11-9
Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-11380-03
Chapter 11 Configuring IGMP Snooping and MVR
Understanding Multicast VLAN Registration
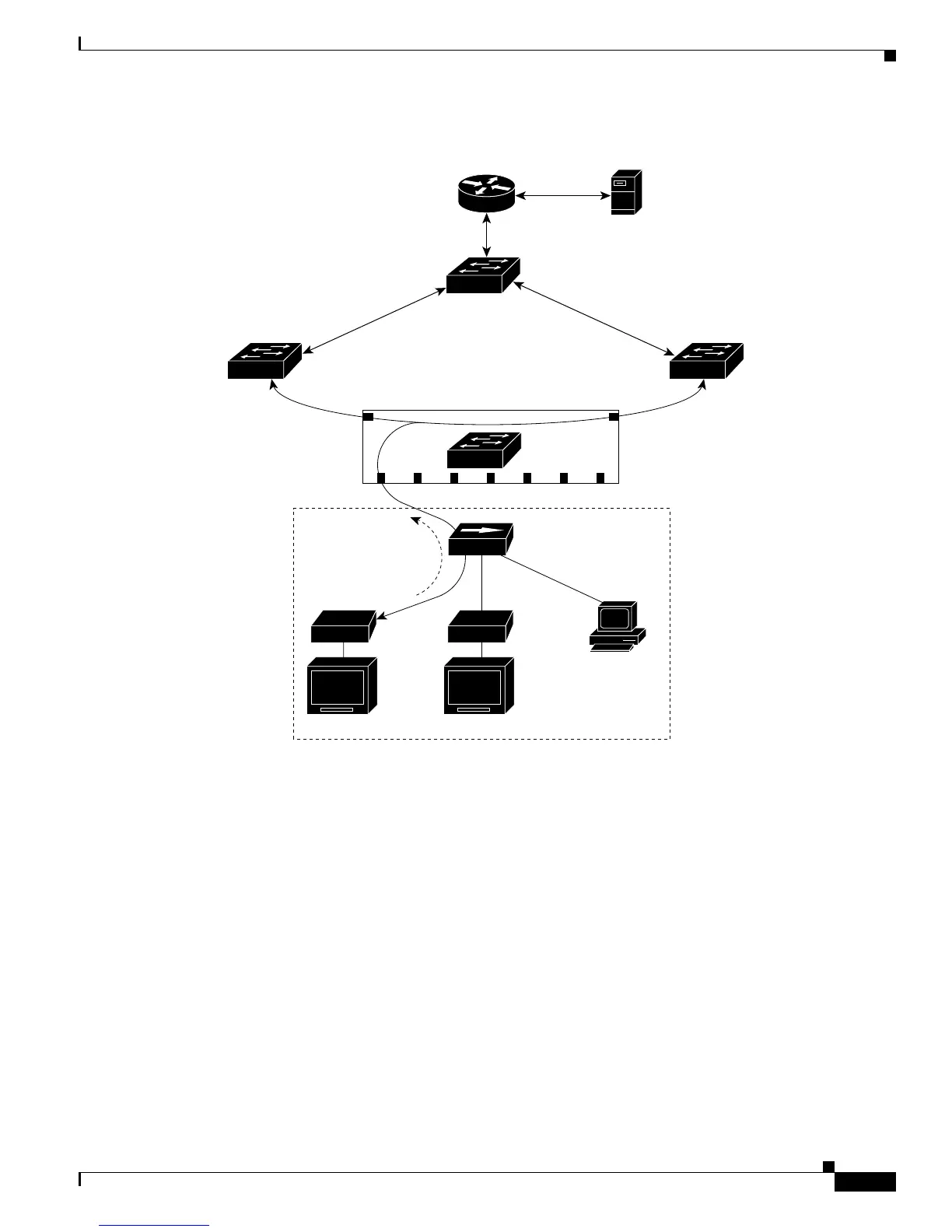
Figure 11-3 Multicast VLAN Registration Example
MVR eliminates the need to duplicate television-channel multicast traffic for subscribers in each VLAN.
Multicast traffic for all channels is sent only once around the VLAN trunk—only on the multicast
VLAN. Although the IGMP leave and join messages originate with a subscriber, they appear to be
initiated by a port in the multicast VLAN rather than in the VLAN to which the subscriber port is
assigned. These messages dynamically register for streams of multicast traffic in the multicast VLAN
on the Layer 3 device. The access layer switch (S1 switch) modifies the forwarding behavior to allow
the traffic to be forwarded from the multicast VLAN to the subscriber port in a different VLAN,
selectively allowing traffic to cross between two VLANs.
IGMP reports are sent to the same MAC addresses as the multicast data. The S1 CPU must capture all
IGMP join and leave messages from receiver ports and forward them to the multicast VLAN of the
source (uplink) port.
SP1
Multicast
data
Multicast
data
Customer
premises
SP
SP
RP = Receiver Port
SP = Source Port
Note: All source ports belong to
the multicast VLAN.
Hub
TV
data
Set-top boxSet-top box
TV TV
PC
SP
SP
SP
SP
IGMP join
Cisco router
Multicast
server
Catalyst
2950 switch
Catalyst
2950 switch
Catalyst
2950 switch
Catalyst
2950 switch
SP2
RP1 RP2 RP3 RP4 RP5 RP6 RP7
65184
S1

 Loading...
Loading...















