Appendix
CCD
Intensied Charge Coupled Devices (ICCD), comprise of a Gated Image Intensier and a CCD-Sensor. A Charge
Coupled Device (CCD) is a silicon-based semiconductor chip bearing a two-dimensional matrix of photo-sensors, or
pixels. This matrix is usually referred to as the image area. The pixels are often described as being arranged in rows and
columns (rows running horizontally, columns vertically).
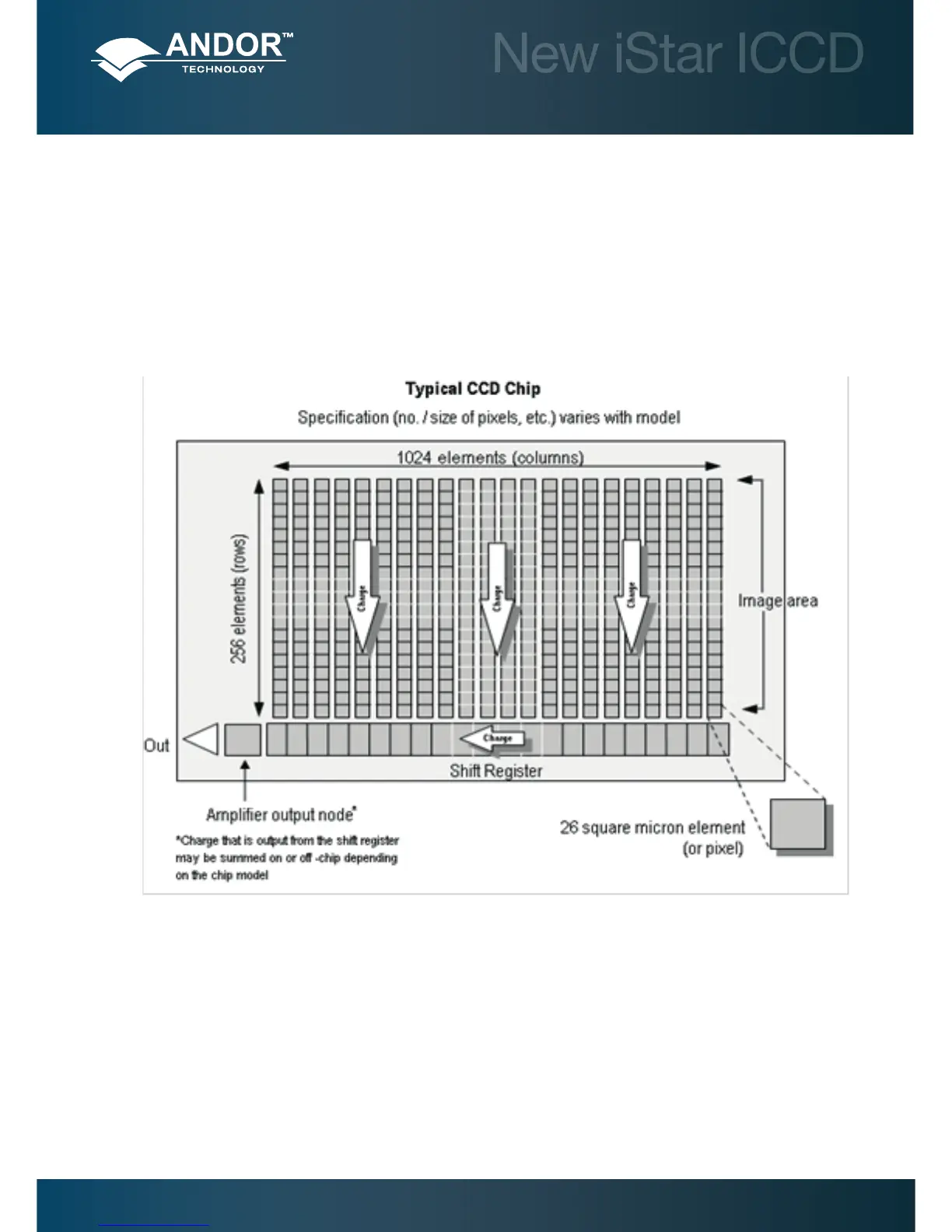
The CCD in your detector is a scientic slow scan device (in contrast to the fast scan CCD used in video cameras to
capture moving images). An example of a typical layout is shown here:
The shift register runs below and parallel to the light collecting rows. It has the same number of pixels as a
light-collecting row, but is itself masked, so that no light can fall on it. When light falls on an element, electrons
(photoelectrons) are produced and (in normal operation), these electrons are conned to their respective elements. Thus,
if an image (or any light pattern) is projected on to the array, a corresponding charge pattern will be produced.
To capture the image pattern into computer memory, the charge pattern must be transferred off the chip, and this is
accomplished by making use of a series of horizontal (i.e. parallel to the rows/shift register) transparent electrodes that
cover the array. By suitable ‘clocking’, these electrodes can be used to shift (transfer) the entire charge pattern, one row
at a time, down into the shift register. The shift register also has a series of electrodes (which are vertical, i.e. parallel
to the columns) which are used to transfer the charge packets, one element at a time, into the output node of the “on-
chip” amplier. The output of the amplier feeds the analog-to-digital (A/D) converter, which in turn converts each charge
packet into a 16-bit binary number.

 Loading...
Loading...