High-quality power regulators typically reduce noise due to power regulation. Using the 50 Hz or
60 Hz first notch frequency (f
N1
) option for CRBasic analog input measurement instructions
often improves rejection of noise sourced from power mains. The CRBasic standard deviation
output instruction, StdDev(), can be used to evaluate measurement noise.
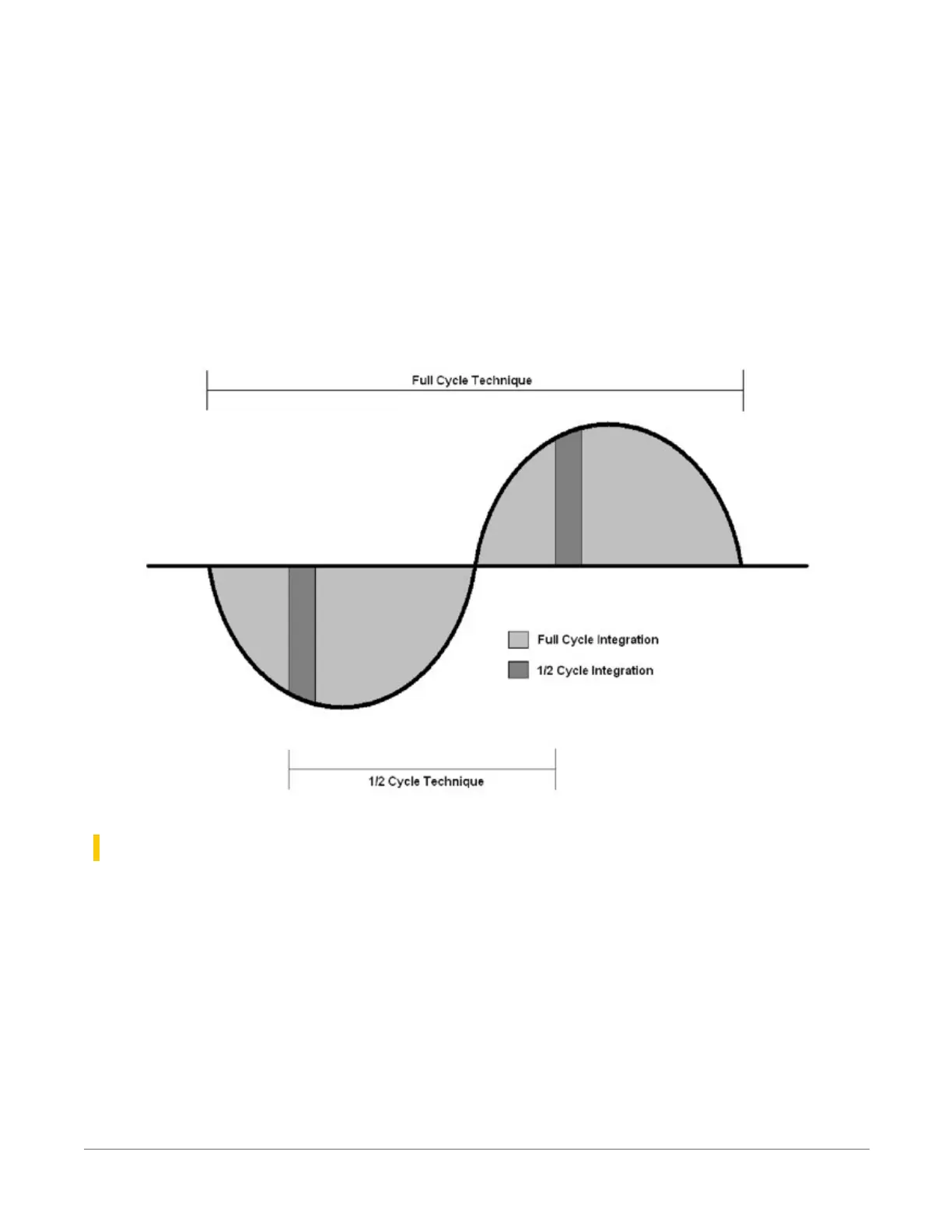
The data logger includes adjustable digital filtering, which serves two purposes:
l
Arrive as close as possible to the true input signal
l
Filter out measurement noise at specific frequencies, the most common being noise at 50
Hz or 60 Hz, which originate from mains-power lines.
Filtering time is inversely proportional to the frequency being filtered.
22.11.3.1 Minimizing electronic noise
Electronic noise can cause significant error in a voltage measurement, especially when measuring
voltages less than 200 mV. So long as input limitations are observed, the PGA ignores voltages,
including noise, that are common to each side of a differential-input pair. This is the common-
mode voltage. Ignoring (rejecting or canceling) the common-mode voltage is an essential
feature of the differential input configuration that improves voltage measurements. The
following image illustrates the common-mode component (V
cm
) and the differential-mode
component (V
dm
) of a voltage signal. V
cm
is the average of the voltages on the V+ and V– inputs.
22. Tips and troubleshooting192
 Loading...
Loading...