Functions
6-1217SJ62 Manual
C53000-G1140-C121-1
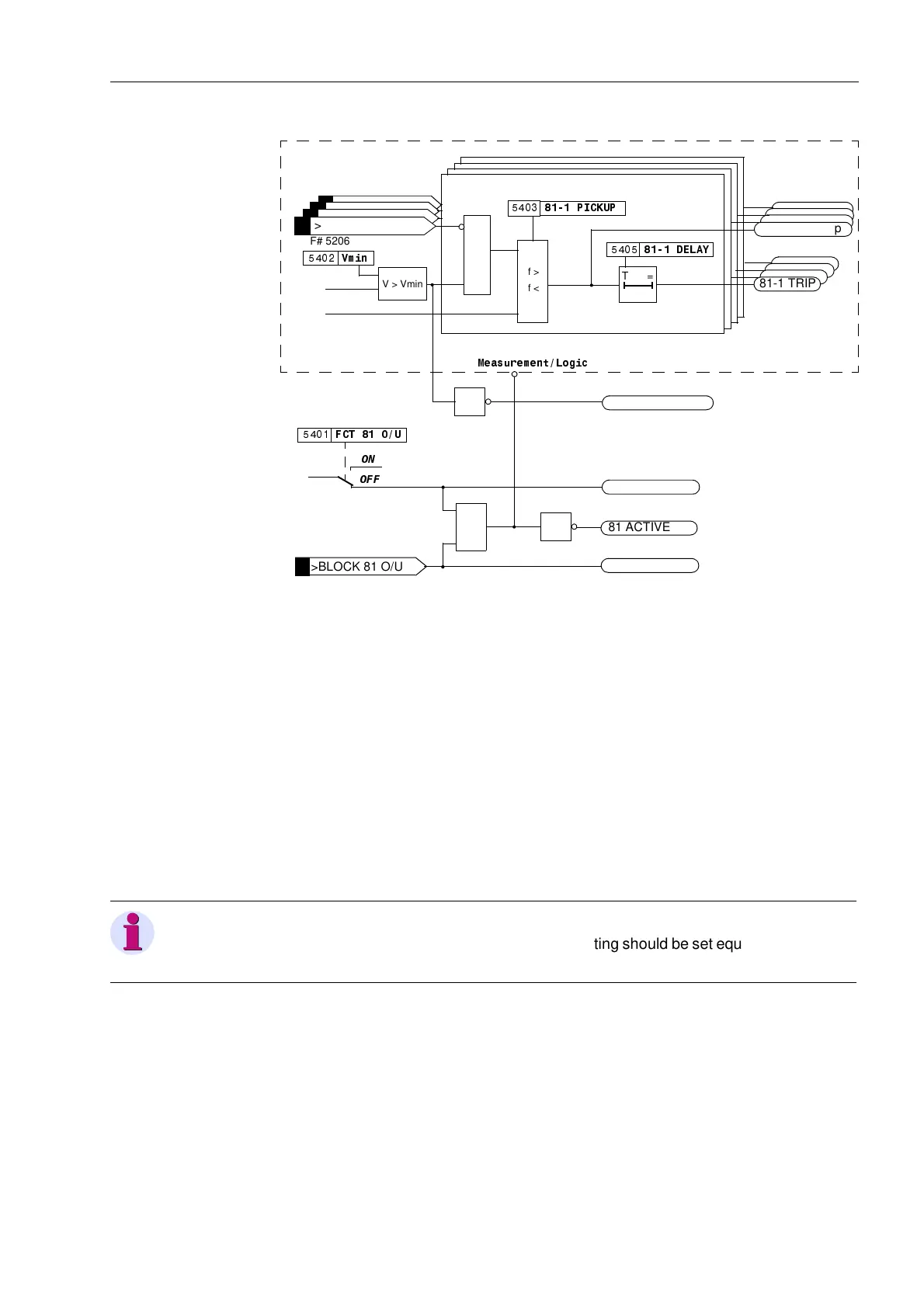
Figure 6-52 Logic Diagram of the Frequency Protection
6.12.2 Programming Settings
General The frequency protection will only be effective and accessible if address is set
to (QDEOHG during configuration of protective functions. If the frequency protection
function is not required, then address should be set to 'LVDEOHG. The function
can be turned 21 or 2)) at address )&728.
Frequency
Protection Settings
The nominal system frequency is programmed in 32:(56<67(0'$7$ and the
pickup settings for each of the frequency elements should be set higher than nominal
frequency if the element is to be used for overfrequency protection or lower than the
nominal frequency if the element is to be used for underfrequency protection.
If underfrequency protection is used for load shedding purpose, then the frequency
settings relative to other feeder relays are generally based on the priority of the cus-
tomers served by the protective relay. The actual settings of the underfrequency ele-
ments must be based on network stability requirements.
For 60 Hz systems, the frequency pickup settings for elements one (1) through four
(4) are entered at addresses , , , and respectively.
For 50 Hz systems, the frequency pickup settings for elements one (1) through four
(4) are entered at addresses , , , and respectively.
&
'(/$<
=T
>BLOCK 81 O/U
„1“
)&728
81 BLOCKED
9PLQ
f
V
ABC
V > Vmin
3,&.83
f >
f <
>BLOCK 81-1
81 ACTIVE
81-1 picked up
81-1 TRIP
F# 5206... F# 5232...
F# 5236...
F#. 5213
F# 5212
F# 5203
or
81 OFF
F#. 5211
81 Under V Blk
F#. 5214
21
2))
0HDVXUHPHQW/RJLF
Note:
If the element is not required, the frequency setting should be set equal to the nominal
frequency, in which case the element becomes inactive.
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com

 Loading...
Loading...











