6.5 Parameters (Pn)
6-7
6.5 Parameters (Pn)
This section describes the classifications, methods of notation, and settings for parameters given in this man-
ual.
6.5.1 Parameter Classification
Parameters of the Σ-V Series SERVOPACK are classified into two types of parameters. One type of parame-
ters is required for setting up the basic conditions for operation and the other type is required for tuning param-
eters that are required to adjust servomotor characteristics
There are two types of notation used for parameters, one for parameter that requires a value setting (parameter
for numeric settings) and one for parameter that requires the selection of a function (parameter for selecting
functions).
The notation and settings for both types of parameters are described next.
6.5.2 Notation for Parameters
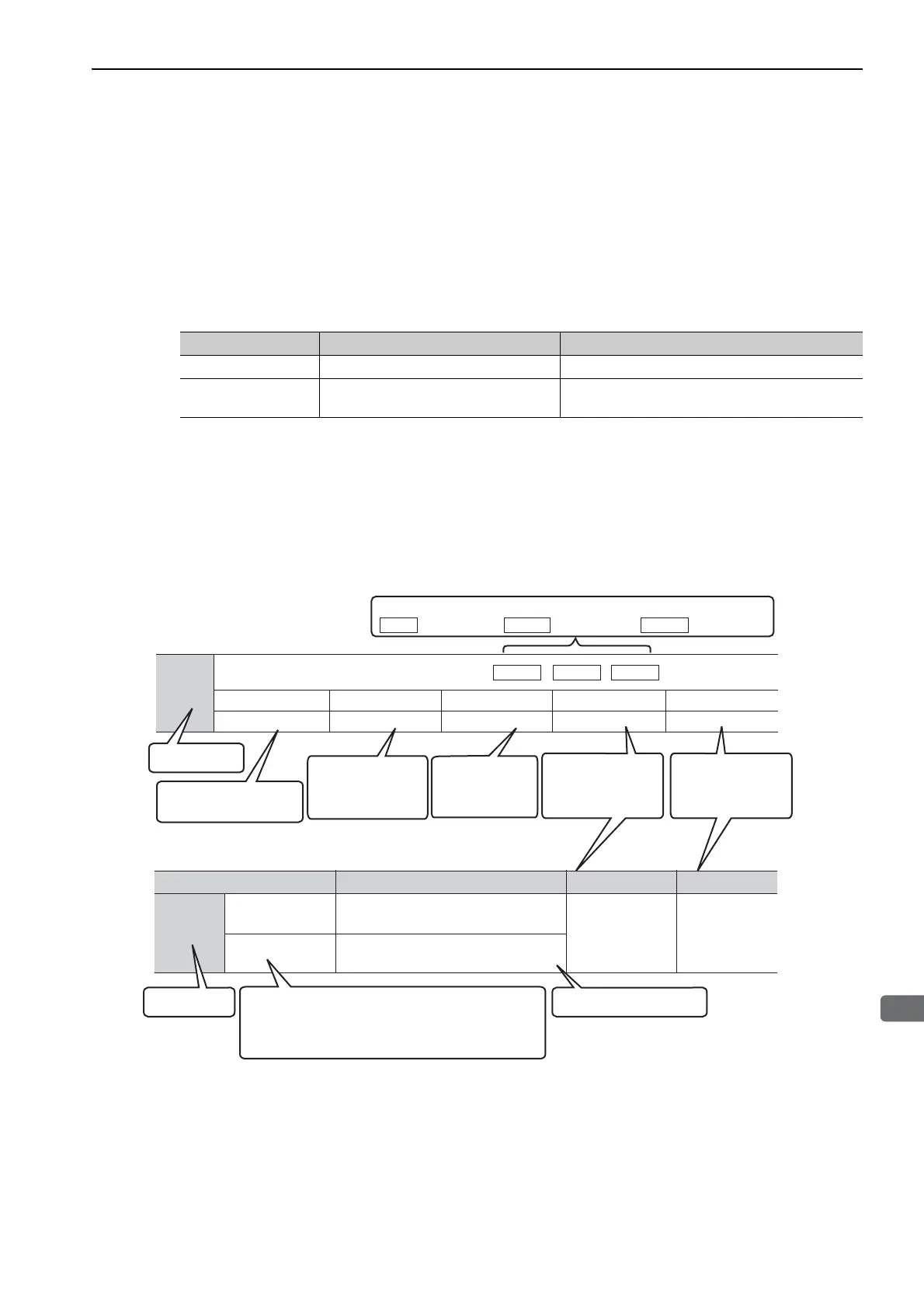
(1) Parameters for Numeric Settings
Classification Meaning Setting Method
Setup Parameters Parameters required for setup. Set each parameter individually.
Tuning Parameters
Parameters for tuning control gain and
other parameters.
There is no need to set each parameter individually.
Pn406
Emergency Stop Torque
Setting Range
0% to 800% 1% 800 After change
Setting Unit Factory Setting When Enabled
Classification
Setup
Parameter
number
Position
Torque
The control methods for which the parameters applies.
Speed
: Speed control
: Position control
: Torque control
Indicates the
parameter setting
before shipment.
Indicates when a
change to the
parameter will be
effective.
Indicates the
parameter
classification.
Indicates the
minimum setting unit
for the parameter.
Torque
PositionSpeed
Indicates the setting
range for the parameter.
Parameter Meaning When Enabled Classification
Pn002
After restart
n.0
[Factory setting]
n.1
Uses the absolute encoder as an
incremental encoder.
Uses the absolute encoder as an
absolute encoder.
Setup
Parameter
number
The notation “n.” indicates a parameter
for selecting functions. Each corresponds to
the setting value of that digit. The notation
shown here means that the third digit is 1.
This section explains the
selections for the function.
(2) Parameters for Selecting Functions

 Loading...
Loading...










