Computer Algebra Commands 4-53
Result: The four functions are displayed above the A to D keys. In Algebraic mode, NOVAL is
returned as item 1.
See also: MENU, TMENU
MKISOM
Type: Command
Description: Returns the matrix representation for a given isometry.
Access: Matrices, !Ø LINEAR APPL
Input: Level 2/Argument 1: For a 3-d isometry, a list of the characteristic elements of the isometry.
For a 2-d isometry, the characteristic element of the isometry (either an angle or a vector).
Level 1/Argument 2: +1 for a direct isometry or -1 for an indirect isometry.
Output: The matrix that represents the given isometry.
Flags: Exact mode must be set (flag –105 clear).
Numeric mode must not be set (flag -3 clear).
Radians mode must be set (flag –17 set).
Example 1: Find the matrix for a rotation of π/2 radians in two dimensions
Command: MKISOM(π/2, 1)
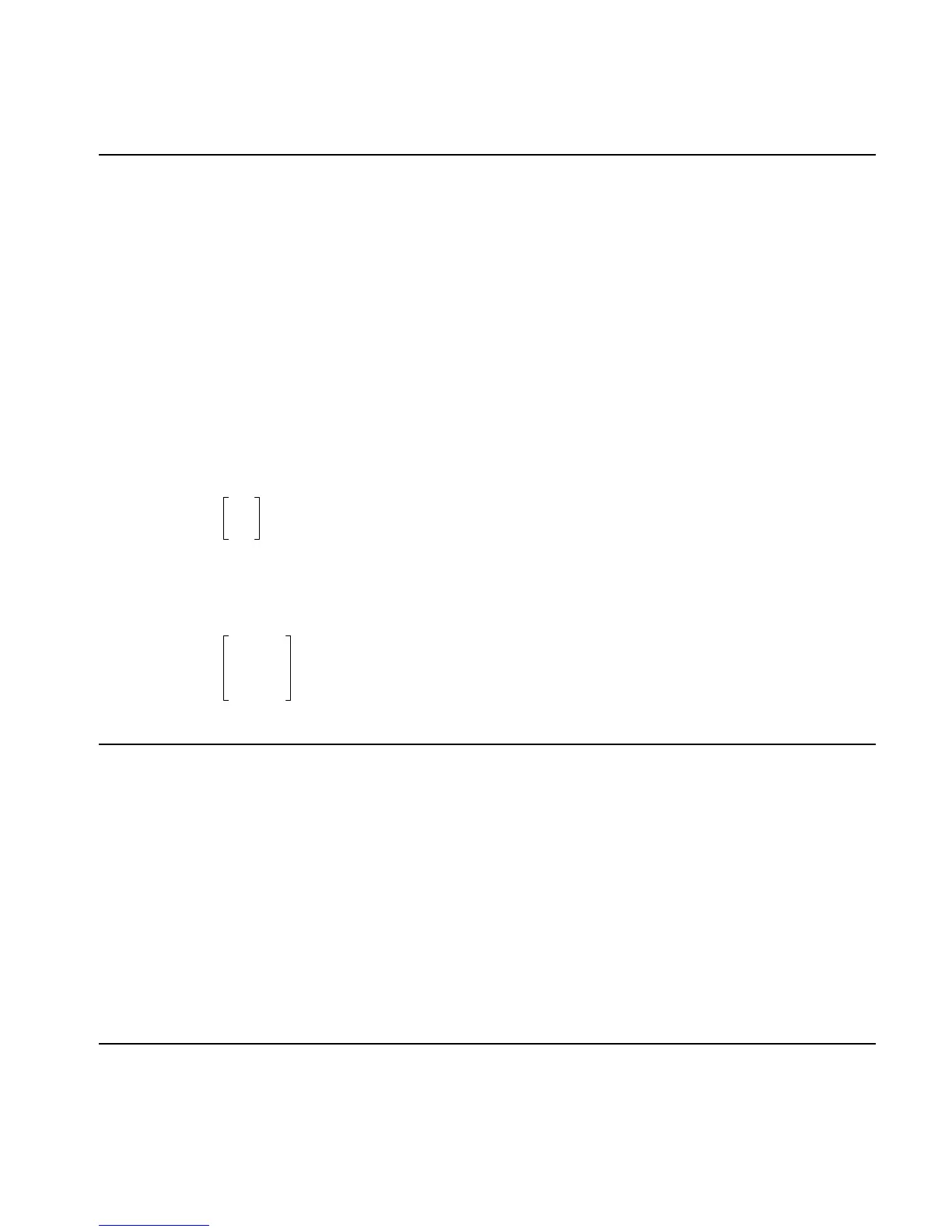
Result:
01–
10
Example 2: Find the matrix for a rotation with axis [1 1 1] and angle π/3 radians combined with a
reflection in the plane
x + y + z = 0
Command: MKISOM({ [1, 1, 1],π/3}, -1) then simplify with EXPAND(ANS(1))
Result:
01–0
00 1–
1–00
See also: ISOM
MODSTO
Type: Command
Description: Changes the modulo setting to the specified number. The number that you set is reflected in
the CAS Modes input form. Negative numbers are replaced by their positive value, 0 and 1 are
replaced by 2.
Access: Arithmetic, !Þ
MODULO L
Input: The modulo value that you want to set, an integer or an expression that evaluates to an
integer.
Output: The modulo setting is changed to the specified number.
In Algebraic mode, NOVAL is
returned as argument 1.
Flags: Exact mode must be set (flag –105 clear).
Numeric mode must not be set (flag -3 clear).
MODULAR
Type: Command
Description: Displays a menu or list of the CAS modulo operations.
Access: Catalog, …µ
 Loading...
Loading...