193 © STULZ GmbH – all rights reserved EN/01.2019/G22
ec tower technical manual
© Danfoss | DCS (az) |2017.06
IC.PD.200.H7.02 | 8
Data sheet | Solenoid valves, type EV250B, dezincification resistant brass
Function NO
1. Coil
2. Closing spring
3. Armature
4. Spindle
5. Opening spring
6. Armature stop
7. Valve plate
8. Assisted lift
9. Pilot orifice
10. Diaphragm
11. Equalising orifice
12. Main orifice
Coil voltage disconnected (valve is open):
When the supply voltage to the coil (1) is
disconnected, the valve plate (7) are lifted clear of
the pilot orifice (9) if there is a differential
pressure across the valve. The pressure above the
diaphragm (10) drops as the pilot orifice is larger
than the equalizing orifice. Therefor the
diaphragm is lifted clear of the main orifice (12).
If there is no differential pressure across the valve,
the opening spring (5) draws the diaphragm (10)
clear of the main orifice (12) using the assisted lift
(8). The valve will be open for as long as there is
no voltage to the coil.
Coil voltage connected (valve is closed):
When the supply voltage to the coil (1) is
connected, the armature (3) will compress the
opening spring (5) and the closing spring will
push the spindle (4)/ valve plate down against
the pilot orifice (9). The pressure across the
diaphragm (10) is built up via the equalising
orifice (11). The diaphragm closes the main orifice
(12) as soon as the pressure across the diaphragm
is equivalent to the inlet pressure below, due to
the larger diameter of the upper side and / or the
tension of the closing spring (2). The valve will be
closed as long as coil voltage is connected.
Function NC
1. Coil
2. Armature
3. Closing spring
4. Valve plate
5. Pilot orifice
6. Diaphragm
7. Main orifice
8. Equalizing orifice
9. Assisted lift
Coil voltage disconnected (closed):
When the supply voltage to the coil (1) is
disconnected, the valve plate (4) is pressed down
against the pilot orifice (5) by the closing spring
(3). The pressure across the diaphragm (6) is built
up via the equalizing orifice (8). The diaphragm
closes the main orifice (7) as soon as the pressure
across the diaphragm is equivalent to the inlet
pressure below, due to the larger diameter of
the upper side and/or the tension of the closing
spring (3). The valve will be closed as long as the
voltage to the coil is disconnected.
Coil voltage connected (open):
When voltage is applied to the coil, the armature
(2) and the valve plate (4) are lifted clear of the
pilot orifice (5).
If there is a differential pressure across the valve,
the pressure above the diaphragm (6) drops as
the pilot orifice is larger than the equalizing
orifice. Therefore the diaphragm is lifted clear of
the main orifice (7). If there is no differential
pressure across the valve, the armature (2) draws
the diaphragm (6) clear of the main orifice (7)
using the assisted lift (9). The valve will be open
for as long as there is voltage to the coil.
© Danfoss | DCS (az) |2017.06
EV250B 18B NO
EV250B 22B NO
EV250B 10B NC/NO
EV250B 12B NC/NO
EV250B 22B NC
EV250B 18B NC
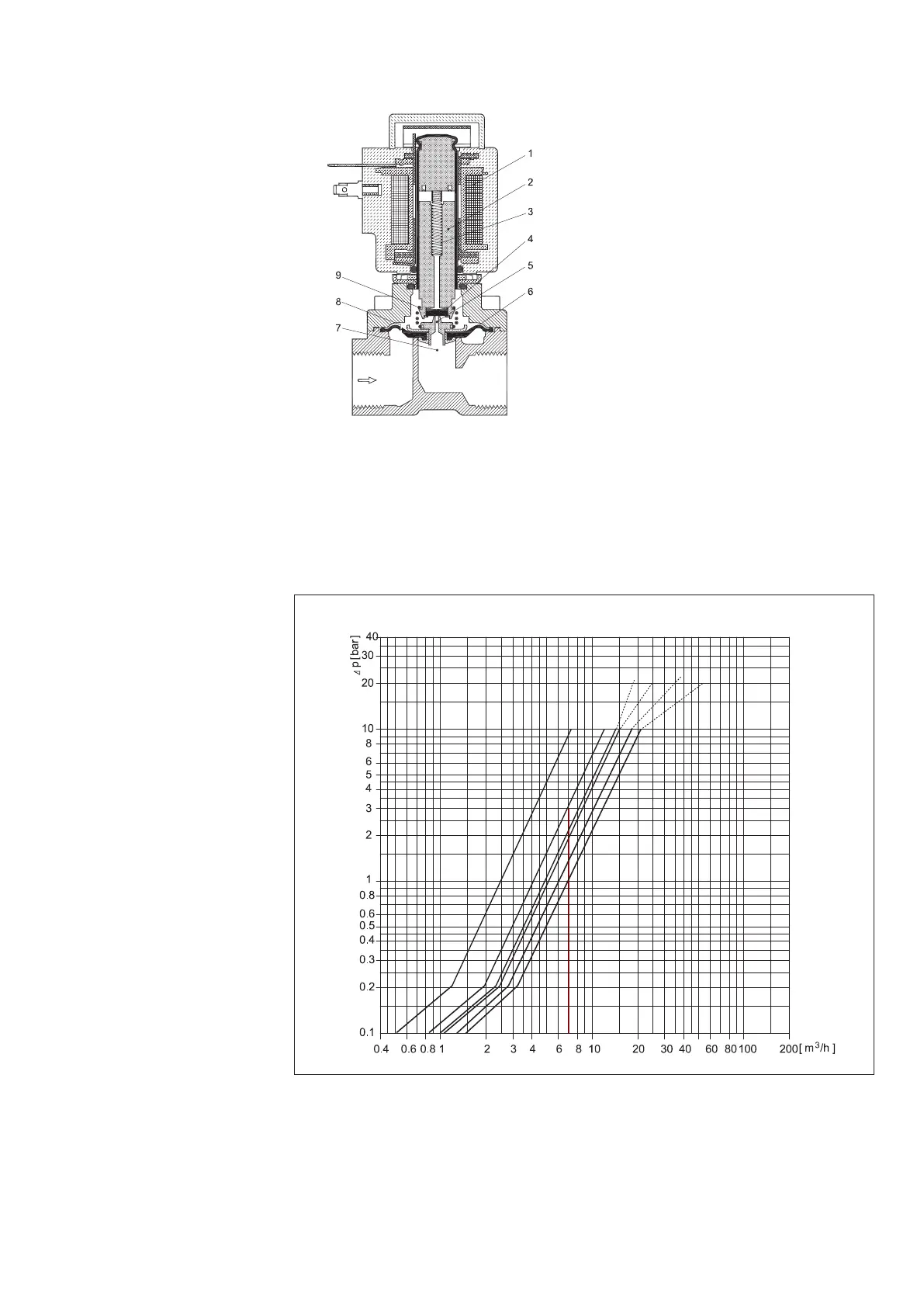
Capacity diagram:
Example, water: EV250B 12
at differential pressure of 3 bar:
Approx. 7 m3/h
 Loading...
Loading...











