Chapter 8 WAN
EMG2306-R10A User’s Guide
56
(TCP) uses the MTU to determine the maximum size of each packet in any transmission. Too large
an MTU size may mean retransmissions if the packet encounters a router that can't handle that
large a packet. Too small an MTU size means relatively more header overhead and more
acknowledgements that have to be sent and handled.
8.3.2 Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1 recipient)
or Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of
hosts on the network - not everybody and not just 1.
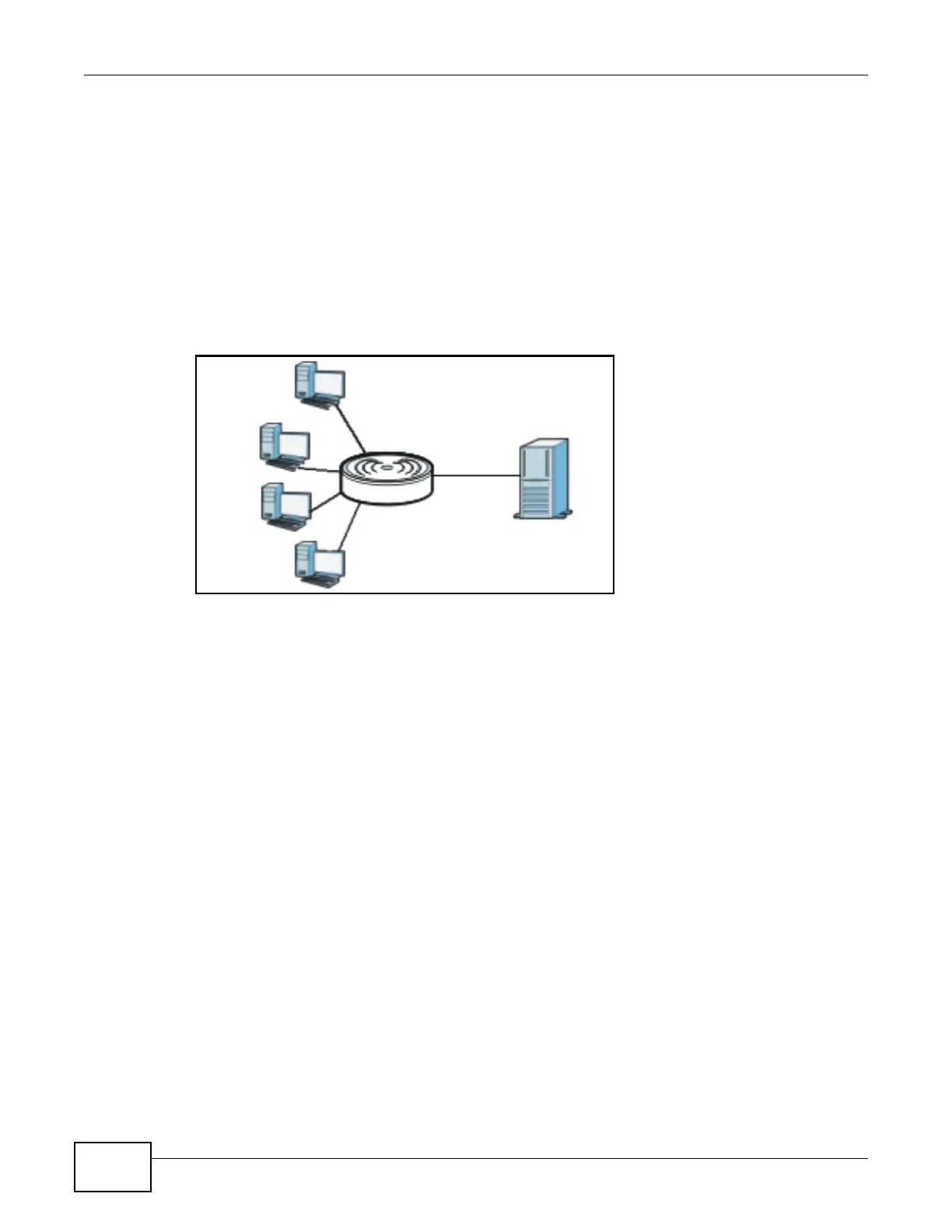
Figure 22 Multicast Example
In the multicast example above, systems A and D comprise one multicast group. In multicasting,
the server only needs to send one data stream and this is delivered to systems A and D.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership
in a multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. The EMG2306-R10A supports both IGMP
version 1 (IGMP-v1) and IGMP version 2 (IGMP-v2).
At start up, the EMG2306-R10A queries all directly connected networks to gather group
membership. After that, the EMG2306-R10A periodically updates this information. IP multicasting
can be enabled/disabled on the EMG2306-R10A LAN and/or WAN interfaces in the Web Configurator
(LAN; WAN). Select None to disable IP multicasting on these interfaces.
Auto-IP-Change
When the EMG2306-R10A gets a WAN IP address which is in the same subnet as the LAN IP
address 192.168.1.1, Auto-IP-Change allows the EMG2306-R10A to change its LAN IP address to
10.0.0.1 automatically. If the EMG2306-R10A’s original LAN IP address is 10.0.0.1 and the WAN IP

 Loading...
Loading...











