10.03
1.2 Comparison of electric and hydraulic drive systems
1-16
Siemens AG, 2003. All rights reserved
SINUMERIK 840D/SIMODRIVE 611 digital, HLA Module (FBHLA) - 10.03 Edition
1.2 Comparison of electric and hydraulic drive systems
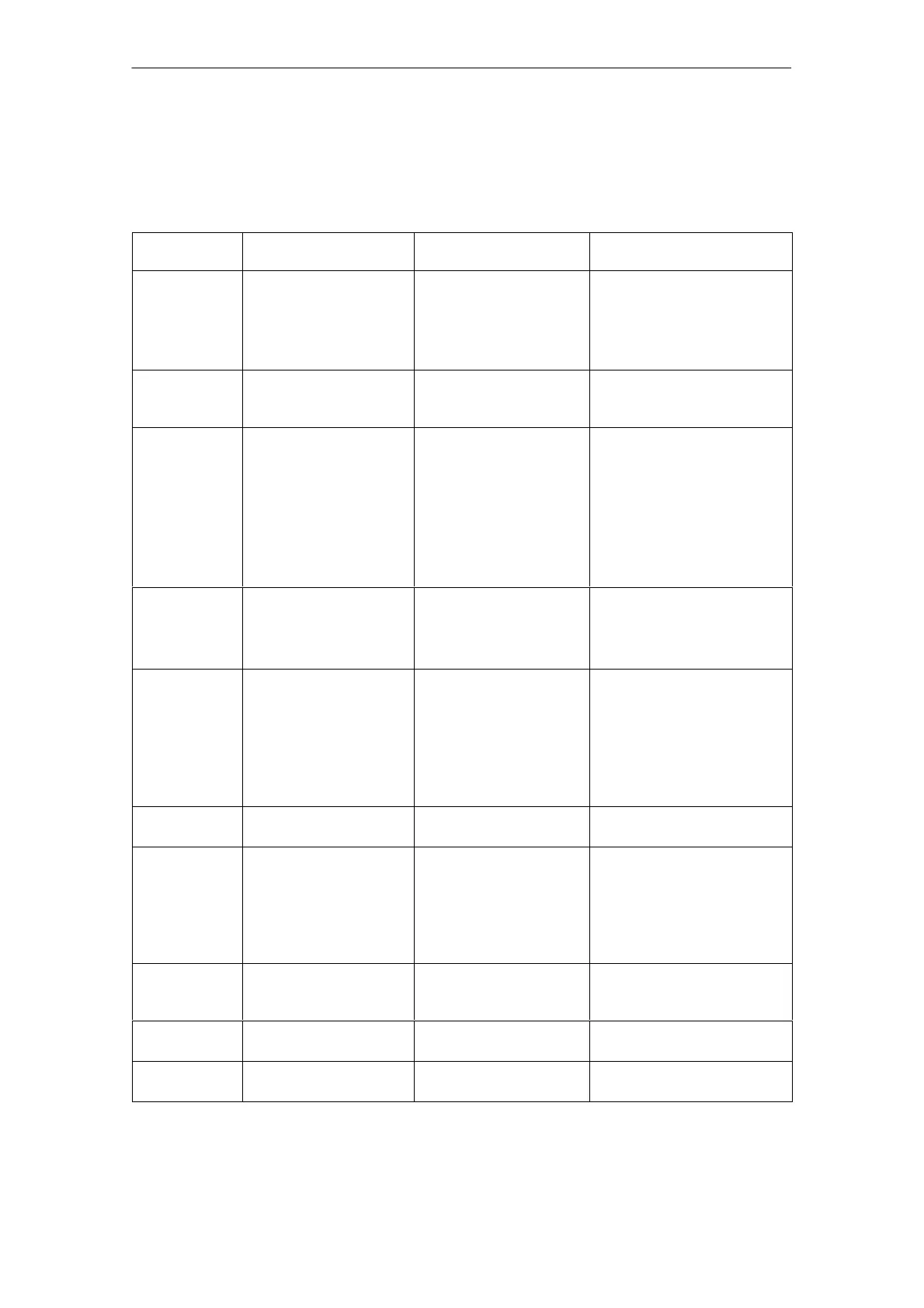
Table 1-1 Comparison of electric and hydraulic drive systems
Criterion Electric direct drive Electric drive with
leadscrew
Hydraulic drive
Power density /
mounting
space require-
ments
S Low weight and
S reduced spatial re-
quirements of the
electric part on the
machine table.
S Servomotor and leads-
crew large and heavy.
S Problematic with lim-
ited mounting space.
S Cylinder and servo sole-
noid valve are light-weight
and compact.
S Transfer of E motor to
hydraulic power unit.
Mass inertia of
moving parts
Electric part on machine
table has low mass.
Servomotor and leads-
crew have high mass mo-
ment of inertia.
Piston and piston rod have
very low mass
Operational
reliability,
service life
Service life depends in
principle only on linear
guides.
S Shock-sensitive.
S Service life limited by
leadscrew.
S Sudden failure
possible.
S Protected against overload
by pressure limitation.
S Sturdy, insensitive to
shocks.
S Cylinder seals and valve
control edges have long
service life.
S Warning of wear.
Servicing Simple replacement Expensive replacement
and repair of leadscrew by
specialists.
S Simple error diagnosis
S Simple replacement and
repair of valves and cylin-
ders.
Energy storage Peak requirement must
be installed as no storage
is possible.
Peak requirement must be
installed as no storage is
possible.
S Compensation of energy
requirement peaks by hy-
draulic accumulator.
S Rapid traverse in differen-
tial circuit.
S Reduction of installed ca-
pacity.
Maximum
forces
Peak thrust per unit area
approx. 40 to 80 kN/m
2
Restriction with larger
forces.
Practically unlimited
(cylinderφ, p
max
=700 bar)
Load stiffness Very good;
Servo gain can be set to
betw. 10-100 times
higher than on the other
two drives.
S Elasticity under large
forces.
S Elasticity of leadscrew
is largely compen-
sated as a control
function.
S Oil compressibility is com-
pensated as a control
function (I component).
S Good zero overlap quality
of valve ensures very high
rigidity under load.
maximum ve-
locity
Up to 500 m/min v
max
=h
s
@ ω
max
/2π
h
s
=thread lead
ω
max
=max. motor speed
30...300 m/min
(depending on which cylinder
seal kit is used)
Maximum
travel path
Unlimited
v 6 m v 3 m
Collision
protection
Mechanically difficult Mechanically possible Mechanically possible

 Loading...
Loading...











