Programming
8.8 Program jumps
8-181
SINUMERIK 802D sl Operation and Programming Nibbling (BP-N), 06/2006 Edition
6FC5 398-3CP10-0BA0
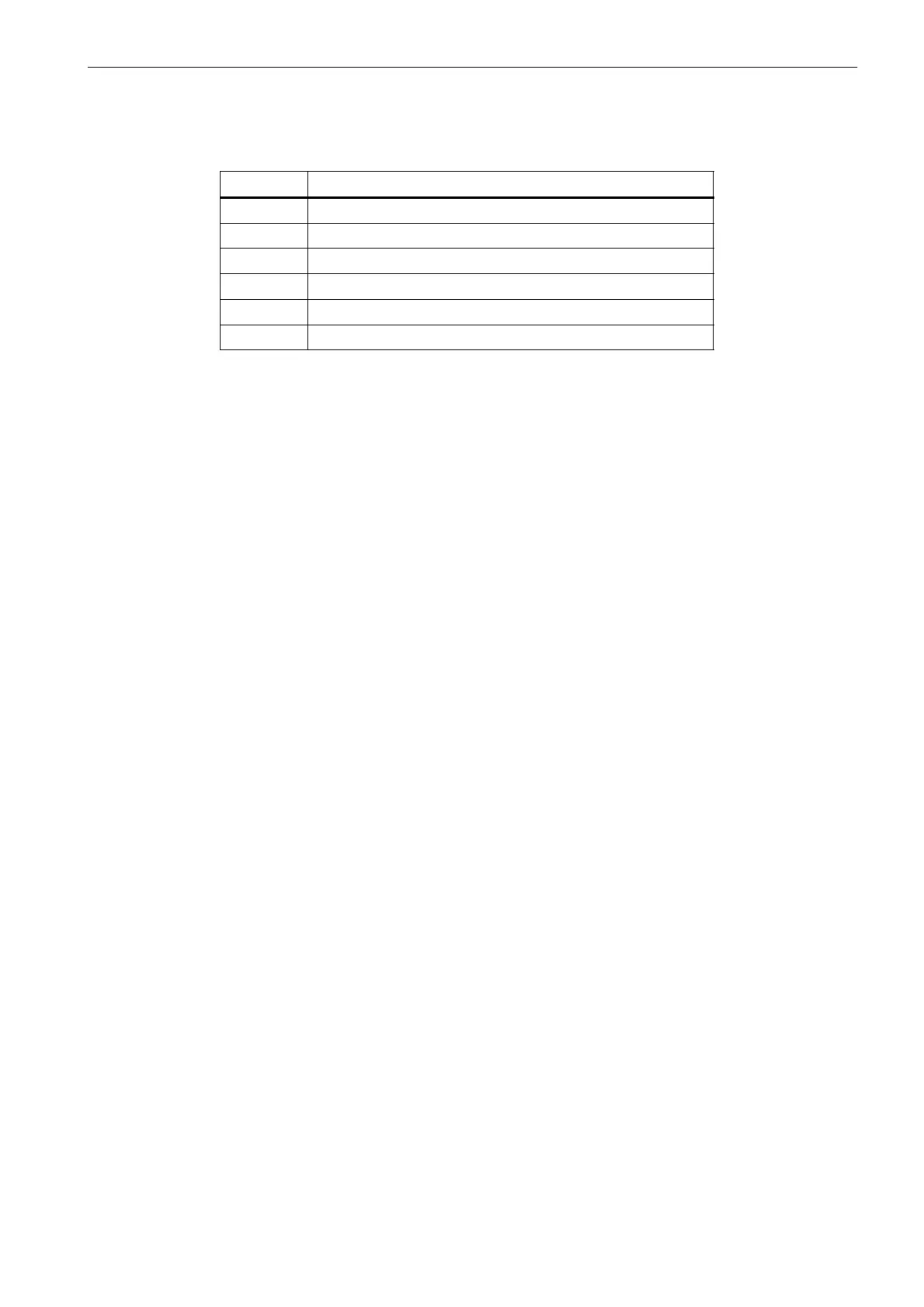
Comparison operations
Operators Meaning
= = Equal to
< > Not equal to
> Greater than
< Less than
> = Greater than or equal to
< = Less than or equal to
The comparison operations support formulating of a jump condition. Arithmetic expressions
can also be compared.
The result of comparison operations is “satisfied” or “not satisfied.” “Not satisfied” sets the
value to zero.
Programming example for comparison operators
R1>1 ; R1 greater than 1
1 < R1 ; 1 less than R1
R1<R2+R3 ; R1 less than R2 plus R3
R6>=SIN( R7*R7) ; R6 greater than or equal to SIN (R7)
2
Programming example
N10 IF R1 GOTOF LABEL1 ; If R1 is not equal to zero, then go to the block with LA-
BEL1
...
N90 LABEL1: ...
N100 IF R1>1 GOTOF LABEL2 ; If R1 is greater than 1, then go to the block with LABEL2
...
N150 LABEL2: ...
...
N800 LABEL3: ...
...
N1000 IF R45==R7+1 GOTOB LABEL3 ; If R45 is equal to R7 plus 1, then go to the block with
; LABEL3
...
Several conditional jumps in the block:
N10 MA1: ...
...
N20 IF R1==1 GOTOB MA1 IF R1==2 GOTOF MA2 ...
...
N50 MA2: ...
Remark: The jump is executed for the first fulfilled condition.

 Loading...
Loading...

















