281
Configuring VLANs
VLANs
Load Sharing Using STP Port Priorities
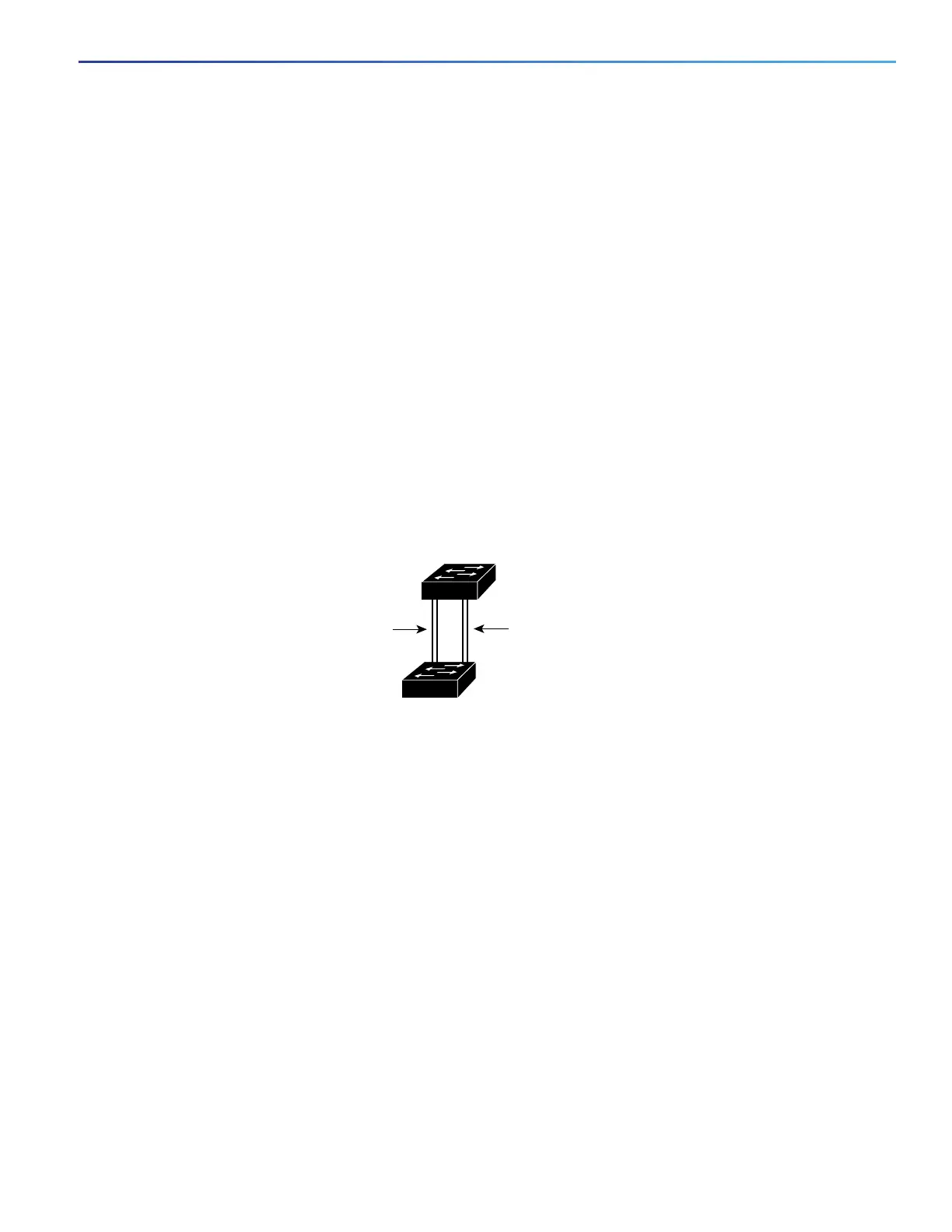
When two ports on the same switch form a loop, the switch uses the STP port priority to decide which port is enabled
and which port is in a blocking state. You can set the priorities on a parallel trunk port so that the port carries all the traffic
for a given VLAN. The trunk port with the higher priority (lower values) for a VLAN is forwarding traffic for that VLAN. The
trunk port with the lower priority (higher values) for the same VLAN remains in a blocking state for that VLAN. One trunk
port sends or receives all traffic for the VLAN.
Figure 30 on page 281 shows two trunks connecting supported switches. In this example, the switches are configured
as follows:
VLANs 8 through 10 are assigned a port priority of 16 on Trunk 1.
VLANs 3 through 6 retain the default port priority of 128 on Trunk 1.
VLANs 3 through 6 are assigned a port priority of 16 on Trunk 2.
VLANs 8 through 10 retain the default port priority of 128 on Trunk 2.
In this way, Trunk 1 carries traffic for VLANs 8 through 10, and Trunk 2 carries traffic for VLANs 3 through 6. If the active
trunk fails, the trunk with the lower priority takes over and carries the traffic for all of the VLANs. No duplication of traffic
occurs over any trunk port.
Figure 30 Load Sharing by Using STP Port Priorities
Load Sharing Using STP Path Cost
You can configure parallel trunks to share VLAN traffic by setting different path costs on a trunk and associating the path
costs with different sets of VLANs, blocking different ports for different VLANs. The VLANs keep the traffic separate and
maintain redundancy in the event of a lost link.
In Figure 31 on page 282, Trunk ports 1 and 2 are configured as 100BASE-T ports. These VLAN path costs are assigned:
VLANs 2 through 4 are assigned a path cost of 30 on Trunk port 1.
VLANs 8 through 10 retain the default 100BASE-T path cost on Trunk port 1 of 19.
VLANs 8 through 10 are assigned a path cost of 30 on Trunk port 2.
VLANs 2 through 4 retain the default 100BASE-T path cost on Trunk port 2 of 19.
93370
Switch A
Switch B
Trunk 2
VLANs 3 – 6 (priority 16)
VLANs 8 – 10 (priority 128)
Trunk 1
VLANs 8 – 10 (priority 16)
VLANs 3 – 6 (priority 128)

 Loading...
Loading...