Page 49
Operation
optoNCDT 1700
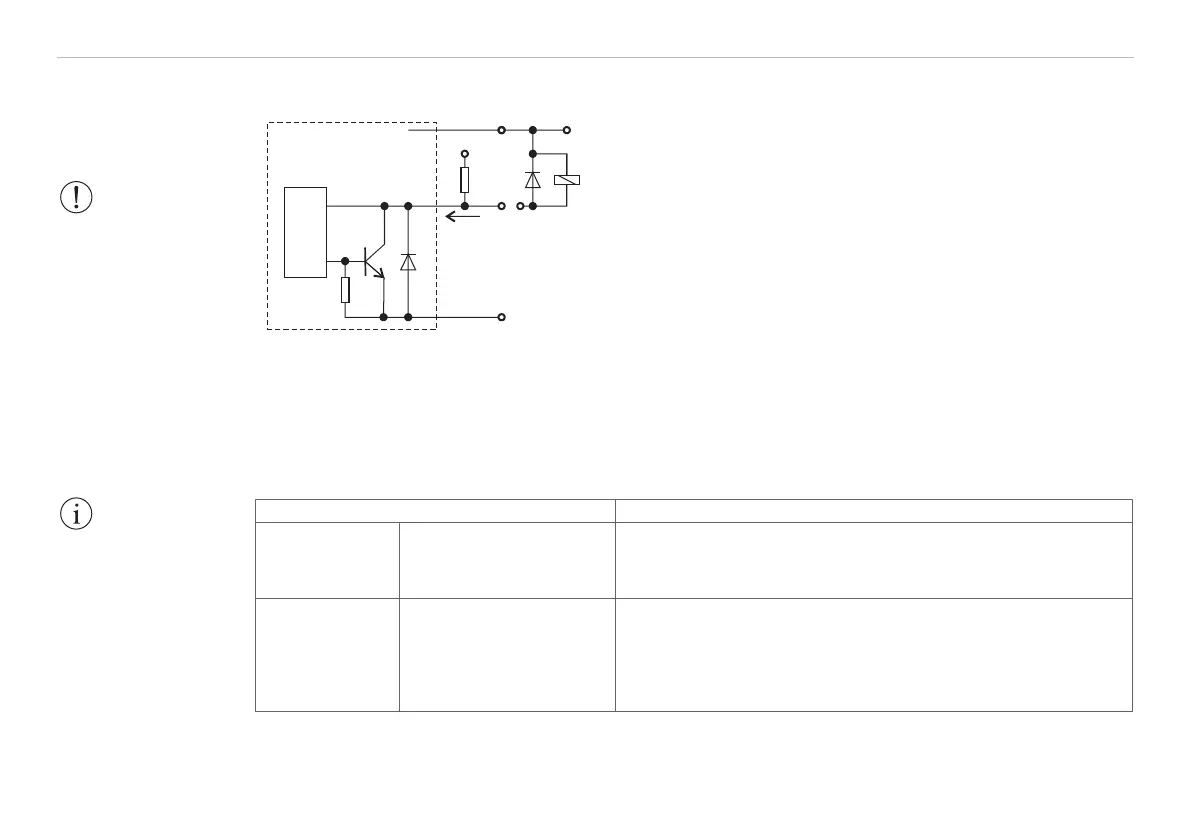
6.10.3 Output Circuit for the Switching Outputs
+24 VDC
T
ILD1700
Switching output
Pin 7 / 8
GND Pin 6
max. 100 mA
+U Pin 5
B
In the active state the transistor T is conductive.
The switch outputs are short-circuit-proof.
To reset the short-circuit protection:
- Clear the external short circuit
- Switch off the sensor and switch on again, or
- Send the software command “Reset“ to the
sensor.
The two limit outputs (Pin 7 and 8) may also be
actuated in parallel as window comparator (OK/
Not OK separation).
Fig. 29 Switching output: Examples of external protective
circuit with pull-up resistor or relay with protective diode
6.11 Synchronization of Sensors
If two sensors are used on a single object to be measured, they can be synchronized with each other. The
optoNCDT1700 distinguishes between two types of synchronization, see Fig. 30.
Type Used for
Simultaneous
synchronization
Both sensors measure in
the same cycle.
Measurement of differences (thickness, difference in height) on
opaque objects. Here, Sensor 1 must be programmed as the
“Master“ and Sensor 2 as the “Slave“.
Alternating
synchronization
Both sensors measure
alternately
Thickness measurements on translucent objects or measure-
ments of difference on closely spaced measurement points.
The alternating synchronization requires that the lasers are
switched on and off alternately so that the two sensors do not
interfere with each other optically.
Fig. 30 Characteristics of and uses for the different types of synchronization
For alternating synchronization the master sensor has to be run in „Master alternating“ mode, see Chap. 6.5.
WARNING!
Never connect the
relay without a
protective diode! Risk
of damage to the
switch output.
IMPORTANT!
Synchronization
requires that the
master and slave
sensors have the
same measurement
frequency.

 Loading...
Loading...