2-38 RPL Programming Examples
Inverse-Function Solver
This section describes the program ROOTR, which finds the value of x at which f(x) = y. You supply the
variable name for the program that calculates f(x), the value of y, and a guess for x (in case there are multiple
solutions).
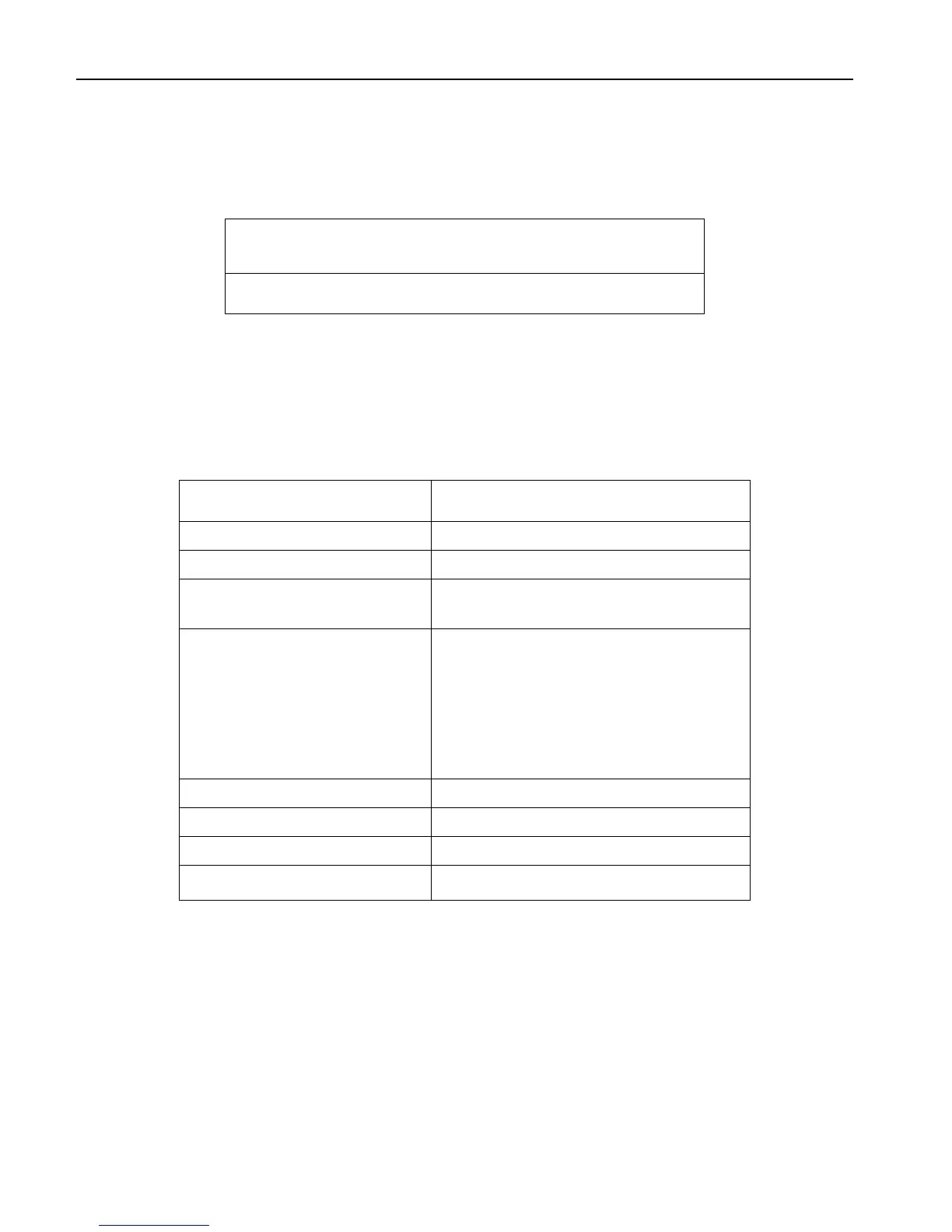
Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 " Level 1
'function name' y x
guess
"
x
Techniques used in ROOTR
! Programmatic use of root-finder. ROOTR executes ROOT to find the desired x-value.
! Programs as arguments. Although programs are commonly named and then executed by calling their
names, programs can also be put on the stack and used as arguments to other programs.
ROOTR program listing
Program: Comments:
"!
#!*G$o)!@w$un)!?mn)ZZ
Creates local variables.
"!
?mn)ZZ!+T:<M2+!D:L!
Begins the defining procedure.
Creates variable XTEMP (to be solved for).
"!T:<M2!*G$o)!
@w$un)!0!1!
!
+T:<M2+!
?mn)ZZ!
KLL:!
!
1!
Enters program that evaluates f(x) - y.
Enters name of unknown variable.
Enters guess for XTEMP.
Solves program for XTEMP.
Ends the defining procedure.
Program:! Comments:
+T:<M2+!25K><!
Purges the temporary variable.
1!
`OROOTR K
Stores the program in ROOTR.
Checksum: # 4708d
Bytes: 163
Example: Assume you often work with the expression
3.7x
3
+ 4.5x
2
+ 3.9x + 5 and have created the program X"FX to calculate the value:
! "!#!?!+Vde.?WV'adQ.?WH'VdX.?'Q+!1!
You can use ROOTR to calculate the inverse function.
 Loading...
Loading...