6-8
Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-11380-03
Chapter 6 Configuring the System
Changing IP Information
After obtaining its host name from the default configuration file or the DHCP reply, the switch reads
the configuration file that has the same name as its host name (hostname-confg or hostname.cfg,
depending on whether network-confg or cisconet.cfg was read earlier) from the TFTP server. If the
cisconet.cfg file is read, the filename of the host is truncated to eight characters.
If the switch cannot read the network-confg, cisconet.cfg, or the host-name file, it reads the
router-confg file. If the switch cannot read the router-confg file, it reads the ciscortr.cfg file.
Note The switch broadcasts TFTP server requests if the TFTP server name is not obtained from the DHCP
replies, if all attempts to read the configuration file through unicast transmissions fail, or if the TFTP
server name cannot be resolved to an IP address.
Example Configuration
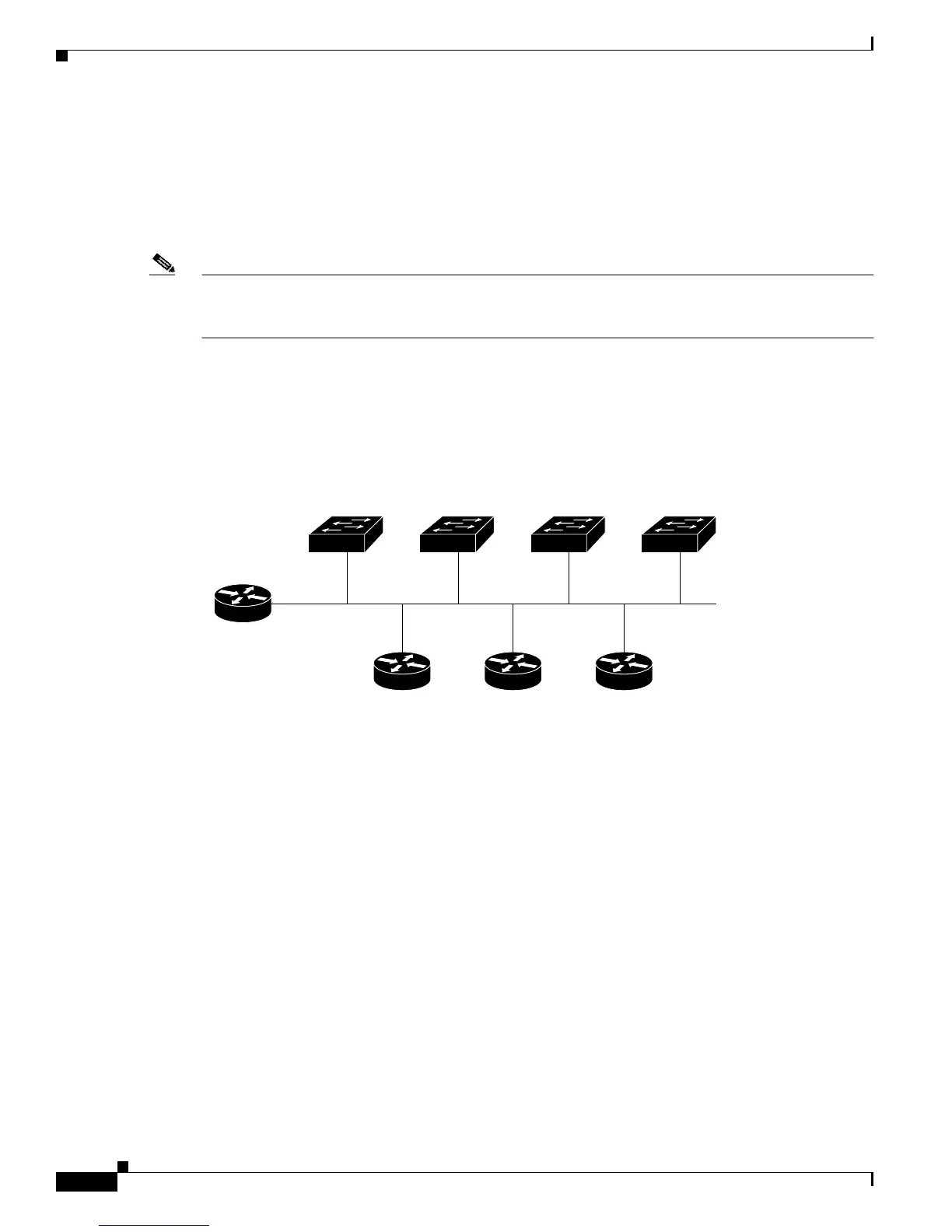
Figure 6-3 shows a sample network for retrieving IP information by using DHCP-based autoconfiguration.
Figure 6-3 DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration Network Example
Table 6-1 shows the configuration of the reserved leases on the DHCP server.
Switch 1
00e0.9f1e.2001
Cisco router
47571
Switch 2
00e0.9f1e.2002
Switch 3
00e0.9f1e.2003
DHCP server DNS server TFTP server
(maritsu)
10.0.0.1
10.0.0.10
10.0.0.2 10.0.0.3
Switch 4
00e0.9f1e.2004

 Loading...
Loading...















