2-32 RPL Programming Examples
SETTS (Superimposing Taylor's polynomials)
SETTS superimposes successive Taylor's polynomials on a sine curve and stores each graphics object in a list.
Techniques used in SETTS
! Structured programming. SETTS calls SINTP to build a sine curve and convert it to a graphics object.
! FOR…STEP (definite loop). SETTS calculates successive Taylor's polynomials for the sine function in a
definite loop. The loop counter serves as the value of the order of each polynomial.
! Programmatic use of PLOT commands. SETTS draws a plot of each Taylor's polynomial.
! Manipulation of graphics objects. SETTS converts each Taylor's polynomial plot into a graphics object.
Then it executes + to combine each graphics object with the sine curve stored in SINT, creating nine new
graphics objects, each the superposition of a Taylor's polynomial on a sine curve. SETTS then puts the nine
new graphics objects, and the sine curve graphics object itself, in a list.
SETTS program listing
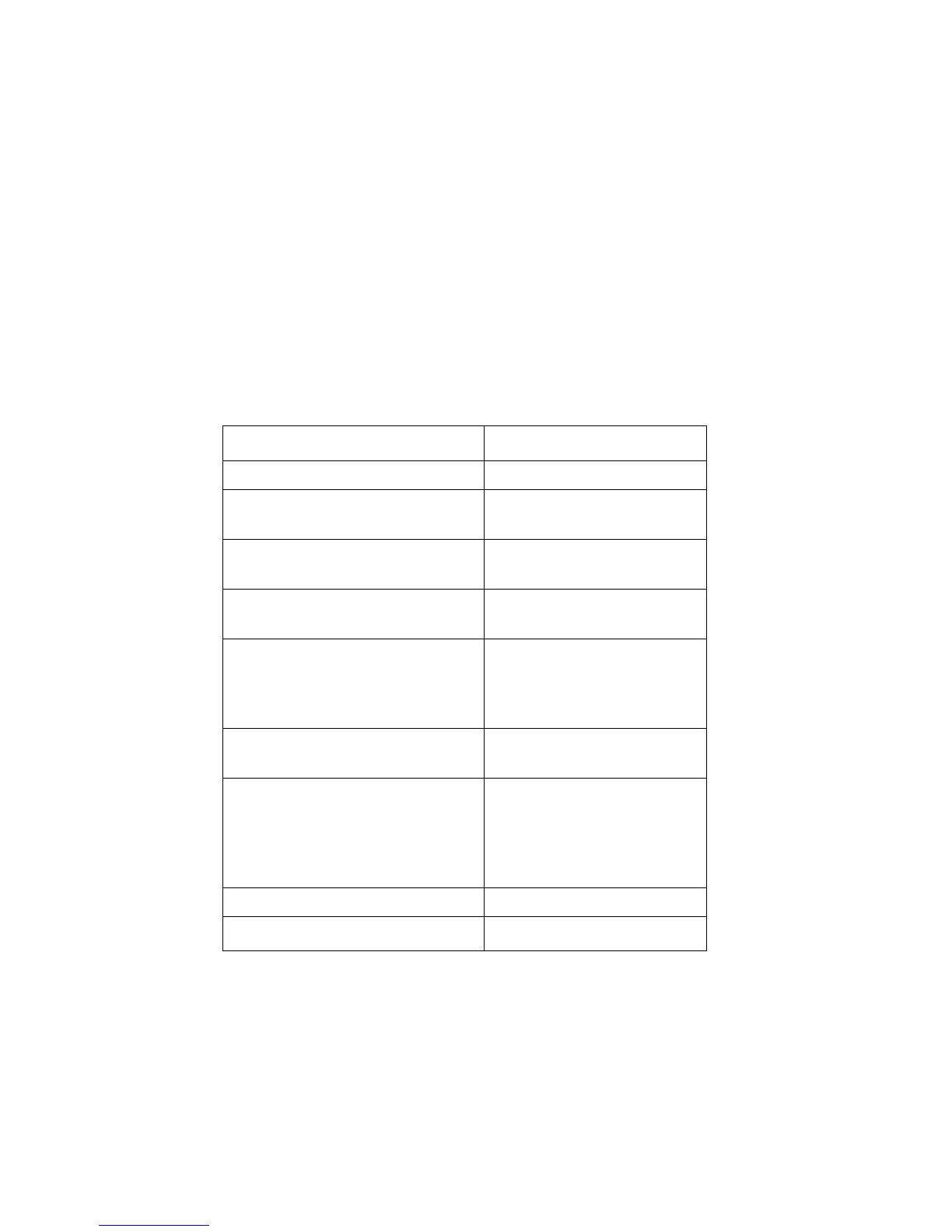
Program: Comments:
"!
D6=:2!
Plots a sine curve and stores the
graphics object in SINT.
3!3e!7LK!G!
Sets the range for the FOR loop
using local variable n.
+D6=-T/+!+T+!G!:BPEK!
D:<U!<KBD<!4KBY!
Plots the Taylor's polynomial of
order n.
26O:!KOE!D6=:!'!
Returns the plot to the stack as a
graphics object and executes + to
superimpose the sine plot from
SINT.
H!D:<2!
Increments the loop counter n by
2 and repeats the loop.
D6=:!
38!#E6D:!
+:DE+!D:L!
Puts the sine curve graphics
object on the stack, then builds a
list containing it and the nine
graphics objects created in the
loop. Stores the list in TSL.
1!
`OSETTS K
Stores the program in SETTS.
Checksum: # 41304d
Bytes: 130.5
SETTS is demonstrated in the program TSA.
 Loading...
Loading...