70
[Required number of event occurrences]:
Allows a 16-bit pass count to be set. The event must occur the specified number of
times before the action is taken. The range of values is D’0 to D’65,535.
[Enable Sequencing]: Allows the event to take part in a sequence of events (setting this requires the event to
use an event detector).
[Configure Sequence…]: Displays the [Event Sequencing] dialog box to allow the event sequencing to be
configured (only available when [Enable Sequencing] has been selected).
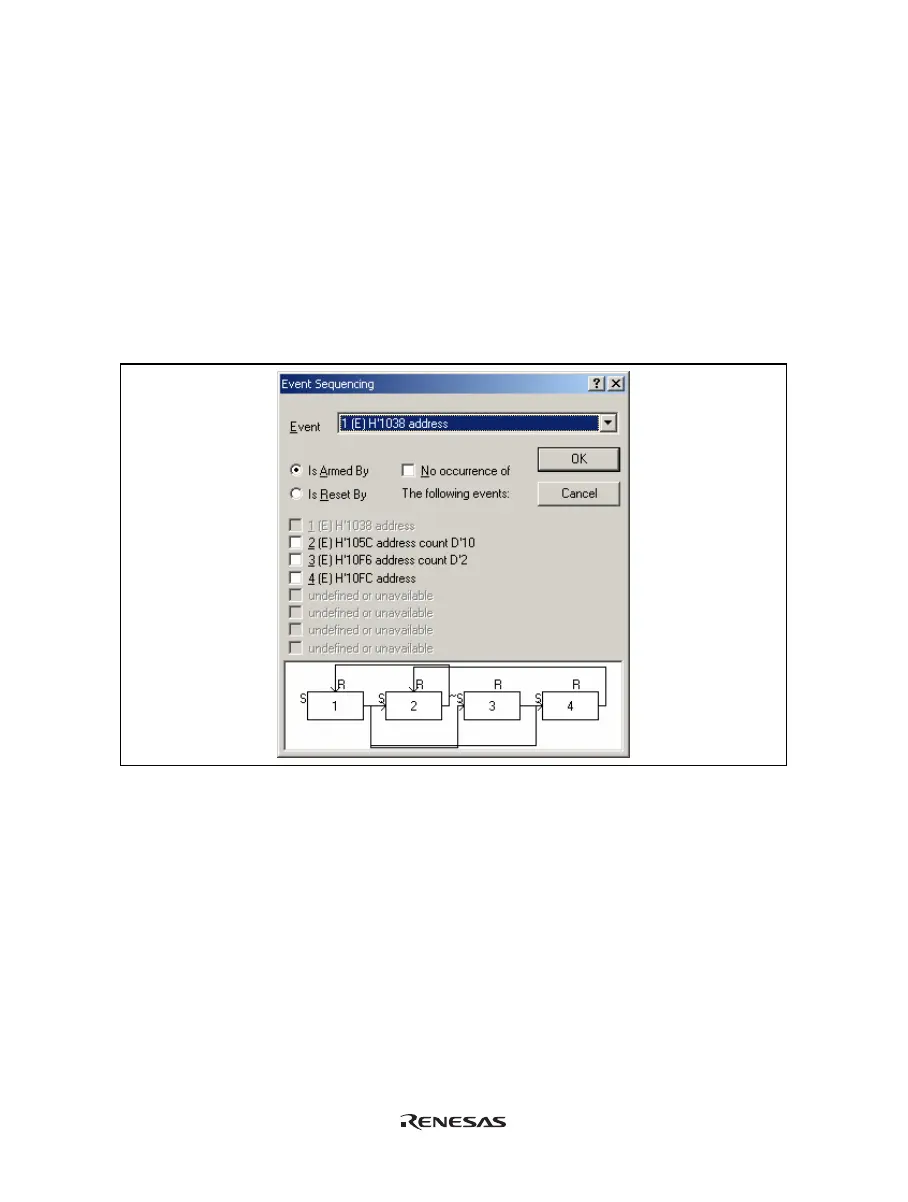
(5) [Event Sequencing] dialog box
This dialog box allows the user to define which events are triggered by other events. If this dialog box is
accessed (directly or indirectly) from [Trace Acquisition…], only those events assigned to the trace subsystem
are displayed. If accessed from the [Eventpoint] window, only the breakpoint or timer events are shown.
Figure 5.26 [Event Sequencing] Dialog Box
[Event]: Selects an event point to be set.
[Is Armed By]: Arms the selected event.
[Is Reset By]: Resets the selected event.
[No occurrence of]: Arms an event when the set of events being selected does not occur (only available
when [Is Armed By] has been selected).
The test of conditions on event points is started with the execution of the user program. The conditions on event
points have not been satisfied immediately after the execution of the user program is started.
Satisfaction of the condition on an event point allows a transition of the state to that where the condition is
satisfied.

 Loading...
Loading...











