PM0215 The STM32 Cortex-M0 instruction set
Doc ID 022979 Rev 1 37/91
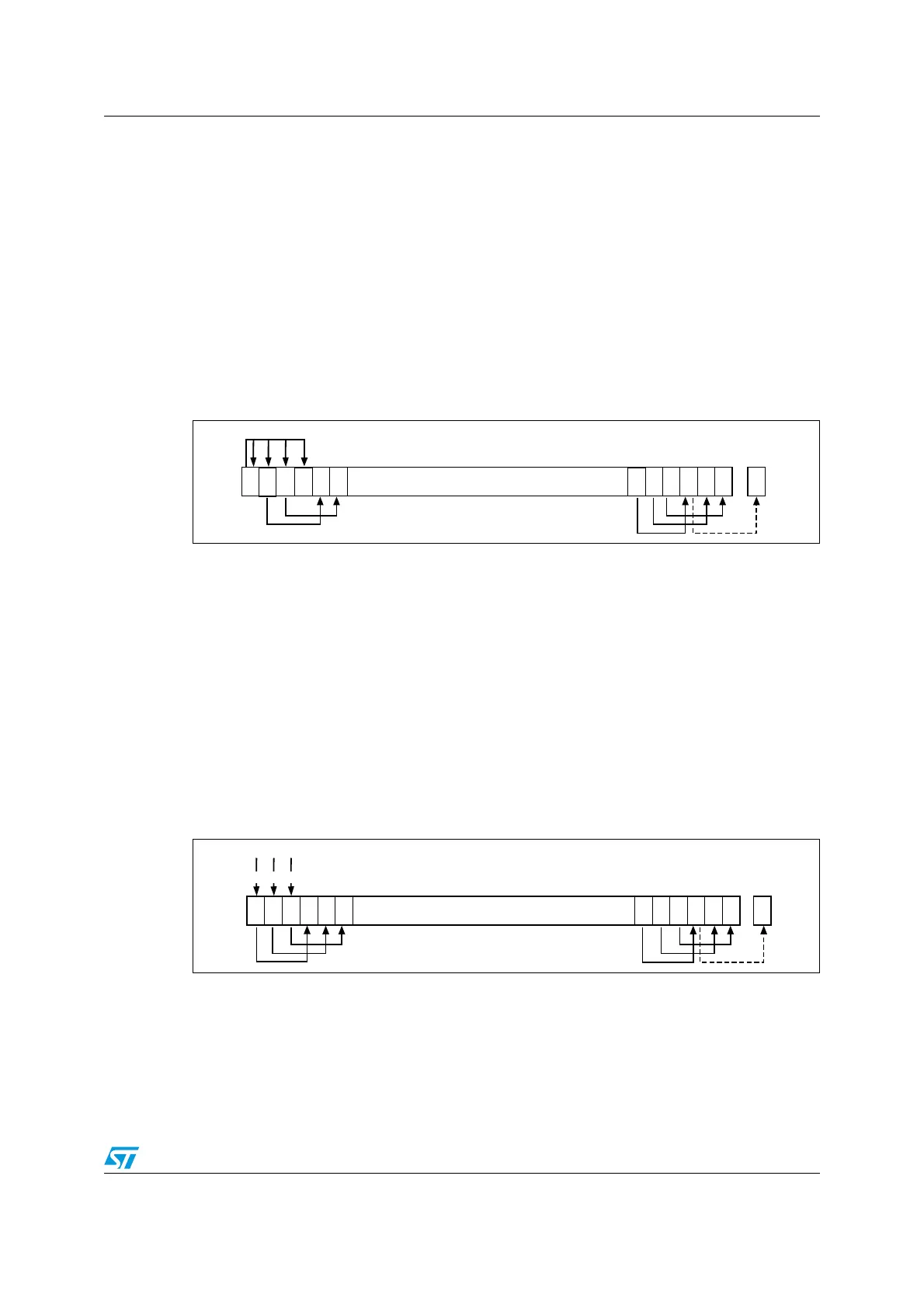
ASR
Arithmetic shift right by
n
bits moves the left-hand
32
-
n
bits of the register
Rm
, to the right by
n
places, into the right-hand
32
-
n
bits of the result. And it copies the original bit[31] of the
register into the left-hand
n
bits of the result (see Figure 10: ASR#3).
You can use the
ASR
operation to divide the signed value in the register
Rm
by 2
n
, with the
result being rounded towards negative-infinity.
When the instruction is ASRS, the carry flag is updated to the last bit shifted out, bit[
n
-1], of
the register
Rm
.
Note: 1 If
n
is 32 or more, all the bits in the result are set to the value of bit[31] of
Rm
.
2If
n
is 32 or more and the carry flag is updated, it is updated to the value of bit[31] of
Rm
.
Figure 10. ASR#3
LSR
Logical shift right by
n
bits moves the left-hand
32
-
n
bits of the register
Rm
, to the right by
n
places, into the right-hand
32
-
n
bits of the result. And it sets the left-hand
n
bits of the result
to 0 (see Figure 11).
You can use the LSR #n operation to divide the value in the register
Rm
by 2
n
, if the value is
regarded as an unsigned integer.
When the instruction is LSRS, the carry flag is updated to the last bit shifted out, bit[
n
-1], of
the register
Rm
.
Note: 1 If
n
is 32 or more, then all the bits in the result are cleared to 0.
2If
n
is 33 or more and the carry flag is updated, it is updated to 0.
Figure 11. LSR#3

 Loading...
Loading...











