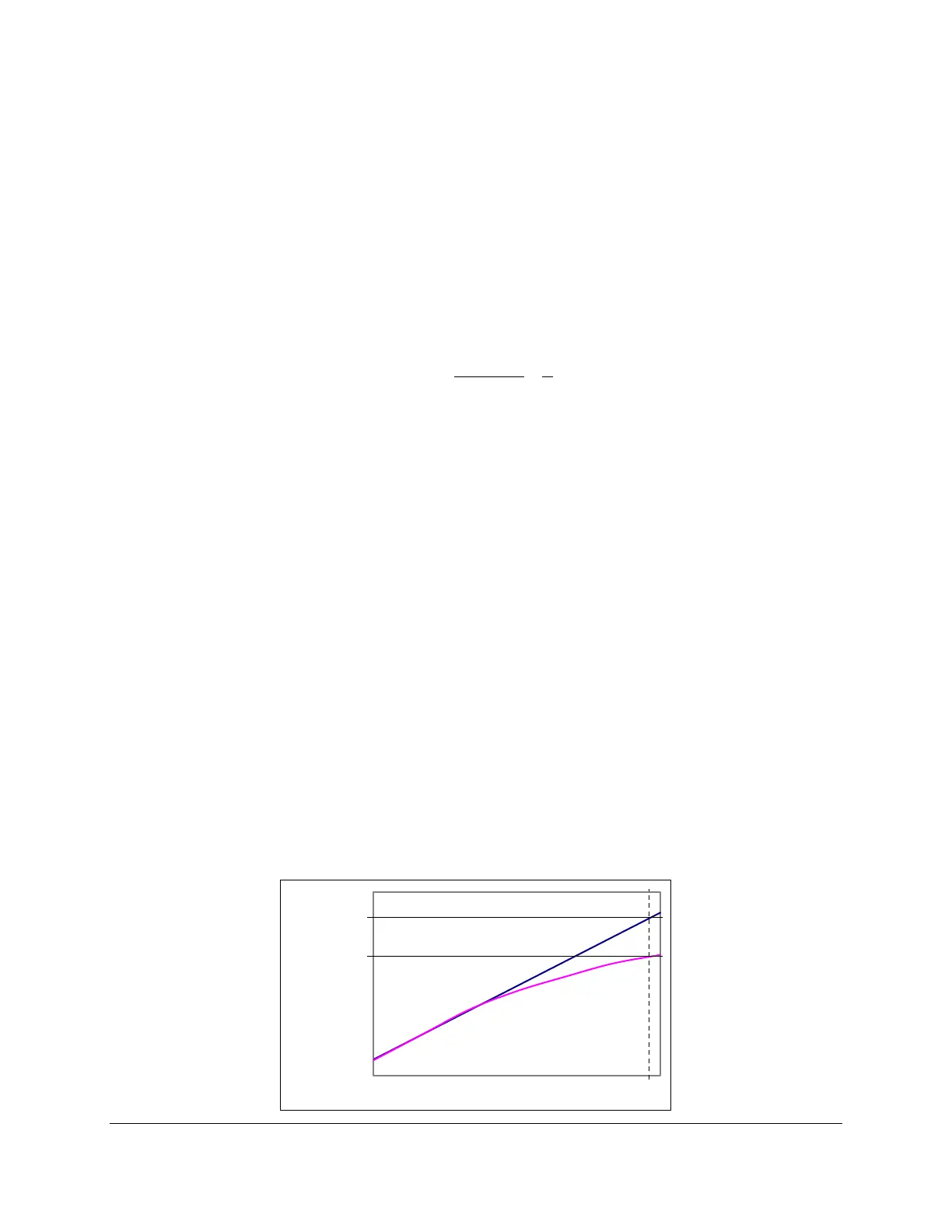
Any leakage should be a function of the concentration difference between the chamber and the exchange
air. Due to leakage, the apparent assimilation rate decreases with time. So leakage would have the effect
of changing the ideal linear C vs T relationship to a non-linear relationship.
Time
To

 Loading...
Loading...