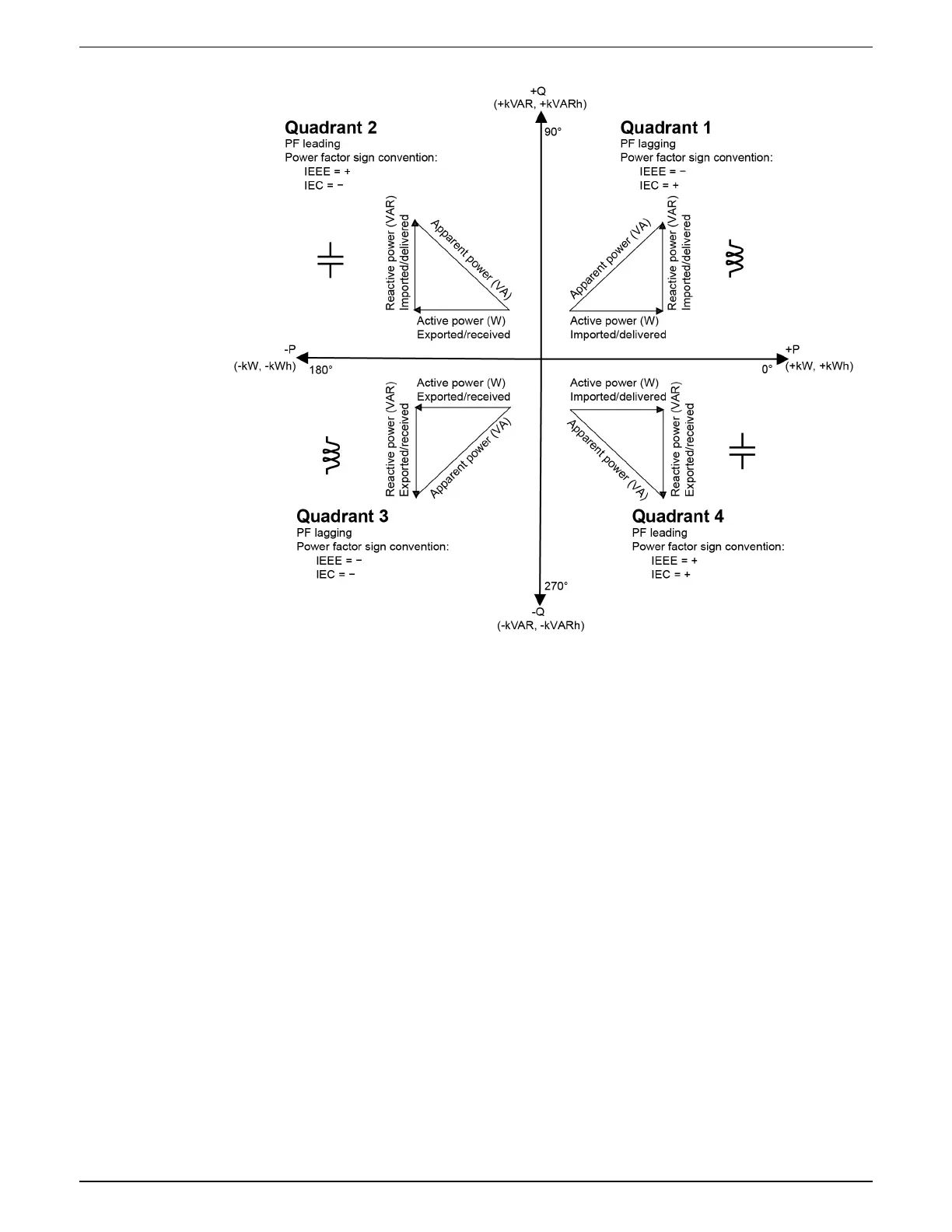
The units for power are watts (W or kW) for real power P, vars (VAR or kVAR) for reactive power
Q, and volt-amps (VA or kVA) for apparent power S.
Positive real power P(+) flows from source to load, and negative real power P(-) flows from the
load to the power source.
Current phase shift from voltage
Electrical current can lag, lead, or be in phase with the AC voltage waveform, and is typically
associated with the type of load — inductive, capacitive or resistive.
For purely resistive loads, the current waveform is in phase with the voltage waveform. For
capacitive loads, current leads voltage. For inductive loads, current lags voltage.
The following diagrams show how voltage and current waveforms shift based on load type under
ideal (laboratory) conditions.
9810 series - User manual Measurements
7EN05-0390-08 250

 Loading...
Loading...











