Chapter 17
| IP Configuration
Setting the Switch’s IP Address (IP Version 6)
– 461 –
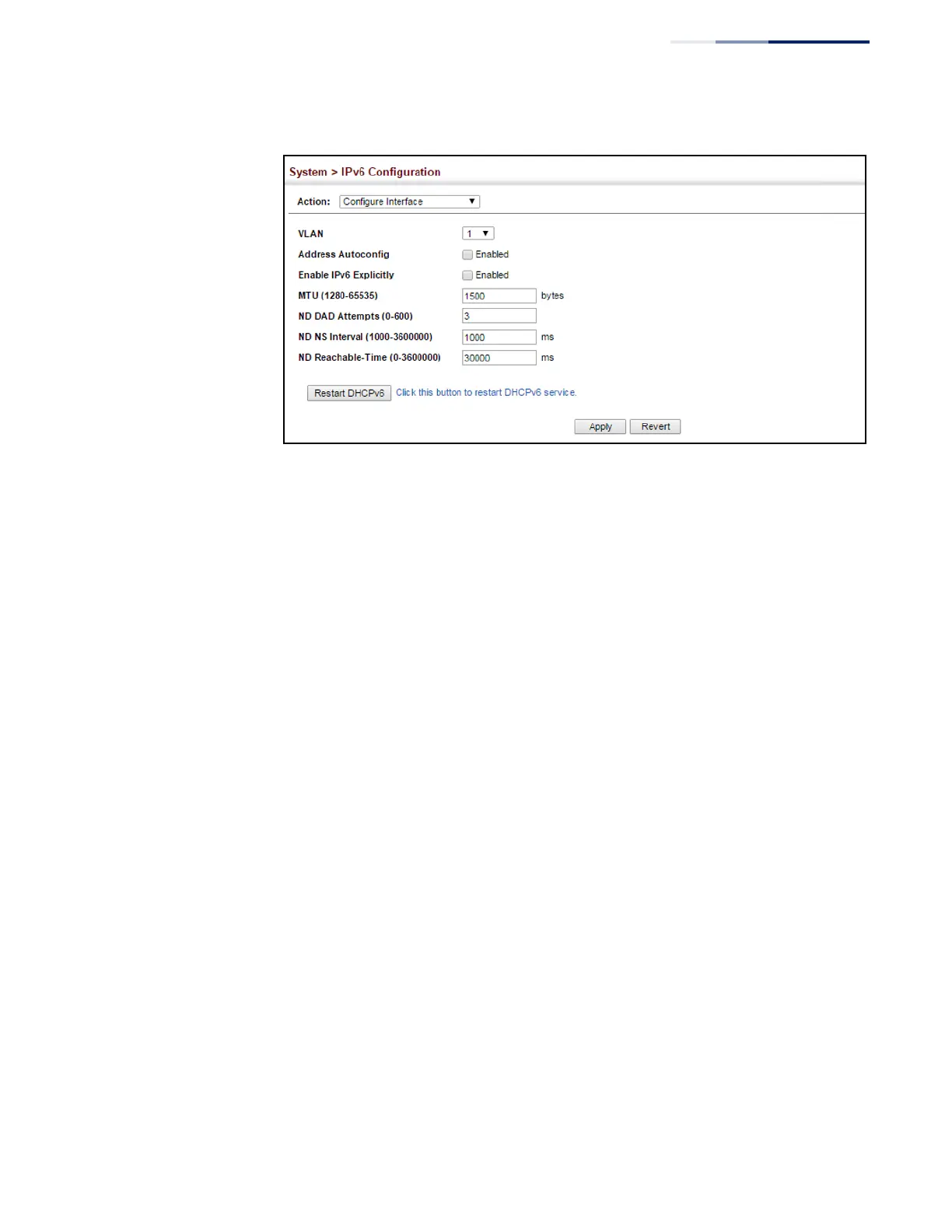
Figure 307: Configuring General Settings for an IPv6 Interface
Configuring an
IPv6 Address
Use the System > IPv6 Configuration (Add IPv6 Address) page to configure an IPv6
interface for management access over the network.
Command Usage
◆
All IPv6 addresses must be formatted according to RFC 2373 “IPv6 Addressing
Architecture,” using 8 colon-separated 16-bit hexadecimal values. One double
colon may be used in the address to indicate the appropriate number of zeros
required to fill the undefined fields.
◆
The switch must always be configured with a link-local address. Therefore any
configuration process that enables IPv6 functionality, or assigns a global
unicast address to the switch, including address auto-configuration or explicitly
enabling IPv6 (see “Configuring IPv6 Interface Settings” on page 457), will also
automatically generate a link-local unicast address. The prefix length for a link-
local address is fixed at 64 bits, and the host portion of the default address is
based on the modified EUI-64 (Extended Universal Identifier) form of the
interface identifier (i.e., the physical MAC address). Alternatively, you can
manually configure the link-local address by entering the full address with a
network prefix in the range of FE80~FEBF.
◆
To connect to a larger network with multiple subnets, you must configure a
global unicast address. There are several alternatives to configuring this
address type:
■
The global unicast address can be automatically configured by taking the
network prefix from router advertisements observed on the local interface,
and using the modified EUI-64 form of the interface identifier to
automatically create the host portion of the address (see “Configuring IPv6
Interface Settings” on page 457).
■
It can be manually configured by specifying the entire network prefix and
prefix length, and using the EUI-64 form of the interface identifier to

 Loading...
Loading...











