Section 5 Listner Input Formats
5-34
(4) Floating-point binary data
Floating-point binary data, whether it is program data or response data, is used as <ARBITRARY BLOCK>-
type transfer data.
Our products do not support floating-point binary data; however, general specifications are
explained below.
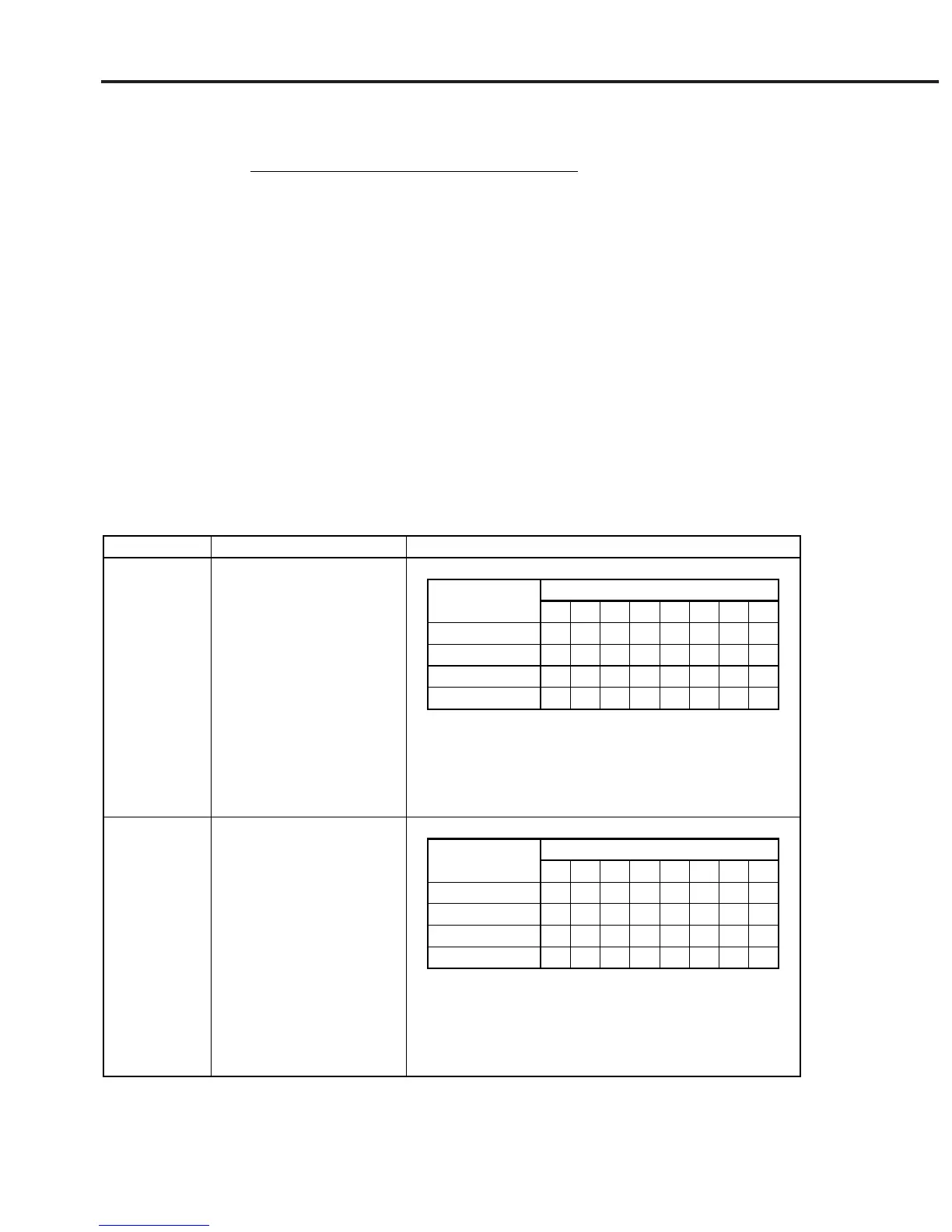
Floating-point binary data must consists of the following three fields:
(a) Sign field (sign bit)
(b) Exponent field (exponent bit)
(c) Mantissa field (mantissa bit)
Numeric data having a decimal point is handled here. It has two types of precision: single precision and double
precision. Field structures and transfer orders are shown below. Meanings of symbols are as follows:
S: Sign bit
EM: Most significant exponent bit
EL: Least significant exponent bit
FM: Most significant mantissa bit
FL: Least significant mantissa bit
Precision
Single
precision
Double
precision
Number of transfer bytes
4 bytes
8 bytes
Field structure and transfer order
DIO line
Transfer byte
1st byte
2nd byte
3rd byte
4th byte
DIO line
Transfer byte
1st byte
2nd byte
3rd to 7th byte
8th byte
8
S
EL
F
F
7
EM
FM
F
F
6
E
F
F
F
5
E
F
F
F
4
E
F
F
F
3
E
F
F
F
2
E
F
F
F
1
E
F
F
FL
Sign bit : 1 bit
Exponnent bit : 8 bits (+127 to –126)
Mantissa bit : 23 bits
Sign bit : 1 bit
Exponnent bit : 11 bits (+1023 to –1022)
Mantissa bit : 52 bits
8
S
E
F
F
7
EM
E
F
F
6
E
E
F
F
5
E
EL
F
F
4
E
FM
F
F
3
E
F
F
F
2
E
F
F
F
1
E
F
F
FL
 Loading...
Loading...