Equation Reference 5-21
Example:
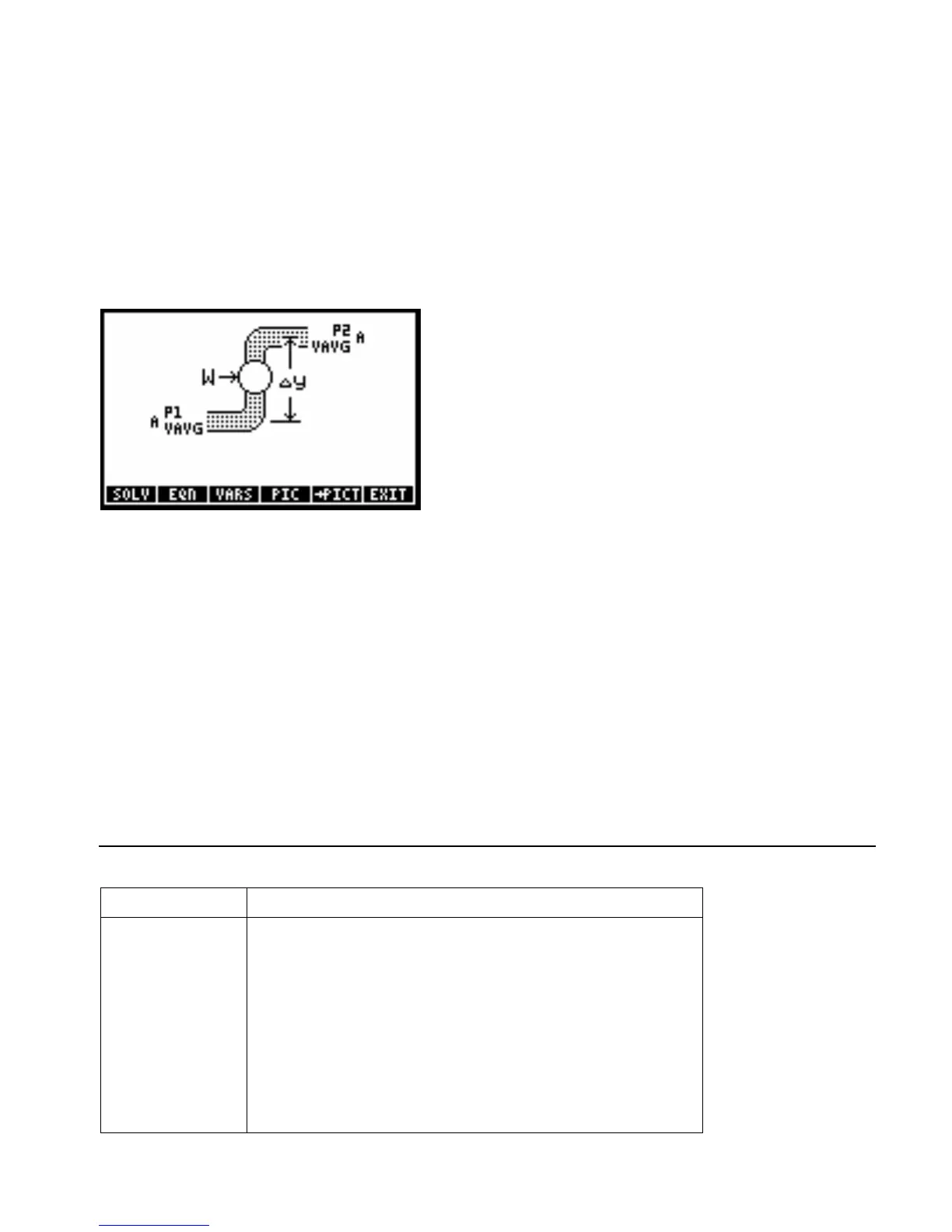
Given: P2=30_psi, P1=65_psi, y2=100_ft, y1=0_ft,
ρ
=64_lb/ft^3, D1=24_in, hL=2.0_ft^2/s^2, W=25_hp,
v1=100_ft / s.
Solution: Q=18849.5559_ft^3/min, M=1206371.5790_lb/min, ∆P=-35_psi, ∆y=100_ft, v2=93.1269_ft /s,
A1=452.3893_in^2, A2=485.7773_in^2, D2=24.8699_in.
Flow in Full Pipes (3, 4)
These equations adapt Bernoulli's equation for flow in a round, full pipe, including power input (or output) and
frictional losses. (See “FANNING” in Chapter 3.)
Equations:
Example:
Given:
ρ=62.4_lb/ft^3, D=12_in, vavg= 8_ft/s, P2=15_psi, P1=20_psi, y2=40_ft, y1=0_ft,
µ
=0.00002_lbf
∗
s/ft^2, ΣK=2.25,
∈
=0.02_in, L=250_ft.
Solution: ∆P=-5_psi, ∆y=40_ft, A=113.0973_in^2, n=1.0312_ft^2/s, Q=376.9911_ft^3/min,
M=23524.2358_lb/min, W=25.8897_hp, Re=775780.5.
Forces and Energy (4)
Variable
Description
α
An
ular acceleration
ω
An
ular acceleration
ωi,ωf
Initial and final an
ular velocities
ρ
Fluid densit
τ
Tor
ue
Θ
An
ular dis
lacemen
α
Acceleration
π
D
2
⋅
4
- - - - - - - - - - - - - -
v a v g
P
∆
- - - - - - -
g + y
∆⋅
v
a v g
2
+ 2
L
D
----
⋅ ⋅
Σ
K
2
--------
+
⋅
⋅ ⋅ ⋅
W=
P
∆
P 2 P 1
=
y
∆
y 2 y 1
=
M
Q
⋅
=
Q
A v a v g
⋅
=
n
µ
---
=
A
π
D
2
⋅
4
- - - - -- - - - - - - - -
=
e
D vavg
⋅ ⋅
µ
- - - - -------------------------
=
 Loading...
Loading...