576
Configuring QoS
Understanding QoS
Figure 78 QoS Classification Layers in Frames and Packets
These sections contain additional information about classification:
Class Maps, page 576
The match Command, page 577
Classification Based on Layer 2 CoS, page 577
Classification Based on IP Precedence, page 577
Classification Based on IP DSCP, page 578
Classification Comparisons, page 579
Classification Based on QoS ACLs, page 580
Classification Based on QoS Groups, page 580
Classification Based on VLAN IDs, page 581
Class Maps
As explained previously, you use an MQC class map to name a specific traffic flow (or class) and to isolate it from all
other traffic. A class map defines the criteria used to match against a specific traffic flow to further classify it. If you have
more than one type of traffic that you want to classify, you can create another class map and use a different name. When
you enter the class-map command with a class-map name, the switch enters the class-map configuration mode. In this
mode, you define the match criterion for the traffic by using the match class-map configuration command. After a packet
is matched against the class-map criteria, it is acted on by the associated action specified in a policy map.
141151
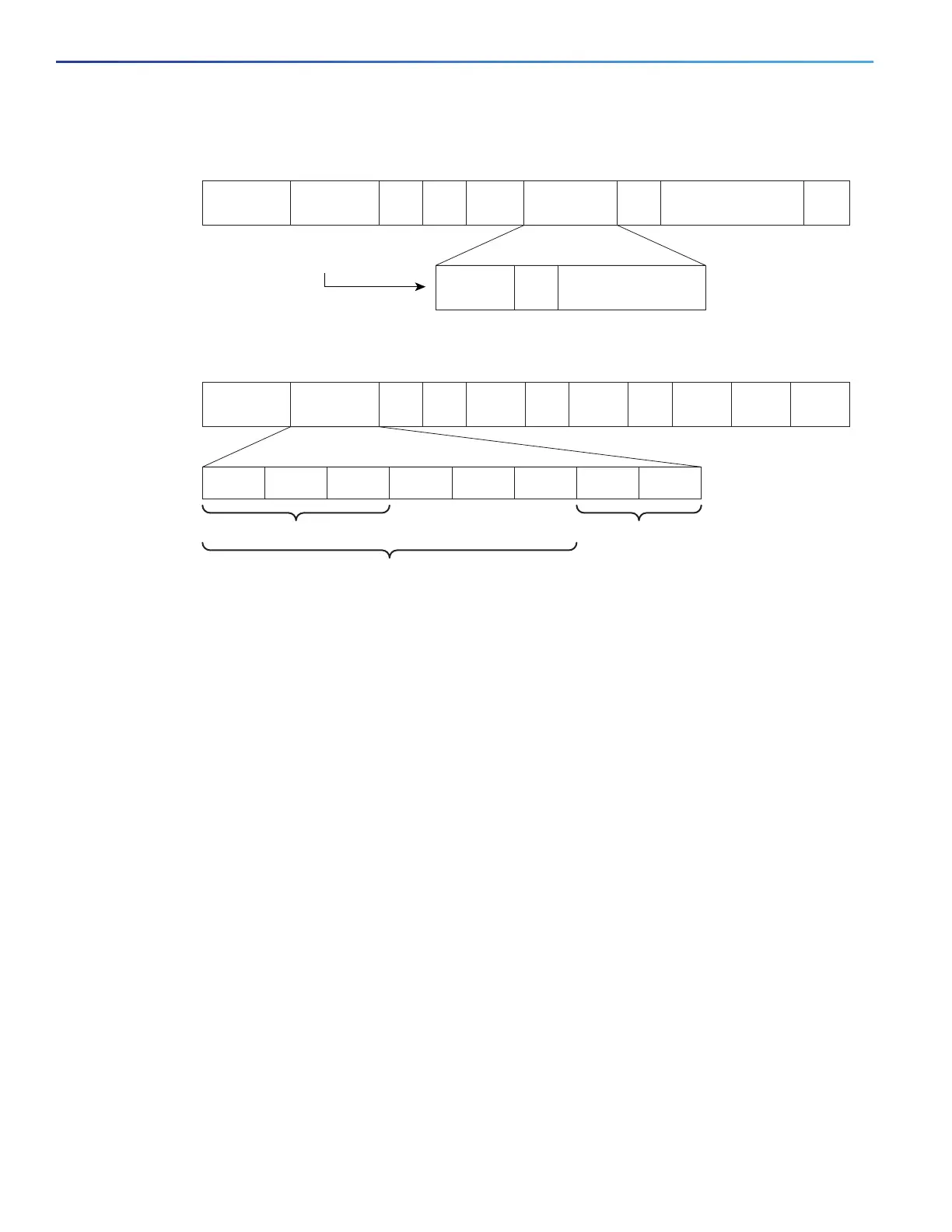
Layer 2 IEEE 802.1Q and IEEE 802.1p Frame
Preamble
Start frame
delimiter
DA
Len
SA Type
TAG
2 Bytes
PT Data FCS
Layer 3 IPv4 Packet
Version
length
To S
1 Byte
ID Offset TTL Proto FCS IP-SA IP-DA
PRI
7
6 5 4 3 2 1 0
CFI VLAN ID
Data
3 bits used for CoS
(IEEE 802.1p user priority)
IP precedence
DSCP
Standard IPv4:
MSBs called IP precedence
Flow control
for DSCP

 Loading...
Loading...











