2
ω1 (rad/s) ω2 (rad/s)
FF1
FF2
Digitax SF Instruction Manual
7. Tuning
1. Introduction
1. Introduction
1. Overview
The goal of drive tuning is having good control over the motor and optimizing equipment performance in
responding to commands from the host controller�
The position control method employs two degrees of freedom with the model-matching control� This method
enables you to adjust command response and transient response independently without compromising the
stability of your equipment�
Digitax SF is a servo system that does not let overshooting and undershooting happen when the equipment
inertia ratio is set appropriately�
Digitax SF features response models with two cutoff frequencies: ω 1 (Control Gain 1) and ω 2 (Control Gain 2)
Code EFFECT
ω1
Control Gain 1
Responsiveness at settling
Increasing
this item will reduce the position error at settling (after command ends)�
ω2
Control Gain 2
Responsiveness during operation
Increasing this item will reduce the position error during operation (while
command being input)�
FF1
FF Compensation 1
Command compensation for ω 1
Increasing this item will improve the ω 1 response�
FF2
FF Compensation 2
Command compensation for ω 2
Increasing this item will improve the ω 2 response�
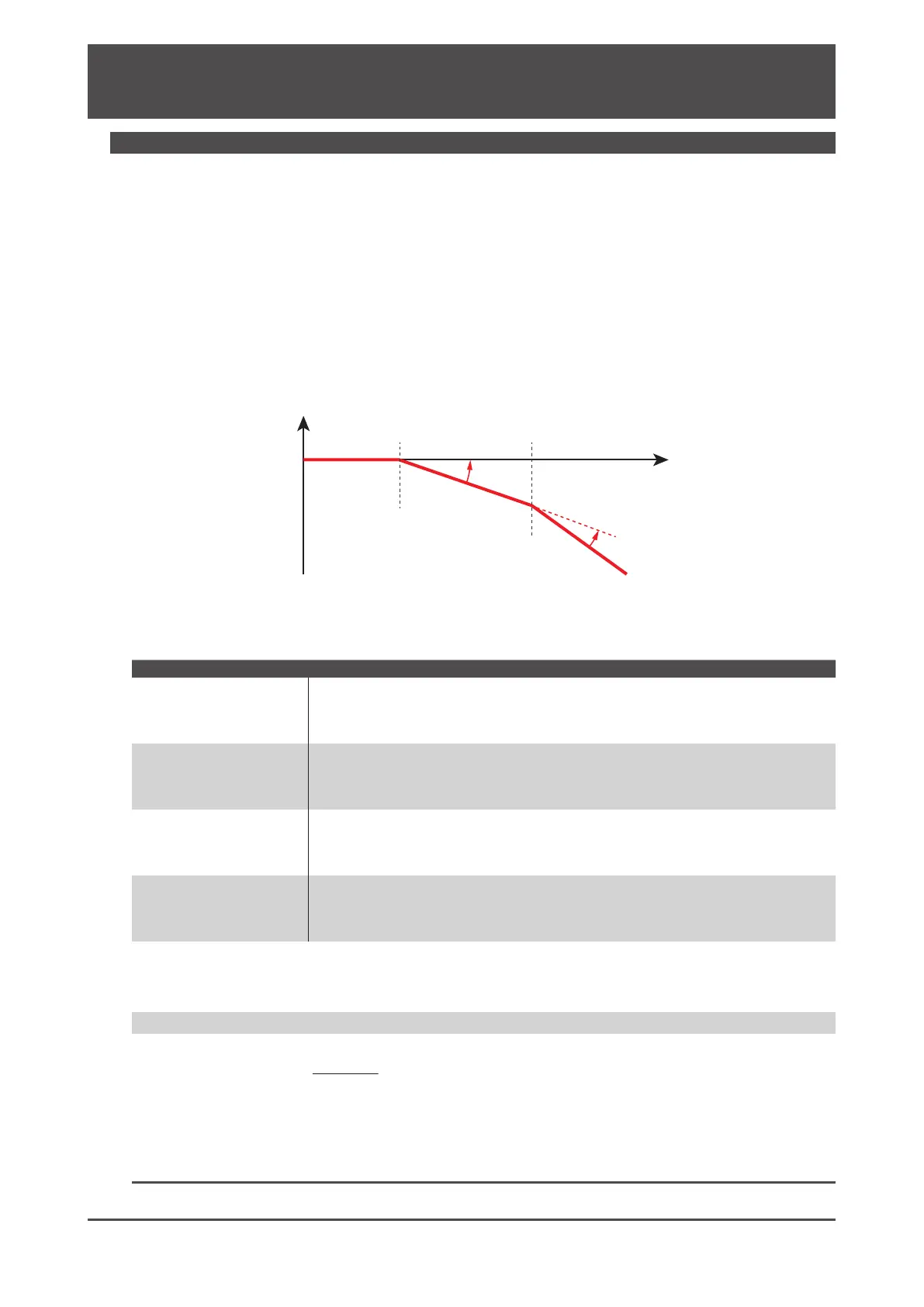
Response model for position control and two cuto frequencies
Angular velocity
Control Gain 1
(Responsiveness
during settling)
Control Gain 2
(Responsiveness
during motion)
Increasing FF1 provides faster response
Increasing FF2 provides faster response
Gain
・Position loop gain
(*1)
:
ω1ω2
ω1 + ω2
・Velocity loop gain
(*2)
: ω 1+ ω2
*
1)Position loop gain It is equivalent to the “Kp” in a P-PI control�
*
2)Velocity loop gain It is equivalent to the “Kv” in a P-PI control�
The relation between cuto frequencies and control gain parameters.

 Loading...
Loading...







