. . . . .
MAINT/DIAG SCREENS
PID Tuning
2-9317-372-00-0 Bravo™ 8105 Programming and Operations Guide 10-107
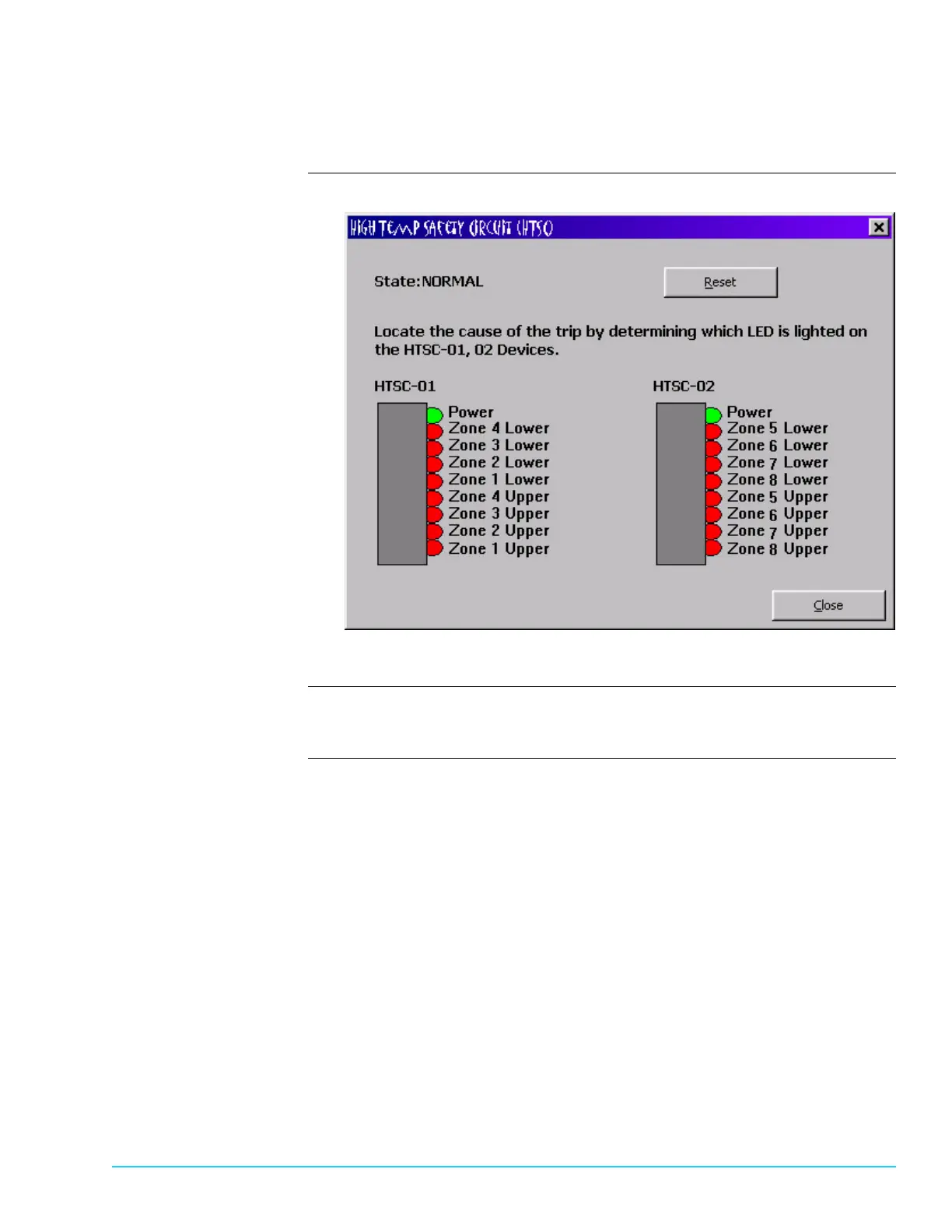
Note that the Bravo™ cannot operate until the Thermal Runaway High
Temperature Safety circuit is Reset.
Photograph
Figure 10–3
PID Tuning
Closed Loop Feedback PID is an acronym for Proportional–Integral–Derivative. Proportional measures the
difference between the measured value and the setpoint value. The controller
output is proportional to a change in measurement. Integral refers to the
controller producing a signal that is determined by the length of time the error
signal is present. (The error signal is produced when the measured value differs
from the setpoint value.) Derivative refers to the controller producing a signal that
is determined by the rate of change in the error signal, i.e., how much time it
takes the measured value to increase or decrease a given amount.
PID Tuning is preset at the factory. The factory defaults for the PID values that
are specific to the machine are shipped with the machine documentation. Only a
technician trained and authorized to perform PID tuning should alter any of the
values.
PID is used for closed loop feedback to accurately control machine components.
It generates an output that applies a corrective effect to the process so that it
drive the (measurable) process variable, in this case, temperature or speed,
toward the setpoint value.
 Loading...
Loading...