7.3 Output Signal Description 53
7.3 Output Signal Description
All models can provide three different digital signals and one analog signal. Digital signals consist
of unmodulated IRIG-B, 1 PPS and Programmable Pulse. With option cards installed, many other
digital signals are available; see Appendix C for output options with listed digital signals. Most of
the information in this section is devoted to IRIG-B, its specifications and differences.
1 PPS occurs once each second and has a duration (pulse width) of 10 milliseconds. Programmable
pulse modes are similar to 1 PPS only they have an adjustable period and pulse width. Pro-
grammable pulse modes include seconds per pulse, pulse per hour, pulse per day, single trigger
(once per year) and slow code.
7.3.1 IRIG-B Description
IRIG-B is a complete serial time code that occurs once per second and, depending on the config-
uration, contains the day of year, hours, minutes, seconds, year and other important information.
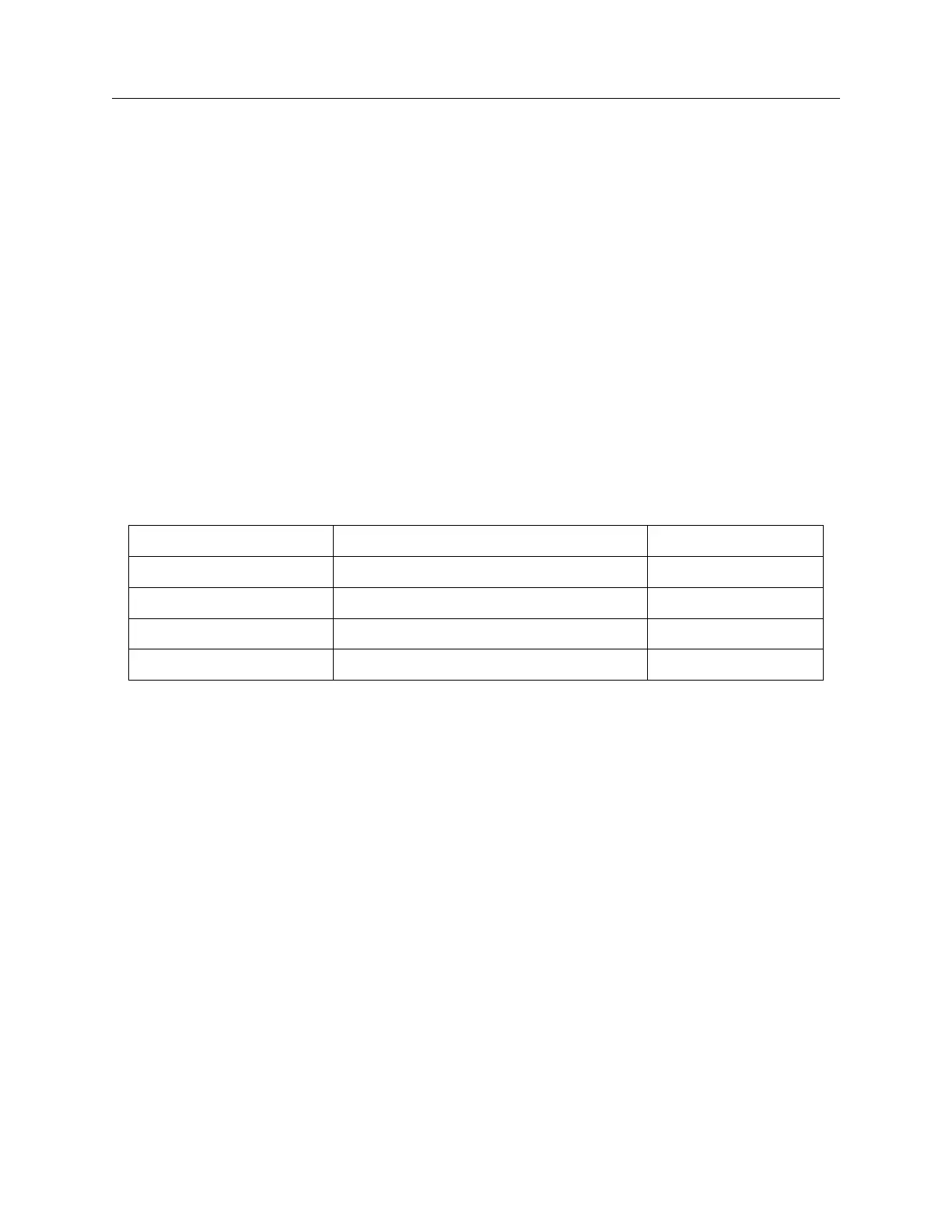
The Model 1084A/B/C transmits Format B with four variations as seen in Table 7.2. Note that
with the newer IRIG Standard 200-04, two of the designations have changed: the older B000 has
become B004 and B120 has become B124.
Designation Old/New Signal Type Code Components
B000/B004 Pulse width code, No carrier BCD
T OY
, CF, SBS
B003 Pulse width code, No carrier BCD
T OY
, SBS
B120/B124 Sine wave, amplitude modulated, 1 kHz BCD
T OY
, CF, SBS
B123 Sine wave, amplitude modulated, 1 kHz BCD
T OY
, SBS
Table 7.2: IRIG-B Time Code Types Available
The IRIG-B time code consists of 100 bits produced every second, 74 bits of which contain
various time, date, time changes and time quality information of the time signal. Consisting of
logic ones, zeros and position identifier bits, the time code provides a reliable method of transmitting
time to synchronize various equipment.
There are three functional groups of bits in the IRIG-B time code, in the following order: Binary
Coded Decimal (BCD), Control Function (CF) and Straight Binary Seconds (SBS). The BCD group
contains only time information including the seconds, minutes, hours and days, recycling yearly.
The CF group contains other time-related information including year, time quality, leap year,
pending leap seconds and parity. The SBS consists of the total elapsed seconds, restarting daily.
Position identifiers separate the various components of the IRIG-B time code.
7.3.2 Modulated and Unmodulated IRIG-B
Figure 7.2 illustrates the primary differences between modulated and unmodulated IRIG-B. You
will notice that the while modulated IRIG-B is distinctive because of the 1 kHz sinewave carrier,
it is similar to unmodulated IRIG-B since the peak-to-peak values of the carrier follow the same
form as the digital waveform, where the information is contained.

 Loading...
Loading...