Setting Up The Networking Feature
Numbering Plan
34 ◆ Networking
Example:
This example shows two separate extension numbers assigned for the networked systems.
System A dials 4xx to reach System B, while system B dials 3xx to reach System A.
The following example shows a uniÞed extension number assignment. All users dial a 4-digit
extension number (2xxx) to reach anyone within the network, regardless of which system they
are connected. System A users have extension numbers 20xx, while system B users have
extension numbers 23xx.
It is also possible to use F-Route to select the correct node for the destination extension num-
ber. The example below shows a numbering scheme where the user must dial an additional
digit 7 before the extension number. This is routed by F-Route to the correct node and ana-
lyzed again in the F-Route tables at the remote Aspire.
When using F-Route, you must translate the dialed number (e.g. 72301 translates to
2301) otherwise the call will not ‘exit’ from the F-Route tables.
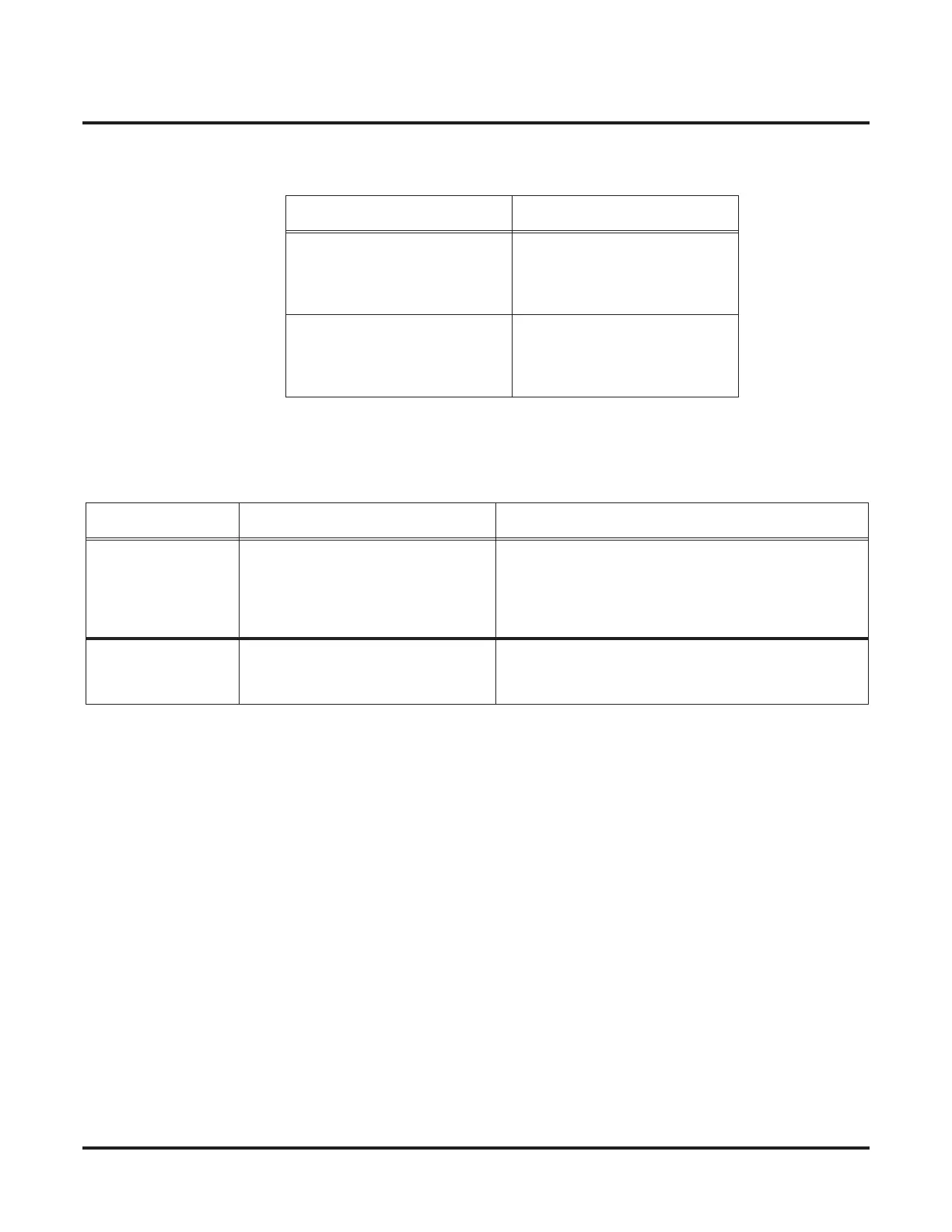
System – A System – B
Dial “3x”:
• Digit “3”
• Type 2 (Intercom)
Dial “3x”:
• Digit “3”
• Type 8 (Networking)
• System ID “1”
Dial “4x”:
• Digit “3”
• Type 8 (Networking)
• System ID “1”
Dial “4x”:
• Digit “3”
• Type 2 (Intercom)
Programming System – A System – B
Program 11-01 Dial “2”:
• 2x = Digit “0”
• 20 = Digit “4”, Type 2 (Intercom)
• 23 = Digit “4”, Type 8 (Network),
System ID “1”
Dial “2”:
• 2x = Digit “0”
• 20 = Digit “4”, Type 8 (Network),
System ID “1”
• 23 = Digit “4”, Type 2 (Intercom)
Program 11-02 Port 1 = extension number 2001
Port 2 = extension number 2002
Port 3 = extension number 2003, etc.
Port 1 = extension number 2301
Port 2 = extension number 2302
Port 3 = extension number 2303, etc.

 Loading...
Loading...