10.03
2.3 Configuring the hydraulic drive
2-30
Siemens AG, 2003. All rights reserved
SINUMERIK 840D/SIMODRIVE 611 digital, HLA Module (FBHLA) - 10.03 Edition
2.3 Configuring the hydraulic drive
Hydraulic drives are generally configured by technical sales personnel from the
hydraulics supplier, Rexroth.
The configuration is based on the data from the questionnaire in
Subsection 2.1.2 .
Please refer to Appendix A for a description of hydraulic components.
The hydraulic drive is configured in the sequence of steps described below.
2.3.1 Cylinder selection
The piston and rod diameters are calculated according to Pascal’s theorem on
the basis of the necessary compressive and tensile forces F and a standard
pressure value of P=40...100 bar for machine tools (a maximum pressure set-
ting of 350 bar is permitted).
p =
F
O
The force value calculation must include friction and acceleration forces
as well as the actual feed force. Pistons and rods with the following standard
diameter dimensions are available:
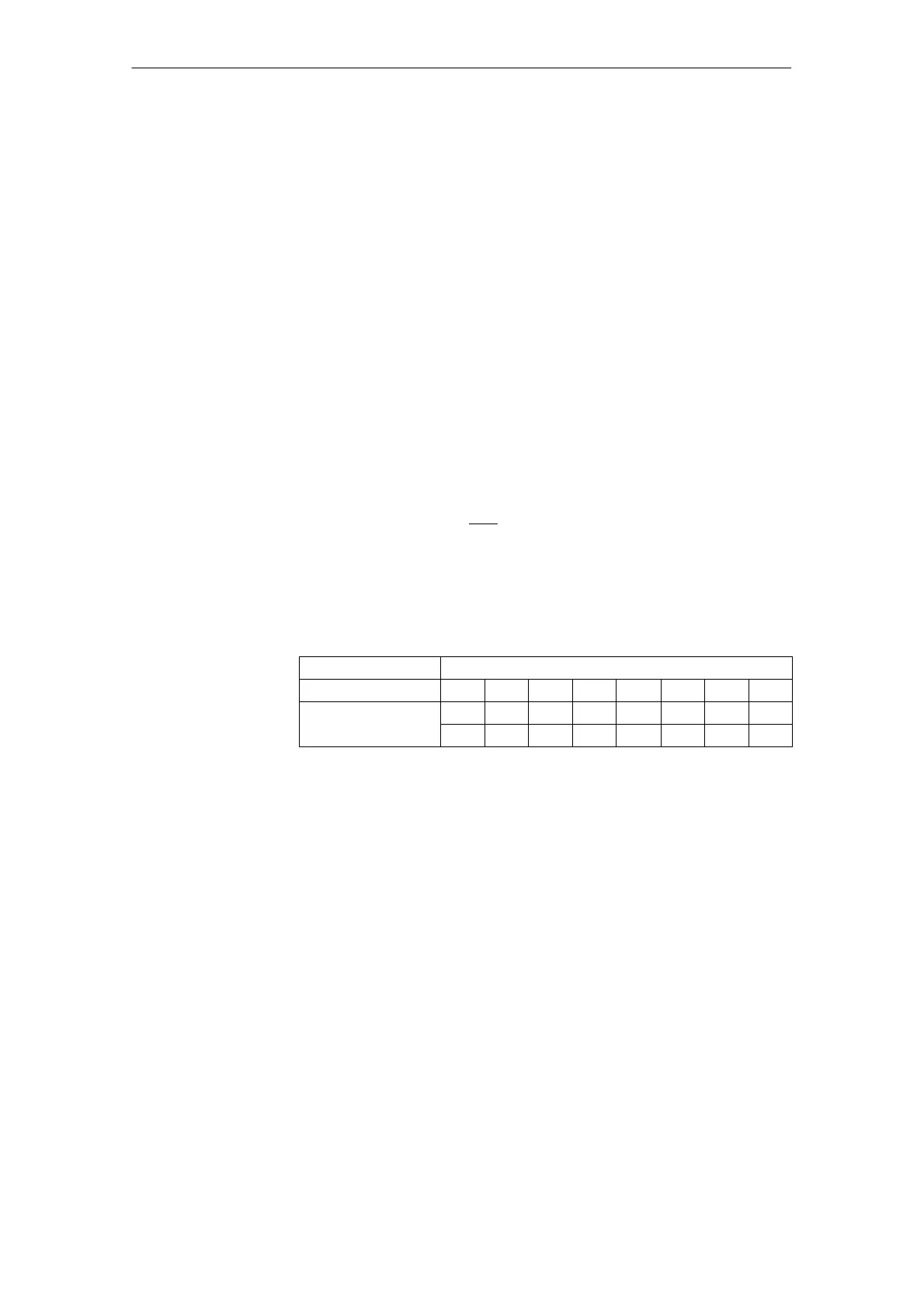
Table 2-2 Typical cylinder data
Description Diameter
Piston ∅ 25 32 40 50 63 80 100 125
Rod ∅ Standard 12 14 18 22 28 36 45 56
Rod ∅ Optional 18 22 28 36 45 56 70 90
The stroke is identical to the working stroke of the drive except that
it includes a few additional safety reserves.
General
Piston and rod
diameter
Stroke length
 Loading...
Loading...











