4-16 Computer Algebra Commands
Output: If the input is a list, returns the corresponding array. If the input is an array, returns the
corresponding list.
Example: Convert the following matrix to a list:
01
10
Command: AXL([[0,1][1,0]])
Result: {{0,1},{1,0}}
See also: AXM, AXQ
AXM
Type: Command
Description: Converts a numeric array (object type 3) to a symbolic matrix (object type 29), or a symbolic
matrix to a numeric array.
Access: Matrices, !Ø
OPERATIONS
Input: A numeric array or a symbolic matrix.
Output: The corresponding symbolic matrix or numeric array.
Flags: Exact mode must be set (flag –105 clear).
Numeric mode must not be set (flag –3 clear).
See also: AXL, AXQ
AXQ
Type: Command
Description: Converts a square matrix into the associated quadratic form.
Access: Convert, !Ú MATRIX CONVERT, or matrices !Ø QUADRATIC FORM
Input: Level 2/Argument 1: An n×n matrix.
Level 1/Argument 2: A vector containing n variables.
Output: Level 2/Item 1: The corresponding quadratic form.
Level 1/Item 2: The vector containing the variables.
Flags: Exact mode must be set (flag –105 clear).
Numeric mode must not be set (flag –3 clear).
Radians mode must be set (flag –17 set).
Example: Find the quadratic form, expressed in terms of x, y, and z, associated with the following
matrix:
360
241
111
Command:
AXQ([[3,6,0][2,4,1][1,1,1]],[X,Y,Z])
Result: {3*X^2+(8*Y+Z)*X+(4*Y^2+2*Z*Y+Z^2),[X,Y,Z]}
See also: AXL, AXM, GAUSS, QXA
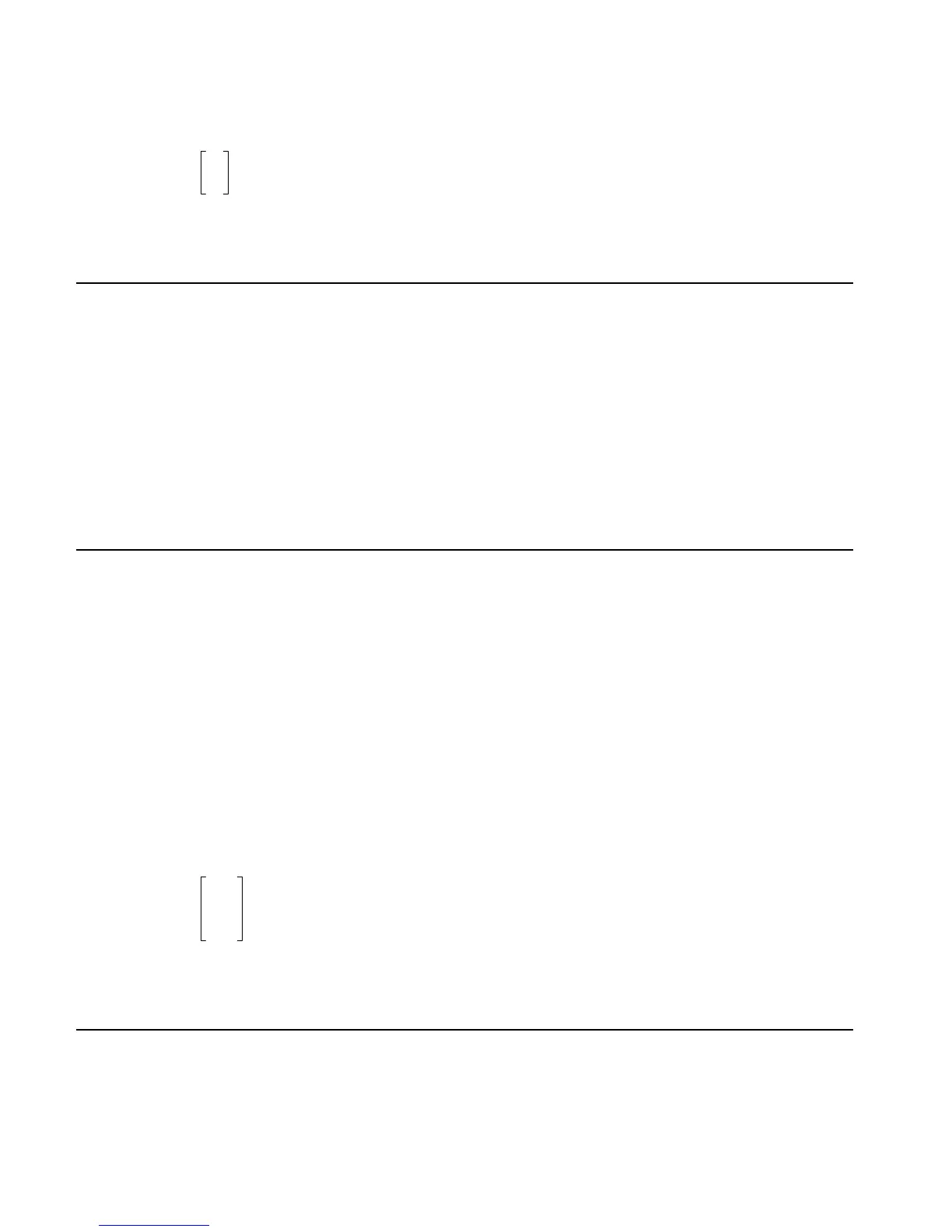
BASIS
Type: Command
Description: Determines the basis of a sub-space of the n-space R
n
.
Access: Matrices, !Ø LVECTOR
 Loading...
Loading...