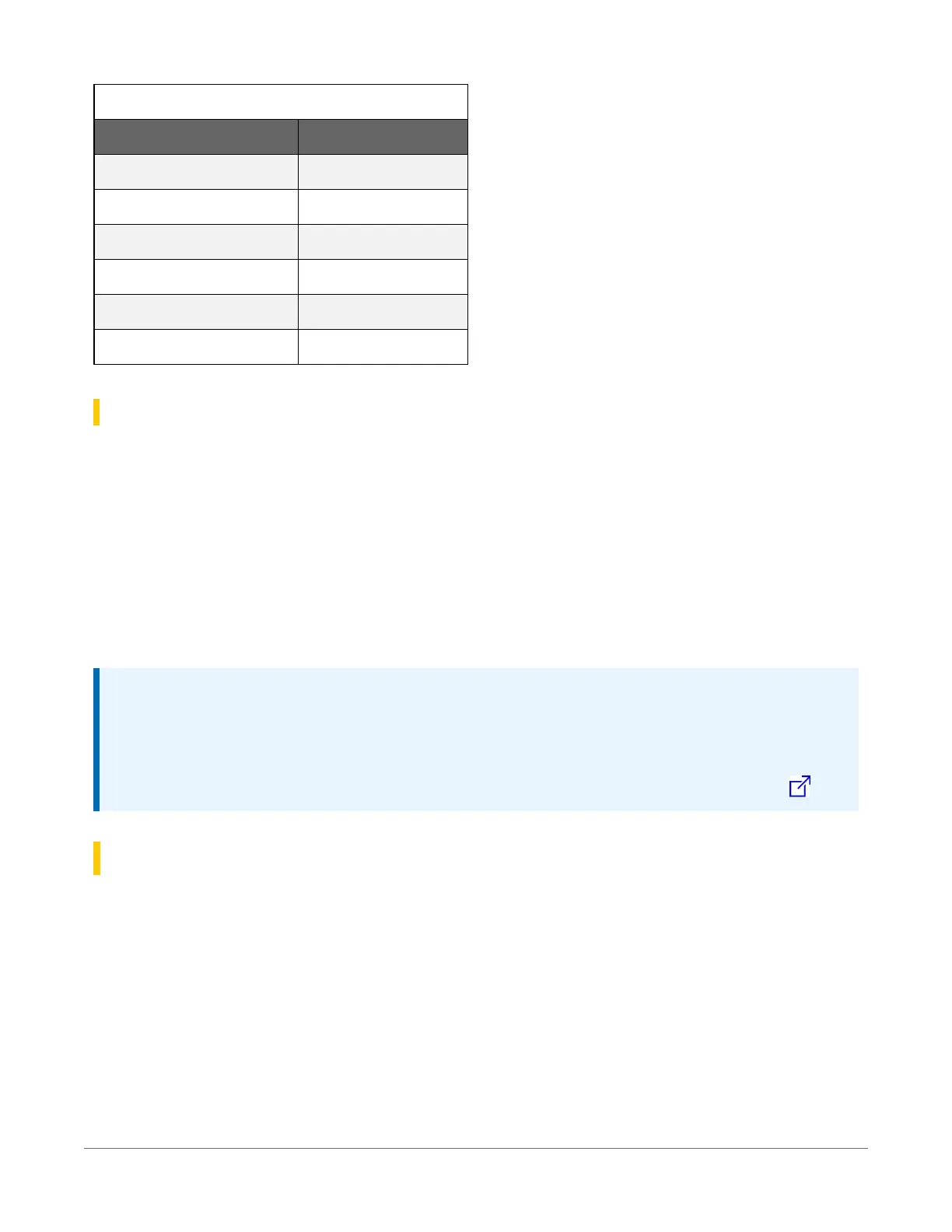
Table 16-5: Data processing abbreviations
Data processing name Abbreviation
WindVector
WVc
Median
Med
ET
ETsz
Solar Radiation (from ET)
RSo
Time of Max
TMx
Time of Min
TMn
16.5.1.2 Data records
Subsequent rows are called data records. They include observed data and associated record
keeping. The first field is a time stamp (TS), and the second field is the record number (RN).
The time stamp shown represents the time at the beginning of the scan in which the data is
written. Therefore, in record number 3 in the previous Example data(p. 82), Temp_C_Avg shows
the average of the measurements taken over the minute beginning at 14:26:01 and ending at
14:27:00. As another example, consider rainfall measured every second with a daily total rainfall
recorded in a data table written at midnight. The record time stamped 2019-03-08 00:00:00 will
contain the total rainfall beginning at 2019-03-07 00:00:01 and ending at 2019-03-08 00:00:00.
NOTE:
TableName.Timestamp syntax can be used to return the timestamp of a data table record,
expressed either as a time into an interval (for example seconds since 1970 or seconds since
1990) or as a date/time string. For more information,
see:https://www.campbellsci.com/blog/programmatically-access-stored-data-values .
16.6 Creating data tables in a program
Data is stored in tables as directed by the CRBasic program. In Short Cut, data tables are created
in the Output steps. See Creating a Short Cut data logger program(p. 71) Data tables are created
within the CRBasic data logger program using the DataTable()/EndTable instructions. They
are placed after variable declarations and before the BeginProg instruction.
16. Working with data85
 Loading...
Loading...