6243/44 DC Voltage Current Source/Monitor Operation Manual
2.3.2 Battery Charge Test and Discharge Test
2-36
2.3.2 Battery Charge Test and Discharge Test
The following explain examples of a charge test and a discharge test of secondary batteries such as NiCad
and nickel metal hydride batteries.
As the charge and discharge tests by nature require a long time, they should be performed in a system uti-
lizing GPIB. However, the examples given here describe the manual operations with the aim of using and
demonstrating the functions of the 6243/44.
A DC constant-current, constant-voltage charge is used for charging, which is finished when the charging
current drops below the specified current.
A pulse constant current is used for discharge, which is finished when the battery voltage drops below the
specified voltage. The voltage values registered during discharge are stored in the memory and read out
upon completion of the test.
However, the memory accommodates up to 5000 data items only and if exceeded, the discharge continues
but the data is not stored.
Consequently, only data up to 5000 seconds (= 1.38 hour) are acquired in this example.
NOTE:
1. Use a 4-wire connection to ensure accurate voltage measurement.
2. Note for the settings of the source value and limiter value in order to prevent application of a high voltage/
current in relation to the battery’s rated voltage and capacity.
The measurement conditions are listed below.
Charge test: Charging is performed with a 1 A constant current, and when a charge voltage of
1.45 V is reached the charging begins using the constant voltage.
When the charge current drops below 100 mA, the charge is completed.
Discharge test: As shown in Figure 2-11, discharging is performed with a constant current of 2 A,
pulse width 100 ms and a cycle of 1 sec. The discharge is completed when the volt-
age reaches 1.0 V during the discharge.
The battery voltage values registered during the discharge are stored in the memory
and read out upon completion of the test.
However, the number of stored data is restricted by the memory capacity. This
means that only up to 5000 seconds of data from the start of the discharging can be
stored.
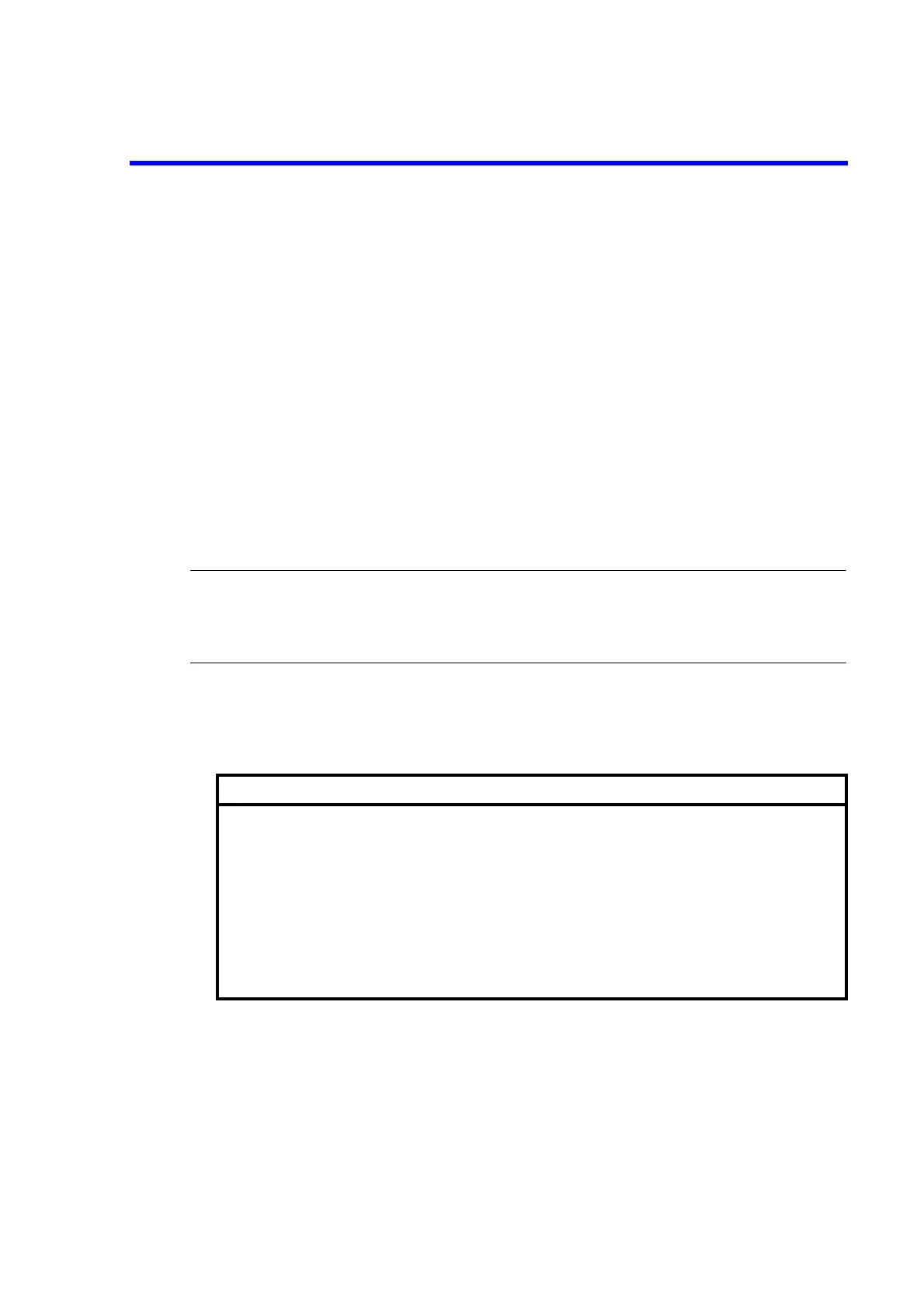
Electric-charge test conditions
Source mode
Source current
Limiter
Period
integration time
Measurement range
Memory
Comparator
Remote sensing
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
DC
1 A
1.45 V
1 s
1 PLC
2A range fixed
OFF
ON
When the charged voltage falls to 100 mA or less, the test is completed.
4 Wire
 Loading...
Loading...