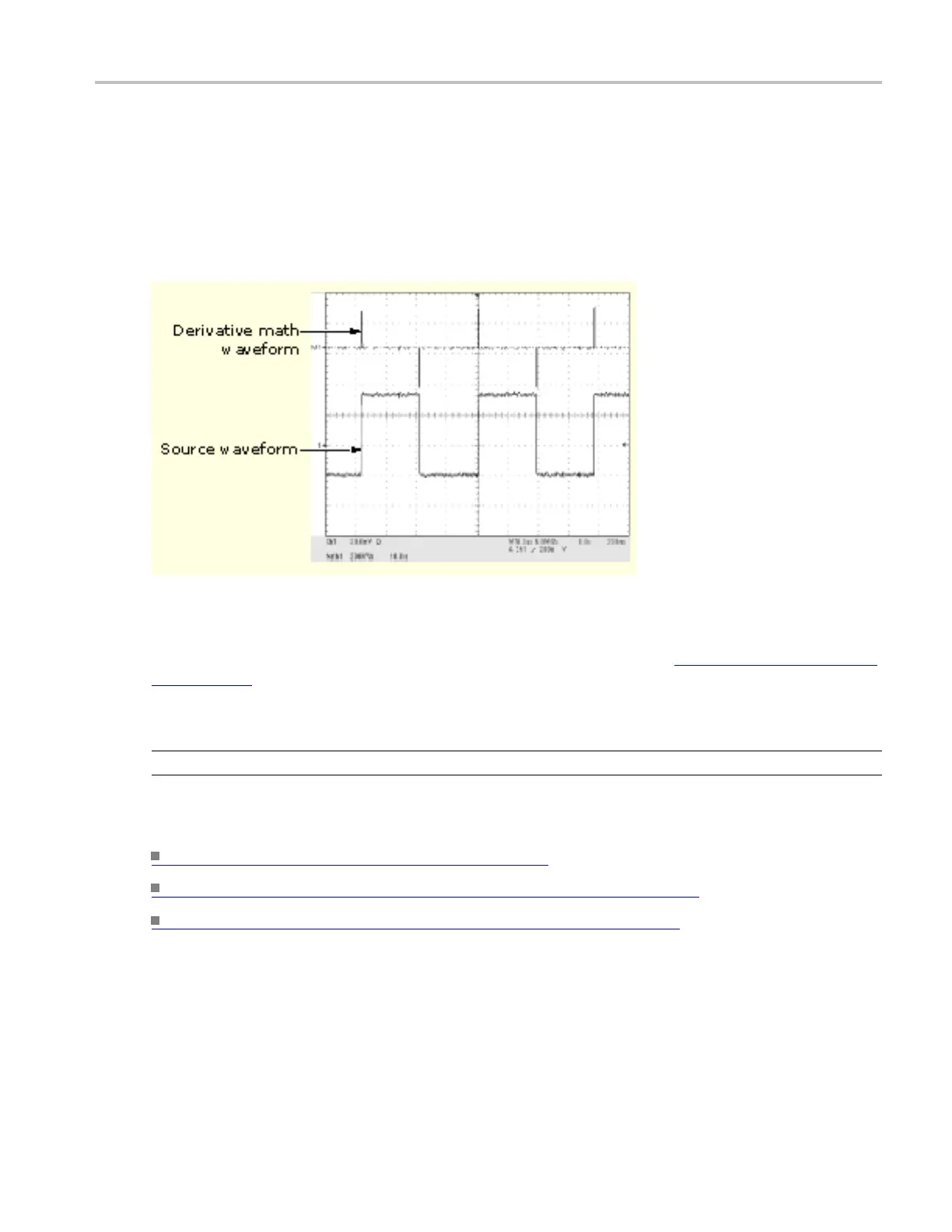
Oscilloscope Reference Math waveform differentiation
The math waveform, derived from the sampled waveform, is computed based on the following equation:
Yn = (X( n + 1) - Xn) 1/T
Where: X is the source waveform, Y is the derivative math waveform, and T is the time between samples.
Since the resultant math waveform is a derivative waveform (see the next figure), its vertical scale is in
volts/second (its horizontal scale is in seconds). The source signal is differentiated over its entire record
length; therefore, the math waveform record length equals that of the s ource waveform.
Cursor Measurements
You ca
nalsousecursorstomeasurederivative waveforms. Use the steps in Taking Cursor Measurements
(see page 601). When using that procedure, note that the amplitude measurements on a derivative
waveform will be in volts per second rather than in volt-seconds as is indicated for the integral waveform
measured in the procedure.
NOTE. Cursor measurements are not available on digital channels.
What do you want to do next?
Learn more about cur sor measurements. (see page 82)
Go to a step-by-step procedure for creating math waveforms. (see page 612)
G
o to a step-by step procedure for using math waveforms.
(see page 606)
DSA/DPO70000D, MSO/DPO/DSA70000C, DPO7000C, and MSO/DPO5000 Series 747
 Loading...
Loading...