2-2 RPL Programming Examples
Techniques used in FIB1
! IFTE (if -then-else function). The defining procedure for FIB1 contains the conditional function IFTE,
which can take its argument either from the stack or in algebraic syntax.
! Recursion. The defining procedure for FIB1 is written in terms of FIB1, just as F
n
is defined in terms of F
n-1
and F
n-2
.
FIB1 program listing
Program: Comments:
"!
#!G!
+67:<-G]3F!
GF!
76S3-G03/'76S3-G0H//
+!
Defines local variable n.
The defining procedure, an
algebraic expression. If n ≤
1, F
n
= n, else F
n
= F
n-1
+F
n-2
.
»
`OFIB1 K
Stores the program in FIB1.
Checksum: # 14909d (press O%FIB1% !°#MEM# %BYTES%)
Bytes: 113.5
Example: Calculate F
6
. Calculate F
10
using algebraic syntax.
First calculate F
6
.
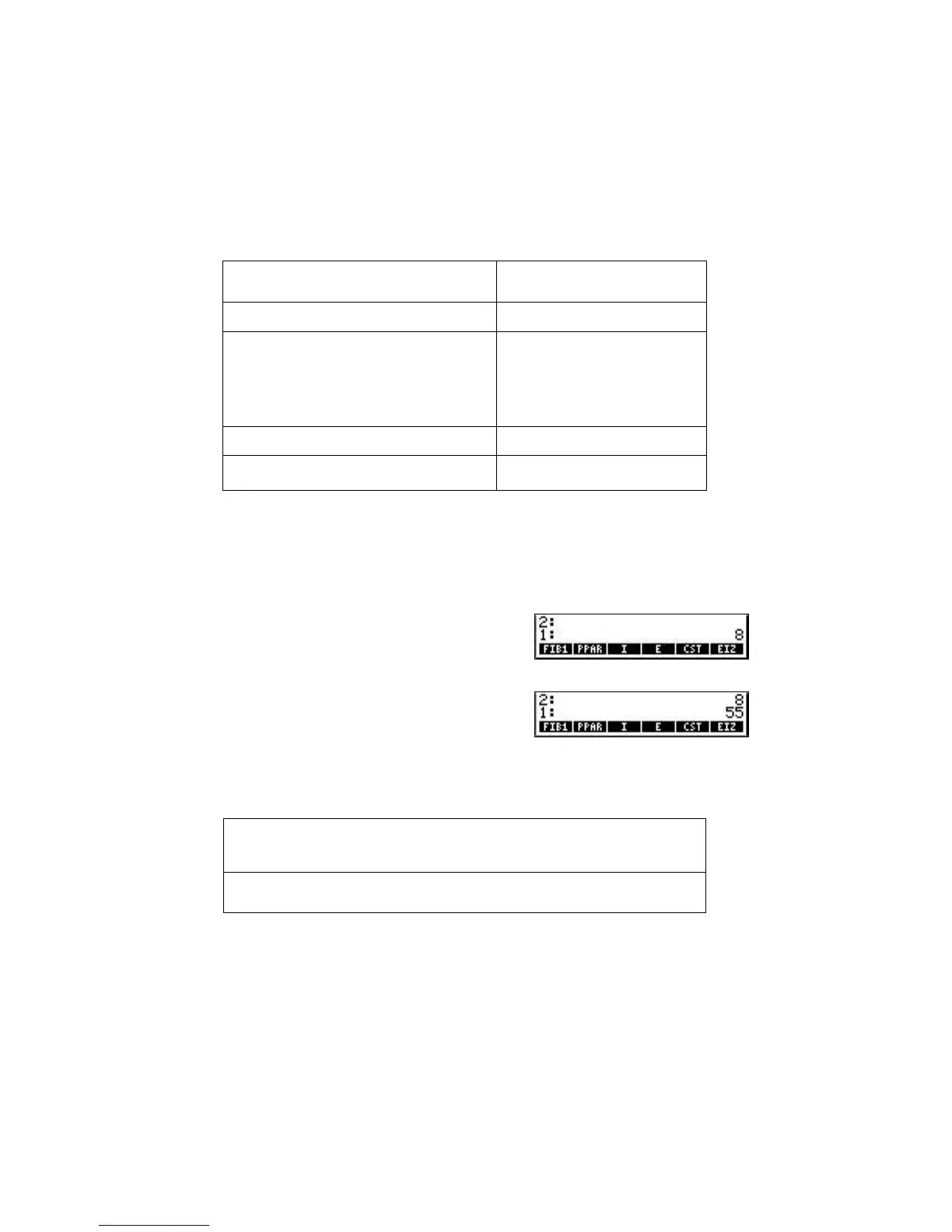
J
6 %FIB1%
Next, calculate F
10
using algebraic syntax.
O%FIB1% !Ü10 N
FIB2 (Fibonacci Numbers, Loop Version)
Level 1 " Level 1
n
"
F
n
Techniques used in FIB2
! IF…THEN…ELSE…END. FIB2 uses the program-structure form of the conditional. (FIB1 uses IFTE.)
! START…NEXT (definite loop). To calculate F
n
, FIB2 starts with F
0
and F
1
and repeats a loop to calculate
successive values of F
i
.
 Loading...
Loading...