42
5.1.4 Opening the [Memory Mapping] Dialog Box
Selecting [Setup -> Emulator -> Memory Resource…] or clicking the [Emulator Memory Resource] toolbar
button (
) opens the [Memory Mapping] dialog box.
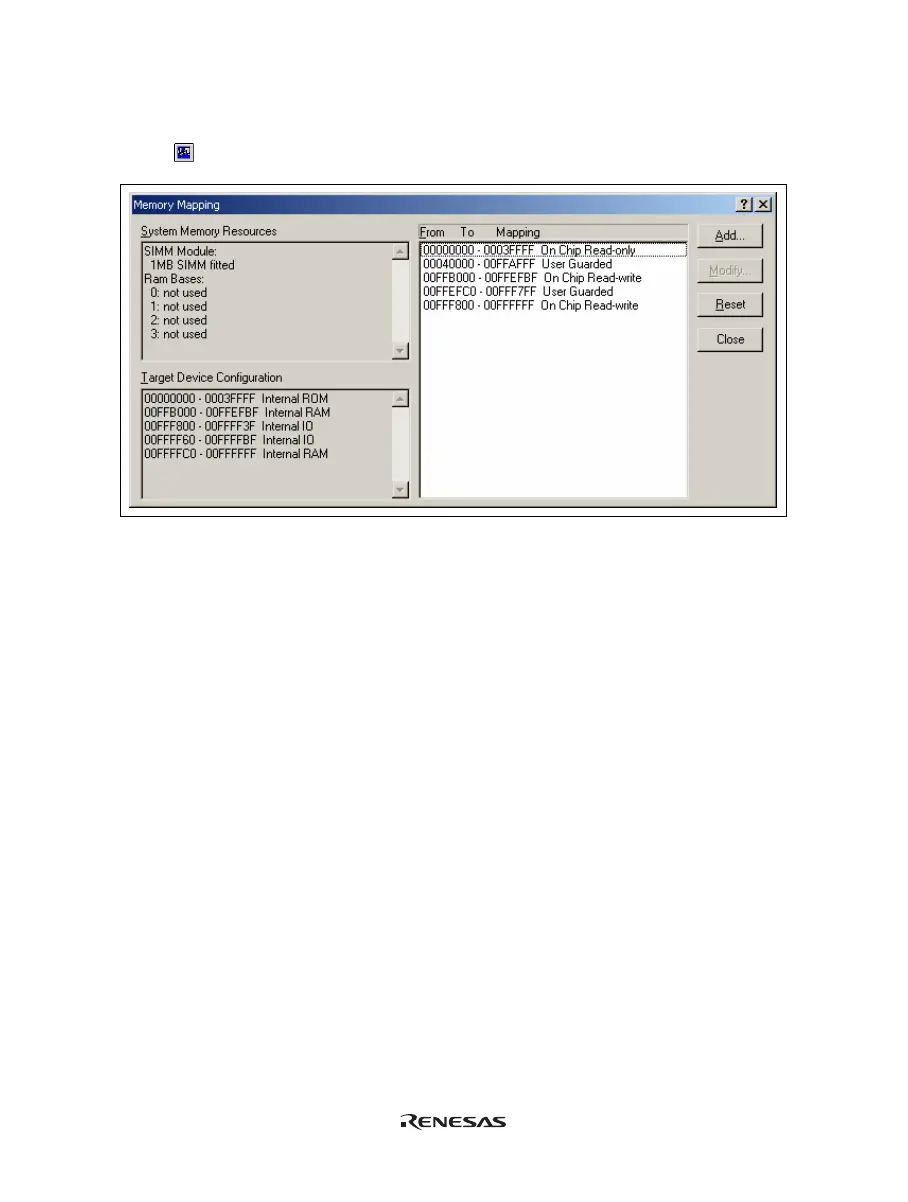
Figure 5.4 [Memory Mapping] Dialog Box
This dialog box displays the current memory map. The E6000 H8S or H8/300 series supports four blocks of user
memory. These can be 256 kbyte or 1 Mbyte each, depending on the SIMM fitted. Each block can be placed in
the address space on a 256-kbyte or 1-Mbyte boundary.
The memory mapping has a granularity of H'40 (D'64) byte. Each 64-byte block can be set to the internal
(emulation) or external memory and can be guarded (access-prohibited), write-protected or read-write.
The H8/300 series E6000 generally incorporates an emulation memory.
In the memory map, the memory can be set as an internal (emulation) or external, guarded (access-prohibited),
write-protected, or read/write in a byte unit.
[Add...]: Displays the [Edit Memory Mapping] dialog box, allowing the user to modify the address
range and attributes of a memory map.
[Modify...]: Displays the [Edit Memory Mapping] dialog box, allowing the user to modify the address
range and attributes of a memory map.
[Reset]: Resets the map memory to its default settings.
[Close]: Closes the dialog box.
The memory configuration of the device being emulated is displayed by the [Memory] sheet in the [Status]
window.
Note: Some emulators may not support the emulation memory or the memory mapping function. For details,
refer to section 8, Software Specifications Specific to This Product, or the online help.

 Loading...
Loading...











