5-3
Listner Input Formats
5
5.1 Summary of Listener Input Program Message
Syntactical Notation
This section gives a general description of program messages functional units ( Section 5.2) and program
data formats (
Section 5.3). (Compound commands and common commands are excluded.)
5.1.1 Separator, terminator, and space before header
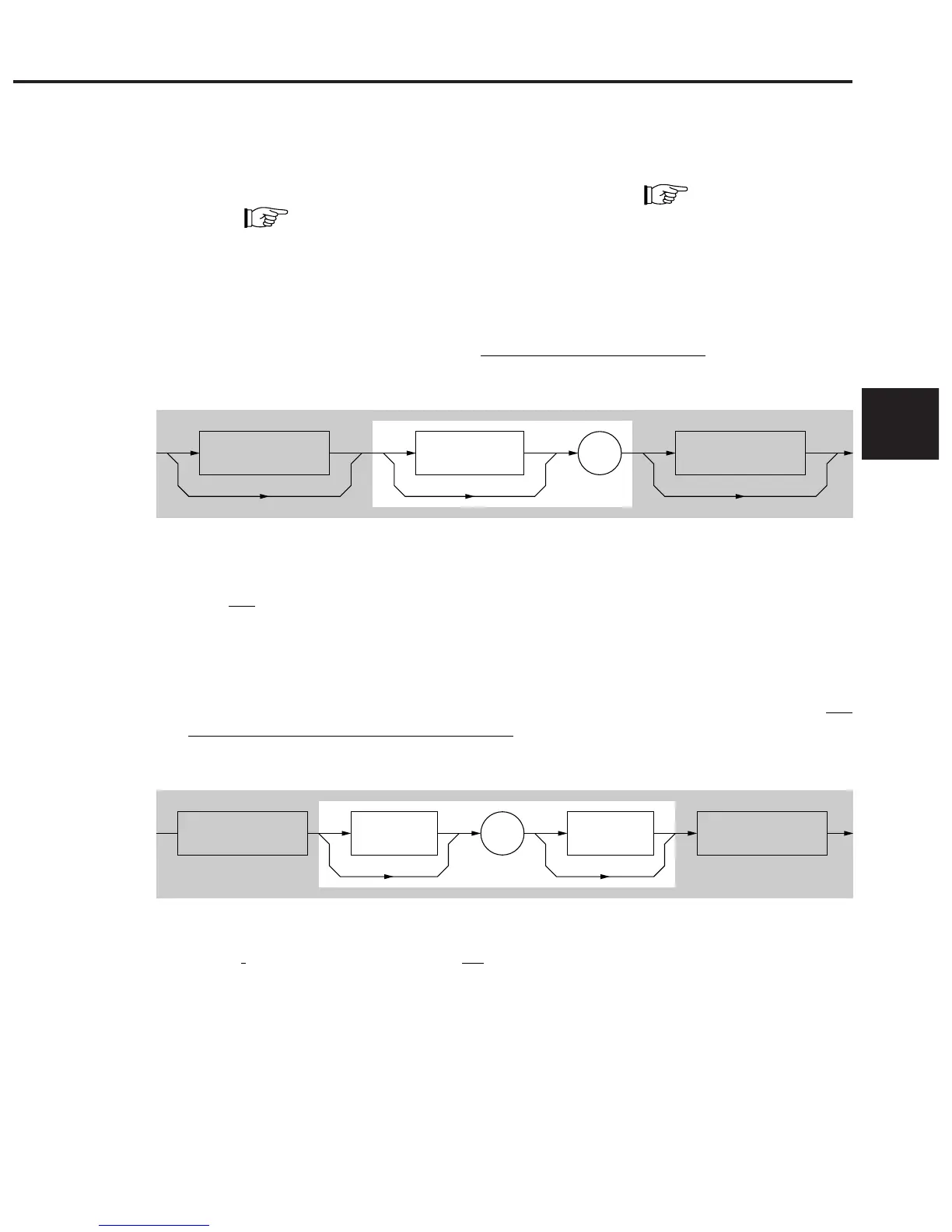
(1) PROGRAM MESSAGE UNIT SEPARATOR
Link two or more program message units using
zero or more spaces and a semicolon.
<Example 1> General format for linking two program message units
<PROGRAM
MESSAGE UNIT>
<white space>
;
<PROGRAM
MESSAGE UNIT>
<Example 2> One space + Semicolon
LOG∆1
0∆ ;RLV∆–20 LOG 10 ;RLV –20: Set the log scale to 10 dB/div and the reference level to –20
dBm.
(2) PROGRAM DATA SEPARATOR
When there are two or more pieces of program data, separate two contiguous pieces of program data using
zero
or more spaces, a command, and zero or more spaces.
<Example 1> General format for separating two pieces of program data
<PROGRAM DATA> <PROGRAM DATA><white space> <white space>
,
<Example 2> Comma only <Example 3> Comma + One space
TIME∆10
, 15 TIME ∆10, ∆15 Set the times to 10:15.
5.1 Summary of Listener Input Program Message Syntactical Notation

 Loading...
Loading...