BL702/704/706 Reference Manual
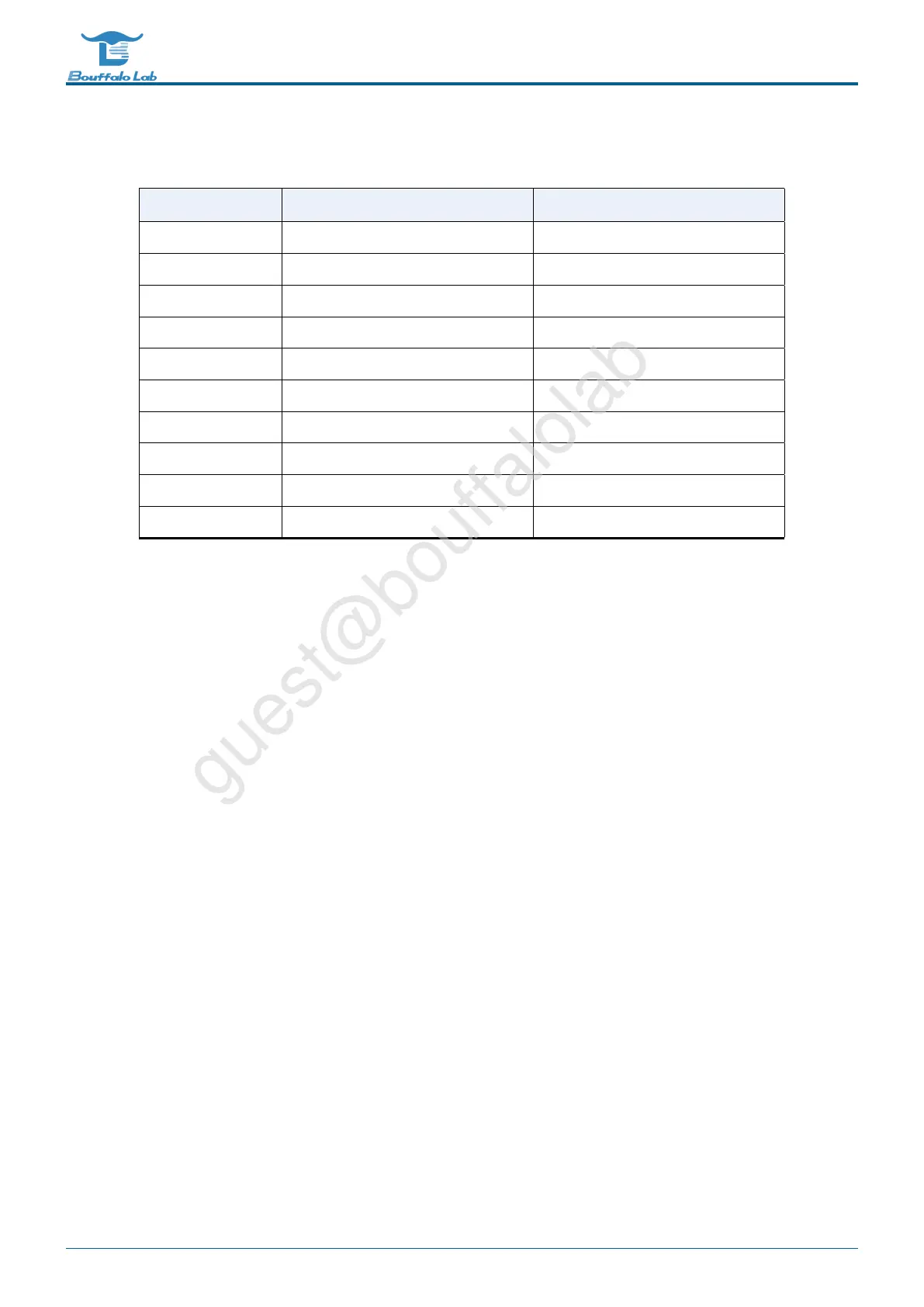
Table 17.1: Transmission signal
Name
MII RMII
ECOL ECOL: collision detection -
ERXDV ERXDV: data valid ECRSDV: Carrier detect/data valid
ERX0-ERX3 ERX0-ERX3: 4-bit receive data ERX0-ERX1: 2-bit receive data
ERXER ERXER: Receive error indication ERXER: Receive error indication
ERXCK ERXCK: Receive clock signal -
ETXEN ETXEN: transmit enable ETXEN: transmit enable
ETX0-ETX3 ETX0-ETX3: 4-bit transmit data ETX0-ETX1: 2-bit transmit data
ETXER ETXER: Send error indication -
EMDC MDIO Clock MDIO Clock
EMDIO MDIO Data Input Output MDIO Data Input Output
The RMII interface has fewer pins, and a 2-bit data line is used for receiving and sending. At a rate of 100Mbps, a
50MHz reference clock is required.
17.7 Programming process
17.7.1 PHY initialization
• According to the PHY type, set the RMII_EN bit in the EMAC_MODE register to select the appropriate connection
method
• Set the MAC address of EMAC to EMAC_MAC_ADDR0 and EMAC_MAC_ADDR1
• Set the appropriate clock for the MDIO part by programming the field CLKDIV in the EMAC_MIIMODE register
• Set the corresponding PHY address to the FIAD field of the register EMAC_MIIADDRESS
• According to the PHY manual, send commands through the EMAC_MIICOMMAND and EMAC_MIITX_DATA
registers
• The data read from the PHY will be stored in the EMAC_MIIRX_DATA register
• The status of interaction with PHY commands can be queried through the EMAC_MIISTATUS register
After the basic interaction is completed, the PHY should enter the auto-negotiation state. After the negotiation is
completed, program the mode to the FULLD bit in the EMAC_MODE register according to the negotiation result.
BL702/704/706 Reference Manual 293/ 375
@2021 Bouffalo Lab
 Loading...
Loading...