6.1 I/O Signal Allocations
6.1.1 Input Signal Allocations
6-6
Relationship between Parameter Settings, Allocated Pins, and Polari-
ties
The following table shows the relationship between the input signal parameter settings, the
pins on the I/O signal connector (CN1), and polarities.
Note: Refer to the following section for details on input signal parameter settings.
14.1 List of Parameters on page 14-2
Example of Changing Input Signal Allocations
The following example shows reversing the P-OT (Forward Drive Prohibit) signal allocated to
CN1-42 and the /P-CL (External Torque Limit) signal allocated to CN1-45.
Refer to the following section for the parameter setting procedure.
5.1.3
Parameter Setting Methods
on page 5-6
Confirming Input Signals
You can confirm the status of input signals on the I/O signal monitor. Refer to the following sec-
tion for information on the I/O signal monitor.
9.2.3 I/O Signal Monitor on page 9-7
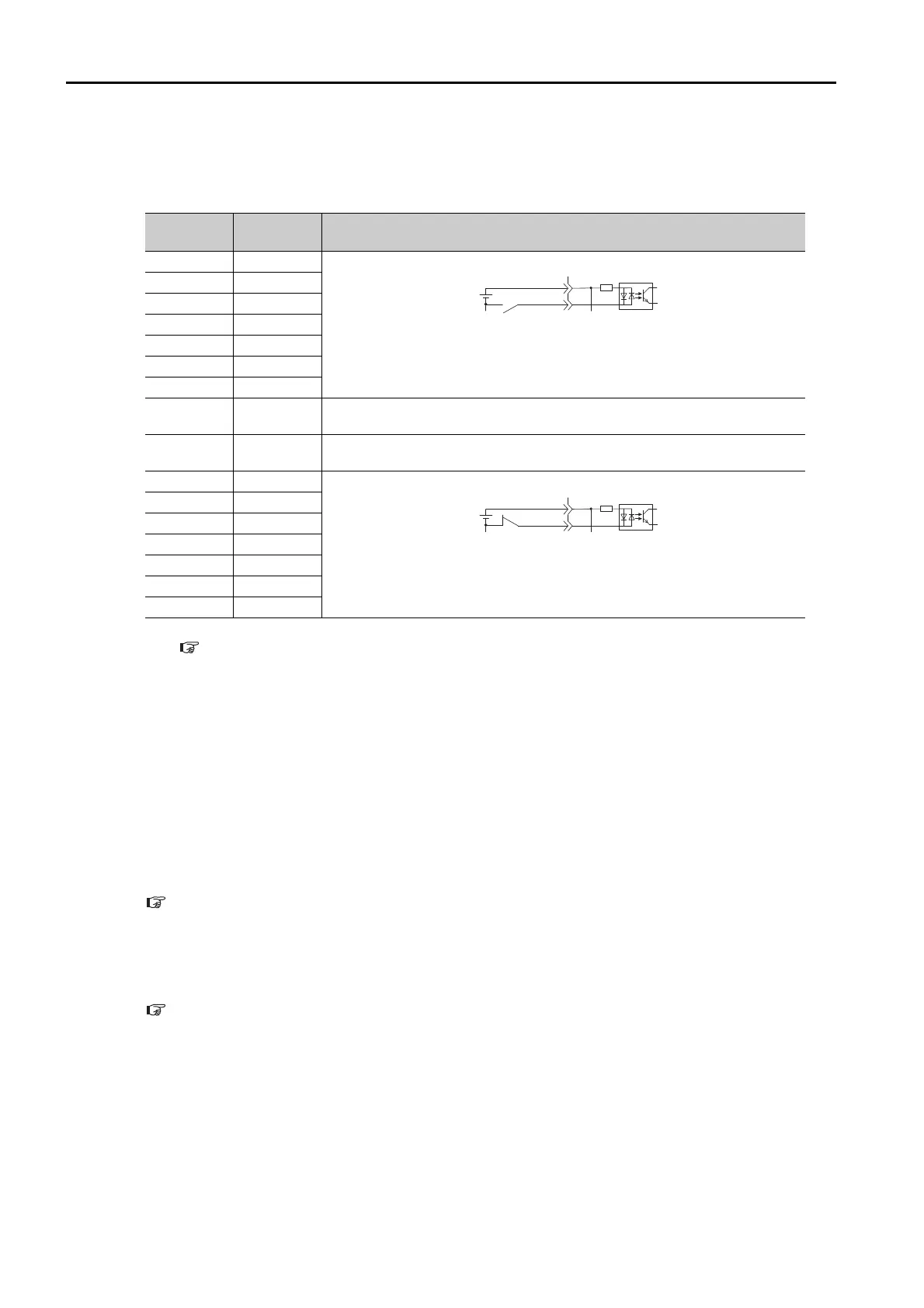
Parameter
Setting
Pin No. Description
040
A reverse signal (a signal with “/” before the signal abbreviation, such as the /
S-ON signal) is active when the contacts are ON (closed).
A signal that does not have “/” before the signal abbreviation (such as the P-
OT signal) is active when the contacts are OFF (open).
141
242
343
444
545
646
7–
The input signal is not allocated to a connector pin and it is always active.
If the signal is processed on a signal edge, then it is always inactive.
8–
The input signal is not allocated to a connector pin and it is always inactive.
Set the parameter to 8 if the signal is not used.
940
A reverse signal (a signal with “/” before the signal abbreviation, such as the /
S-ON signal) is active when the contacts are OFF (open).
A signal that does not have “/” before the signal abbreviation (such as the P-
OT signal) is active when the contacts are ON (closed).
A41
B42
C43
D44
E45
F46
Pn50A = n.2
0 Pn50B = n.
5
Before change
↓↓
Pn50A = n.5
1 Pn50B = n.
2
After change

 Loading...
Loading...