PM0215 The STM32 Cortex-M0 processor
Doc ID 022979 Rev 1 13/91
Stack pointer (SP) register R13
In Thread mode, bit[1] of the CONTROL register indicates the stack pointer to use:
● 0: Main Stack Pointer (MSP)(reset value). On reset, the processor loads the MSP with
the value from address 0x00000000.
● 1: Process Stack Pointer (PSP).
Link register (LR) register R14
Stores return information for subroutines, function calls, and exceptions. On reset, the
processor loads the LR value 0xFFFFFFFF.
Program counter (PC) register R15
Contains the current program address. On reset, the processor loads the PC with the value
of the reset vector, which is at address 0x00000004. Bit[0] of the value is loaded into the
EPSR T-bit at reset and must be 1.
Program status register
The Program Status Register (PSR) combines:
● Application program status register (APSR)
● Interrupt program status register (IPSR)
● Execution program status register (EPSR)
These registers are mutually exclusive bitfields in the 32-bit PSR. They can be accessed
individually or as a combination of any two or all three registers, using the register name as
an argument to the MSR or MRS instructions. For example:
● Read all of the registers using PSR with the MRS instruction
● Write to the APSR using APSR with the MSR instruction.
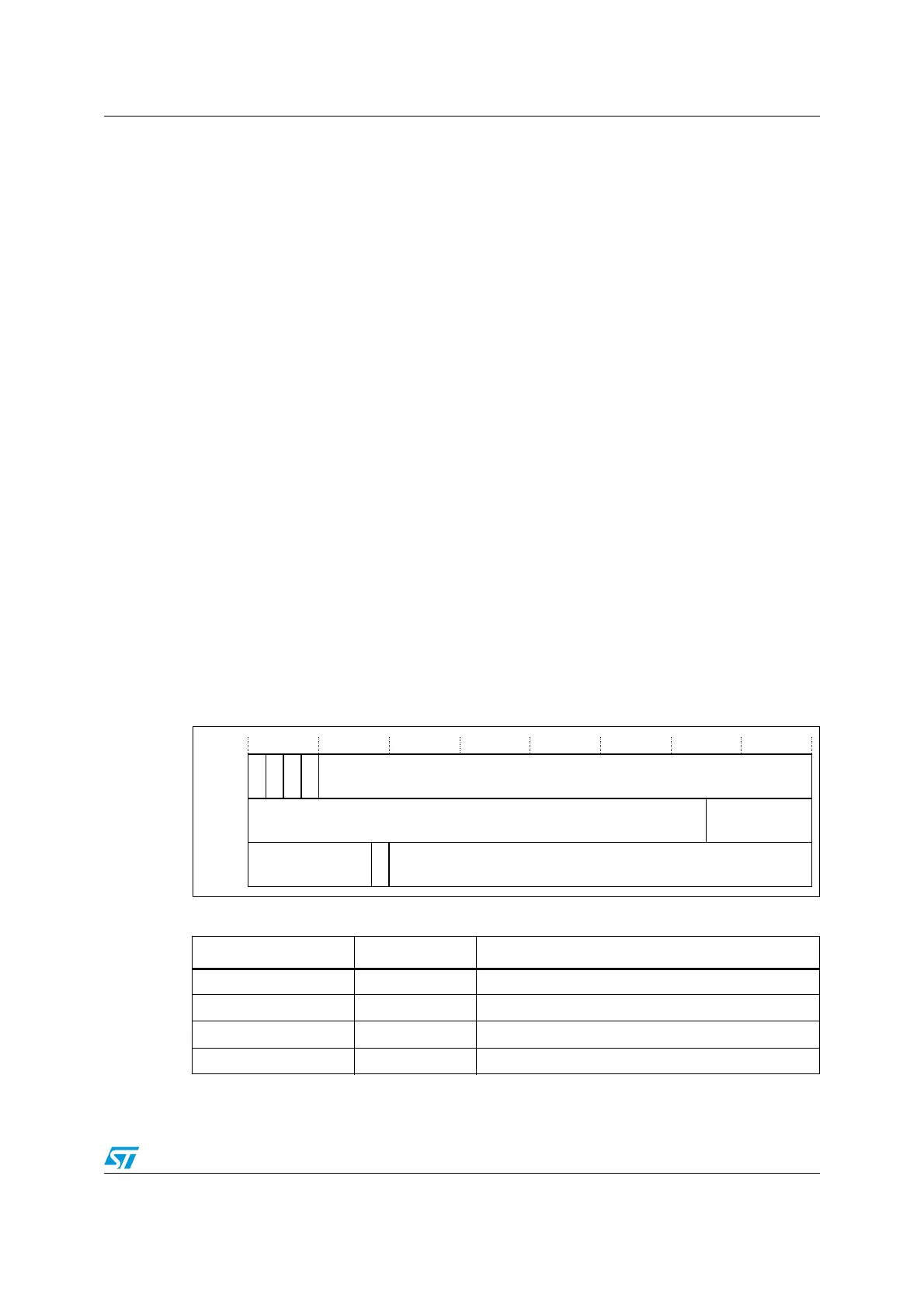
Figure 3. APSR, IPSR and EPSR bit assignments
Table 4. PSR register combinations and attributes
Register Type Combination
PSR read-write
(1), (2)
1. The processor ignores writes to the IPSR bits.
2. Reads of the EPSR bits return zero, and the processor ignores writes to the these bits
APSR, EPSR, and IPSR
IEPSR read-only EPSR and IPSR
IAPSR read-write
(1)
APSR and IPSR
EAPSR read-write
(2)
APSR and EPSR
5HVHUYHG ([FHSWLRQQXPEHU
1=&9
5HVHUYHG
$365
,365
(365
5HVHUYHG 5HVHUYHG7

 Loading...
Loading...











