Brooks Automation 7. Service Procedures
Part Number: PF40-DI-00010 Rev. A Replacing Belts and Motors
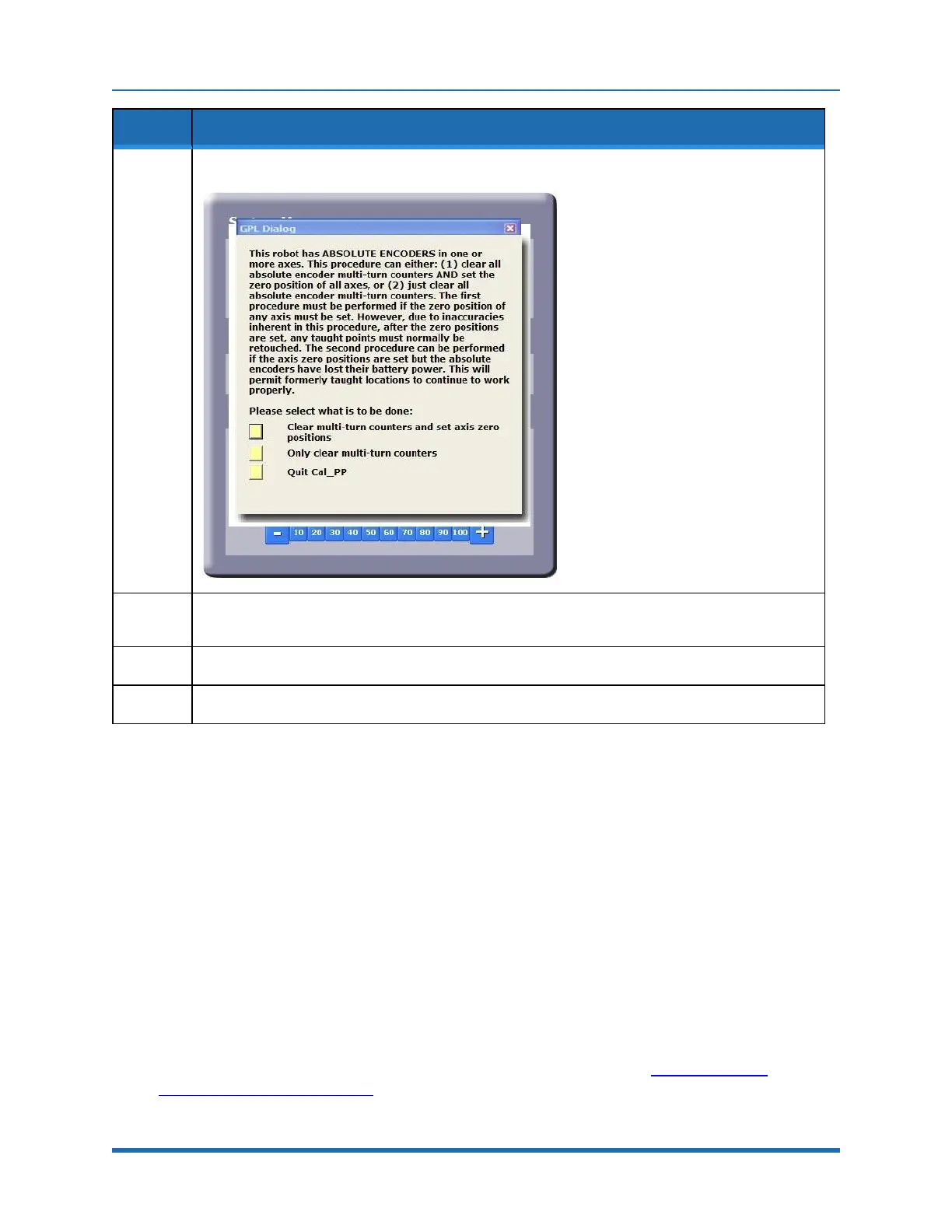
Step Action
13.
The CALPP application takes about 1 minute to run.
14.
After calibration is complete, use the brake release button and move the Z-axis up from the hard
stop. Failing to do this will produce an error as the robot is outside of the soft stop limits.
15.
Ensure that the pins are removed.
16.
Enable power and home the robot. Calibration does not take effect until the robot is homed.
Replacing Belts and Motors
The timing belts and motors are designed to last the life of the robot. It is not expected that they will
need to be replaced in the field. In most cases, if a belt or a motor needs to be replaced, the robot
should be returned to the factory. While there are procedures at the end of this manual for replacing
belts and motors, only experienced service technicians should attempt these procedures.
General Belt Tensioning
The PreciseFlex 400 has been designed to make belt tensioning very simple. Prior to 2014, each
axis had a spring pre-load system that sets the correct belt tension when the axis motor mount plate
screws are loosened. After 2014, the springs were removed from the inner and outer links and
access hatches were added to make belt tensioning more accurate. See Appendix E: Belt
Tensions, Gates Tension Meter for belt tension specifications.
Copyright © 2023, Brooks Automation
100
 Loading...
Loading...