Programming
8.3 Axis movements
8-156
SINUMERIK 802D sl Operation and Programming Nibbling (BP-N), 06/2006 Edition
6FC5 398-3CP10-0BA0
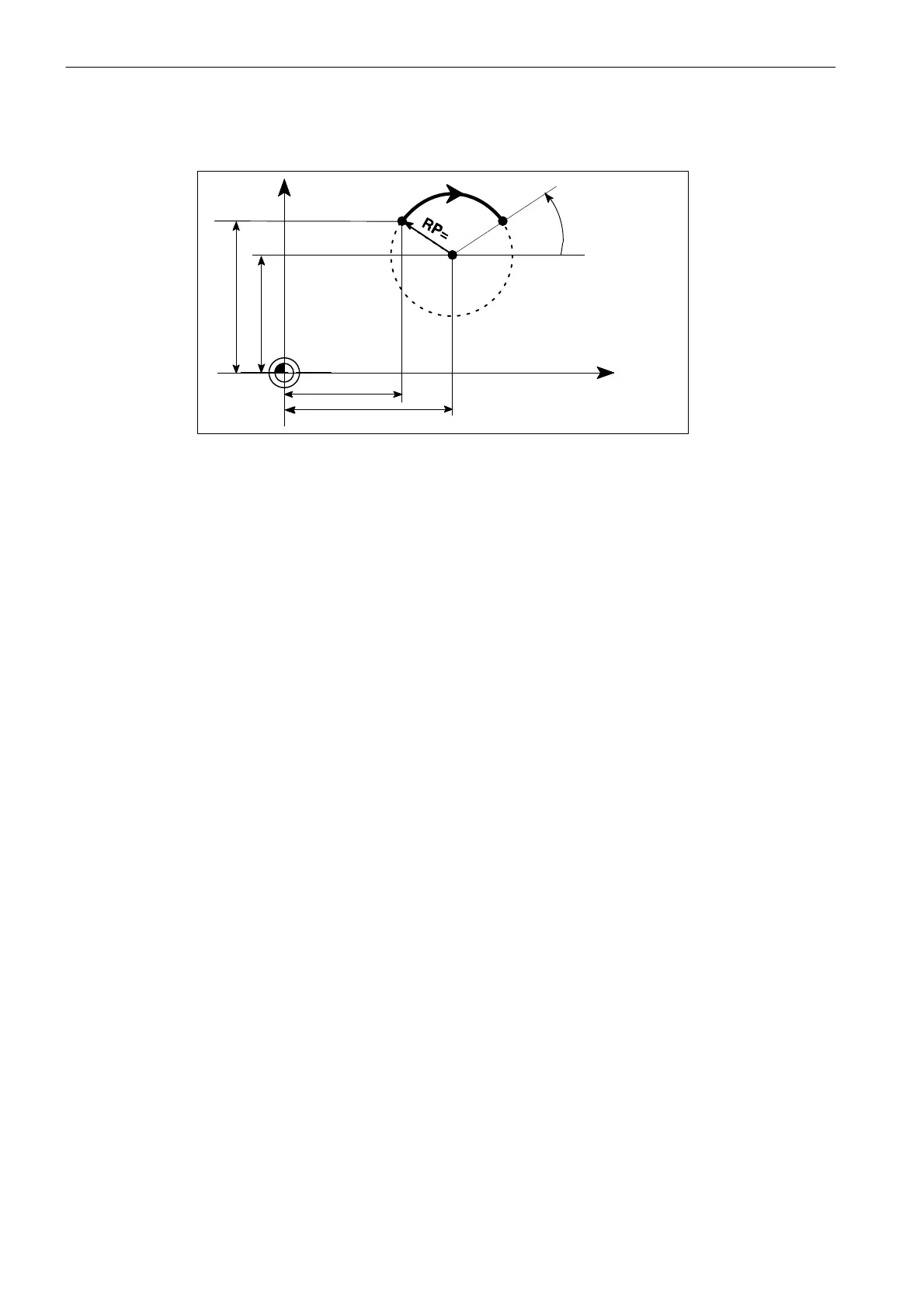
Programming example: Polar coordinates
40
30
X
Y
Center point = pole
Starting point
33
AP=
40
Fig. 8-23 Example for circle with polar coordinates
N1 G17 ; X/Y plane
N5 G90 G0 X30 Y40 ; Circle starting point for N10
N10 G111 X40 Y33 ; Pole = circle center point
N20 G2 RP=12.207 AP=21 ; Polar specifications
8.3.4 Circular interpolation via intermediate point: CIP
Functionality
If you know three contour points of the circle, instead of center point or radius or aperture
angle, then it is advantageous to use the CIP function.
The direction of the circle results here from the position of the intermediate point (between
starting and end points). The intermediate point is written according to the axis assignment
I1=... for the X axis,
J1=... for the Y axis.
CIP remains active until canceled by another instruction from this G group (G0, G1, G2, ...).
Note: The configured dimensional data G90 or G91 applies to the end point and the inter-
mediate point.

 Loading...
Loading...

















