246
without
hunting, integral operation to automatically correct any
of
fset, and deriv
-
ative operation to speed up the response to disturbances.
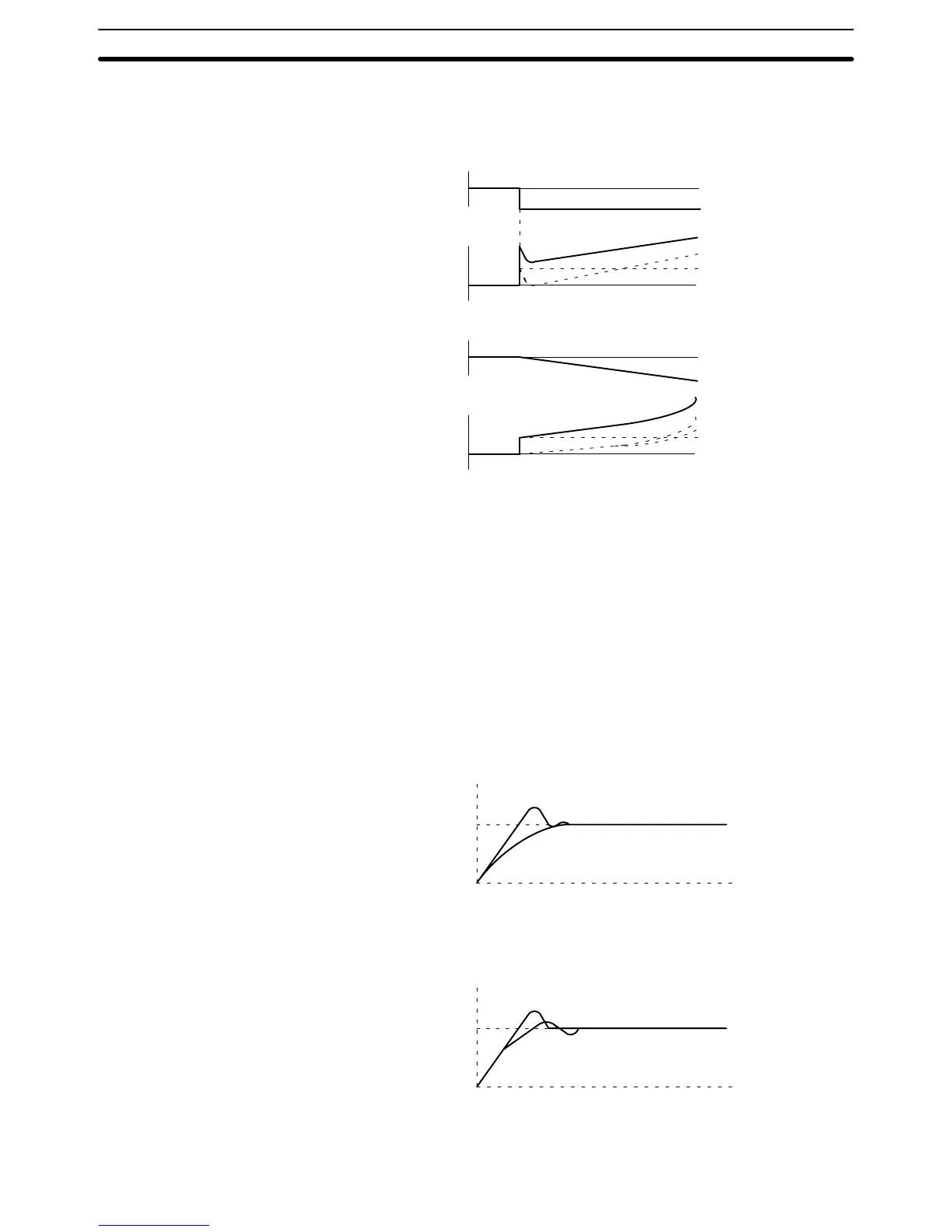
PID
Operation Output Step Response
PID Operation Output Lamp Response
PID operation
I operation
P operation
D operation
Ramp response
0
0
Deviation
Operation
amount
PID operation
I operation
P operation
D operation
Step response
0
0
Deviation
Operation
amount
Direction of Operation When
using PID operation, select either of the following two control directions.
In
either
direction,
the operation amount increases as the dif
ference between the
SV and the PV increases.
• Forward
operation: Control amount is increased when the PV is larger than the
SV.
• Reverse
operation: Control amount is increased when the PV is smaller
than
the
SV
.
Adjusting PID Parameters The
general relationship between PID parameters and control status is shown
below.
• When
it is not a problem if a certain amount of time is required for stabilization
(settlement time), but it is important not to cause overshooting, then enlarge
the proportional band.
SV
Control by measured PID
When P is enlarged
• When
overshooting is not a problem but it is desirable to quickly stabilize
con
-
trol,
then
narrow the proportional band. If the proportional band is narrowed too
much, however, then hunting may occur.
When P is narrowed
Control by measured PID
SV
• When
there is broad hunting, or when operation is tied up by overshooting and
undershooting, it is probably because integral operation is too strong. The
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21
 Loading...
Loading...











