245
integral
time is too short, the correction will be too strong and will cause hunting
to occur.
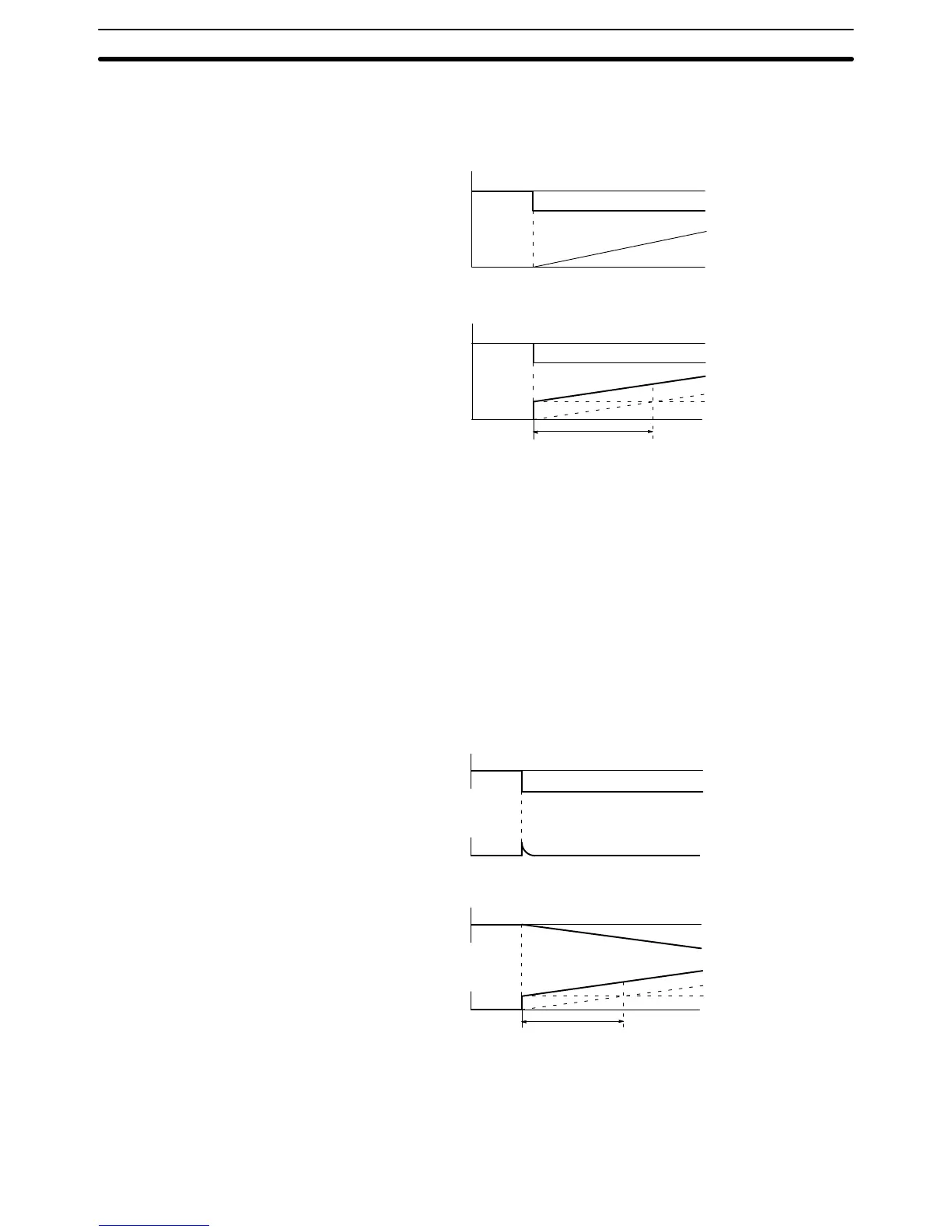
Integral Operation
PI Operation and Integral T
ime
Deviation
Operation
amount
Step response
PI operation
P operation
T
i: Integral time
0
0
0
0
Deviation
Operation
amount
Step response
I operation
Derivative Operation (D)
Proportional operation and integral operation both make corrections with re-
spect to the control results, so there is inevitably a response delay. Derivative
operation
compensates for that drawback. In response to a sudden disturbance
it delivers a large operation amount and rapidly restores the original status. A
correction is executed with the operation amount made proportional to the in-
cline (derivative coefficient) caused by the deviation.
The
strength of the derivative operation is indicated by the derivative time, which
is
the time required for the derivative operation amount
to reach the same level
as the proportional operation amount with respect to the step deviation, as
shown in the following illustration. The longer the derivative time, the stronger
the correction by the derivative operation will be.
Derivative Operation
PD Operation and Derivative T
ime
Step response
PD operation
P operation
Td: Derivative time
D operation
0
0
0
0
Ramp response
Deviation
Operation
amount
Deviation
Operation
amount
PID Operation
PID operation combines proportional operation (P), integral operation (I), and
derivative
operation (D). It produces superior control results even for control
ob
-
jects
with dead time. It employs proportional operation to provide smooth control
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21
 Loading...
Loading...











