Brooks Automation 3. Collaborative Robot Safety
Part Number: PF40-DI-00010 Rev. A Robot Testing and Safety Circuits
expense and complexity of 100% redundant safety systems is not warranted. See Appendix I:
Safety Circuits for PF400 500gm Payload.
Safety circuits, Failure Modes, and TUV Testing for the PF400 robots.
1. Force Limits by Design or Control. The PF400 is a low-power robot by inherent design and
control. For axes 2, 3, 4, and the gripper, the maximum forces that can be applied by the motors,
multiplied by the transmission are well under 140 N. In the case of the Z-axis, the maximum force
required to support the Z-axis gravity load of up to 80 N plus a reasonable additional force for
acceleration against gravity of 60 N, results in a total force of 140 N, and is restricted by current limits
in firmware. A further reduction in force is set by collaborative force limits in software, so that the
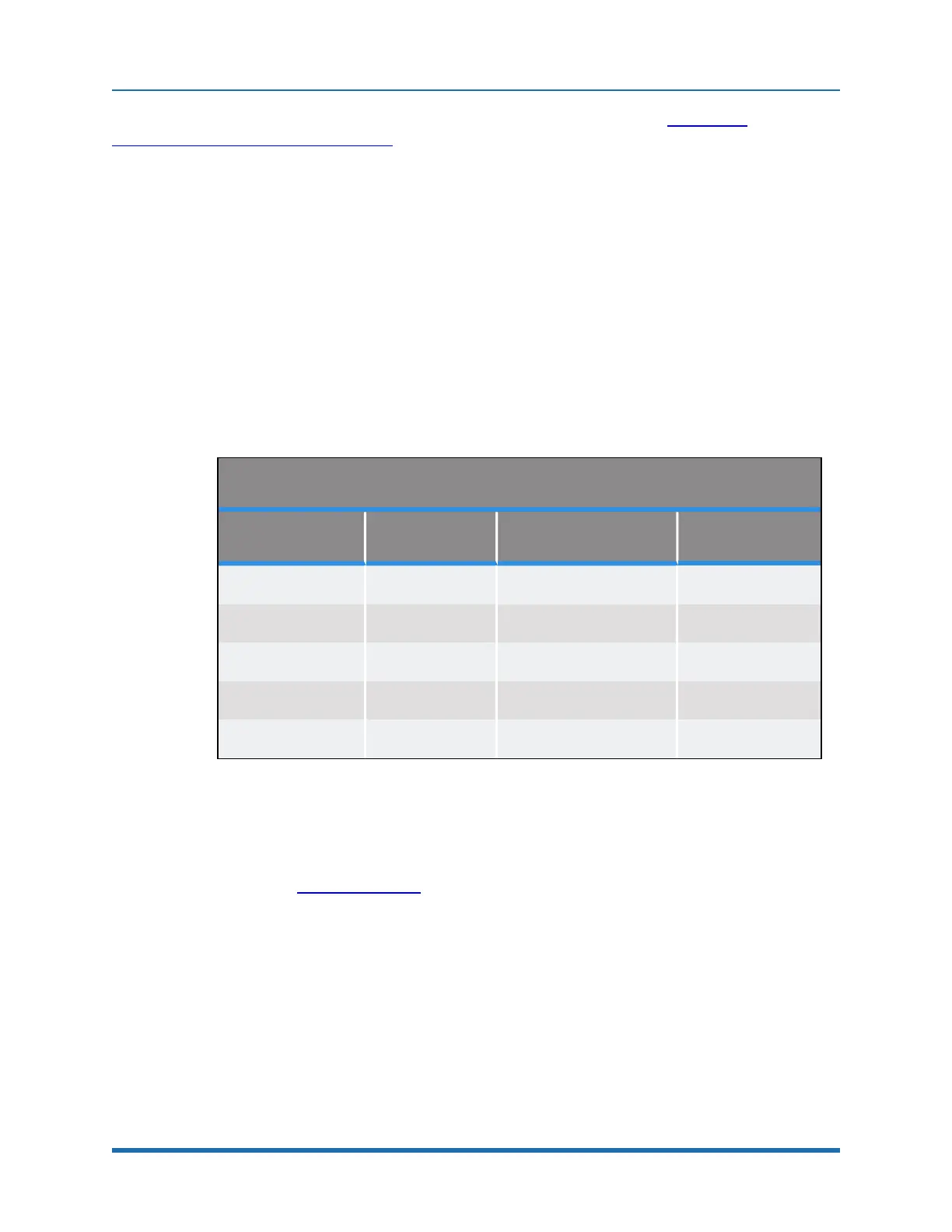
clamping/squeezing force (quasi-static) does not exceed 60 N. See Table 3-1.
PreciseFlex 500 gm
Unlimited Current Limited Collab Limit
Z Axis 314 140 60
J2 at Elbow 33 33 33
J3 at Wrist 18 18 18
J4 at Gripper 11 11 11
Gripper Squeeze 23 23 23
Table 3-1: PreciseFlex 400 Maximum Forces, Newtons
2. E-Stop circuit for 500 gm payload PF400. For the 500 gm payload PF400 plate handler, there is a
single E-Stop circuit. However, the forces applied by this machine are so low (less than 60 N at low
speeds. See TUV test verification) that most users simply use their hand to stop the plate handler and
do not employ an E-Stop button or pendant. If the E-Stop circuit is interrupted the robot will decelerate
and stop in a Category 1 E-Stop (decelerate using motor power then turn off motor power). The E-
Stop circuit for the 500 gm plate handler is not CAT 3 in that there are not two redundant external E-
Stop circuits. However, a redundant E-Stop method is available for this low-power robot: users can
very easily stop it with their hand by grabbing the gripper or links. For TUV testing, the forces required
to stop the robot and trigger an E-Stop are measured with a NIST certified force gauge. For E-Stop
testing, the E-Stop button is depressed and motor power is shut down. TUV has verified this E-Stop
Copyright © 2023, Brooks Automation
32
 Loading...
Loading...