11-5
Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-11380-03
Chapter 11 Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
Understanding and Configuring IGMP Snooping
Note that the switch architecture allows the CPU to distinguish IGMP information packets from other
packets for the multicast group. The switch recognizes the IGMP packets through its filter engine. This
prevents the CPU from becoming overloaded with multicast frames.
The entry in the multicast forwarding table tells the switching engine to send frames addressed to the
0100.5E01.0203 multicast MAC address that are not IGMP packets (!IGMP) to the router and to the host
that has joined the group.
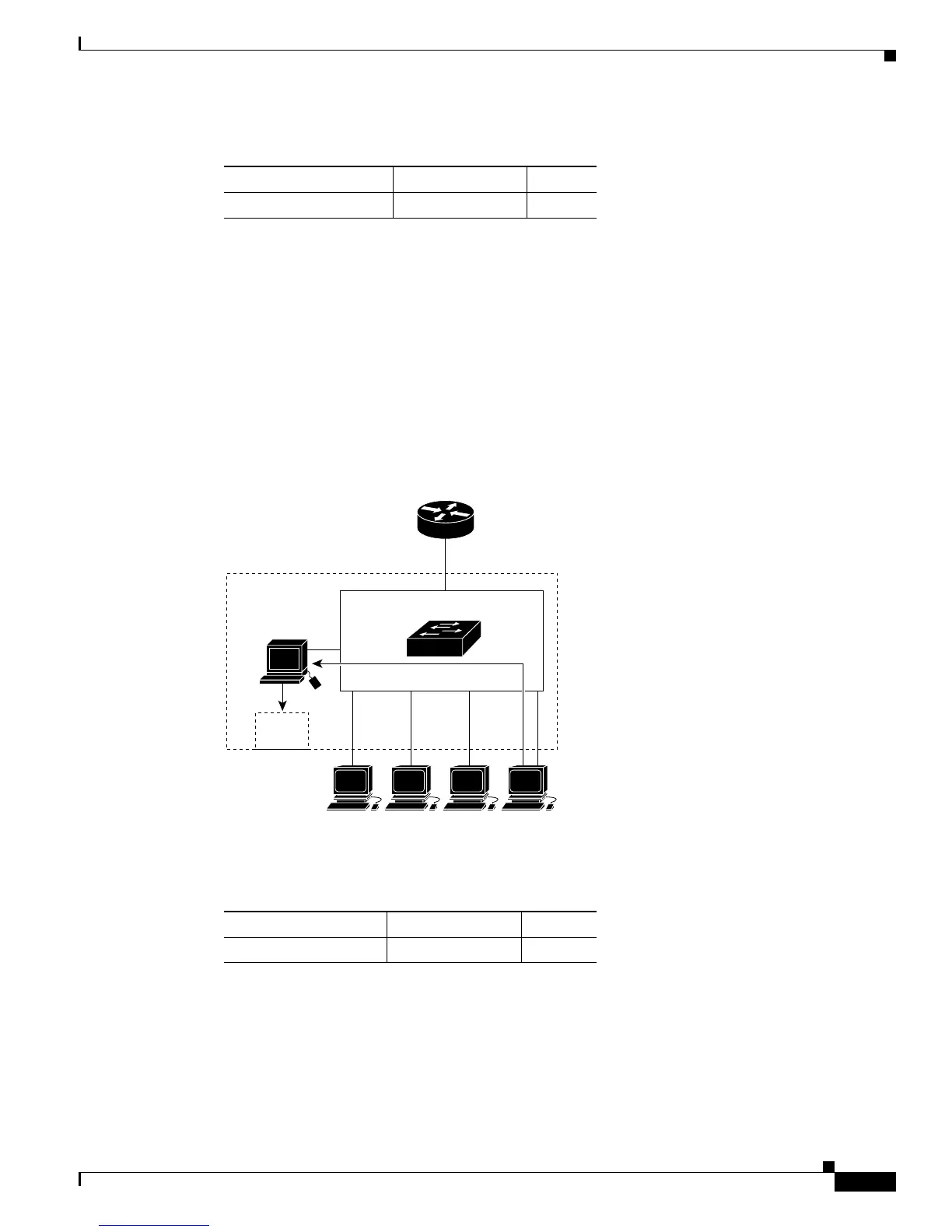
If another host (for example, Host 4) sends an IGMP join message for the same group (Figure 11-2), the
CPU receives that message and adds the port number of Host 4 to the multicast forwarding table as
shown in Table 11-2.
Figure 11-2 Second Host Joining a Multicast Group
Statically Configuring a Host to Join a Group
Ports normally join multicast groups through the IGMP report message, but you can also statically
configure a host on an interface.
Table 11-1 IP Multicast Forwarding Table
Destination Address Type of Packet Ports
0100.5e01.0203 !IGMP 1, 2
Table 11-2 Updated Multicast Forwarding Table
Destination Address Type of Packet Ports
0100.5e01.0203 !IGMP 1, 2, 5
CAM
Tabl e
CPU
Host 1 Host 2 Host 3 Host 4
Router A
Catalyst 2950 switch
1
0
234 5
47216
 Loading...
Loading...
















