The STM32 Cortex-M0 instruction set PM0215
50/91 Doc ID 022979 Rev 1
Examples
Multiword arithmetic examples
Specific example: 64-bit addition shows two instructions that add a 64-bit integer contained
in R0 and R1 to another 64-bit integer contained in R2 and R3, and place the result in R0
and R1.
Specific example: 64-bit addition
ADDS R0, R0, R2 ; add the least significant words
ADCS R1, R1, R3 ; add the most significant words with carry
Multiword values do not have to use consecutive registers. Specific example: 96-bit
subtraction shows instructions that subtract a 96-bit integer contained in R1, R2, and R3
from another contained in R4, R5, and R6. The example stores the result in R4, R5, and R6.
Specific example: 96-bit subtraction
SUBS R4, R4, R1 ; subtract the least significant words
SBCS R5, R5, R2 ; subtract the middle words with carry
SBCS R6, R6, R3 ; subtract the most significant words with carry
Specific example: Arithmetic negation shows the RSBS instruction used to perform a 1's
complement of a single register.
Specific example: Arithmetic negation
RSBS R7, R7, #0 ; subtract R7 from zero
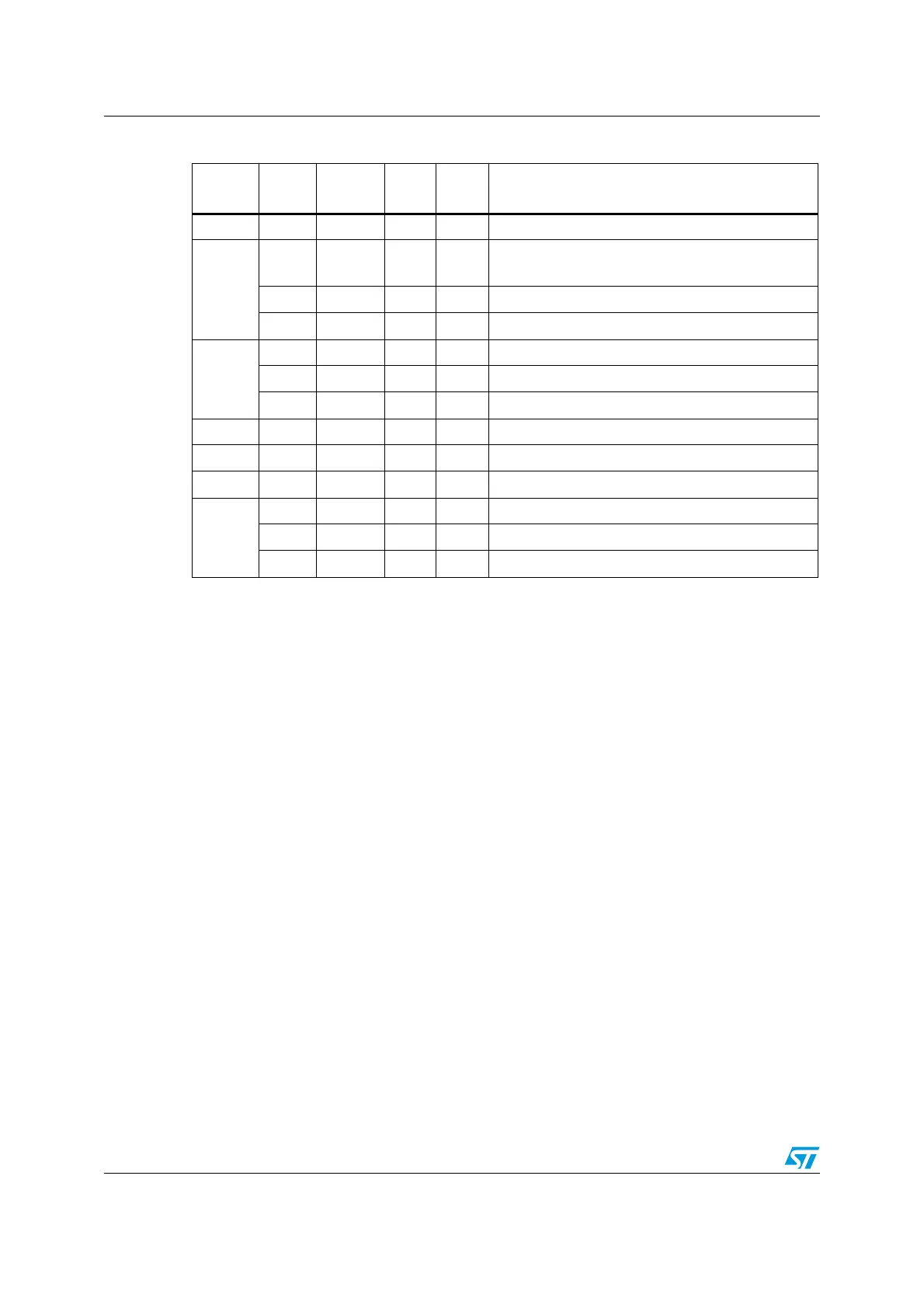
Table 20. ADCS, ADD, RSBS, SBCS and SUB operand restrictions
Instructi
on
Rd Rn Rm imm Restrictions
ADCS R0-R7 R0-R7 R0-R7 - Rd and
Rn must specify the same register.
ADD
R0-R15 R0-R15 R0-PC -
Rd and
Rn must specify the same register.
Rn and Rm must not both specify PC.
R0-R7 SP or PC - 0-1020 Immediate value must be an integer multiple of four.
SP SP - 0-508 Immediate value must be an integer multiple of four.
ADDS
R0-R7 R0-R7 - 0-7 -
R0-R7 R0-R7 - 0-255 Rd and
Rn must specify the same register.
R0-R7 R0-R7 R0-R7 - -
RSBS R0-R7 R0-R7 - - -
SBCS R0-R7 R0-R7 R0-R7 - Rd and
Rn must specify the same register.
SUB SP SP - 0-508 Immediate value must be an integer multiple of four.
SUBS
R0-R7 R0-R7 - 0-7 -
R0-R7 R0-R7 - 0-255 Rd and
Rn must specify the same register.
R0-R7 R0-R7 R0-R7 - -

 Loading...
Loading...











