49-6
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using ASDM
OL-20339-01
Chapter 49 Configuring QoS
Configuring QoS
Determining the Queue and TX Ring Limits
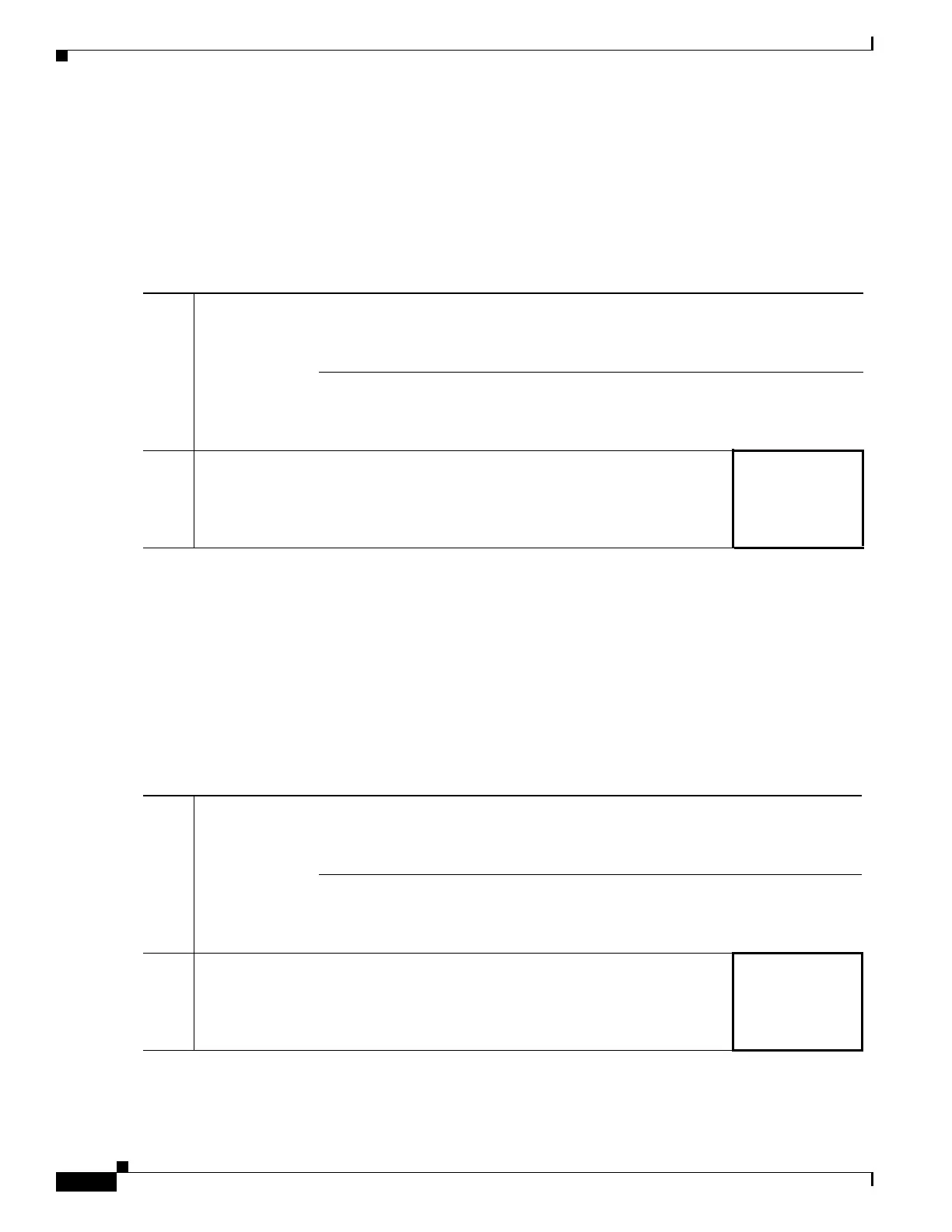
To determine the priority queue and TX ring limits, use the worksheets below.
Table 49-1 shows how to calculate the priority queue size. Because queues are not of infinite size, they
can fill and overflow. When a queue is full, any additional packets cannot get into the queue and are
dropped (called tail drop). To avoid having the queue fill up, you can adjust the queue buffer size
according to the “Configuring the Priority Queue” section on page 49-7.
Table 49-2 shows how to calculate the TX ring limit. This limit determines the maximum number of
packets allowed into the Ethernet transmit driver before the driver pushes back to the queues on the
interface to let them buffer packets until the congestion clears. This setting guarantees that the
hardware-based transmit ring imposes a limited amount of extra latency for a high-priority packet.
Table 49-1 Queue Limit Worksheet
Step 1
__________
Outbound
bandwidth
(Mbps or Kbps)
1
1. For example, DSL might have an uplink speed of 768 Kbps. Check with your provider.
Mbps
x
125
=
__________
# of bytes/ms
Kbps
x
.125
=
__________
# of bytes/ms
Step 2
___________
# of bytes/ms
from Step 1
÷
__________
Average packet
size (bytes)
2
2. Determine this value from a codec or sampling size. For example, for VoIP over VPN, you might use 160 bytes. We recommend 256
bytes if you do not know what size to use.
x
__________
Delay (ms)
3
3. The delay depends on your application. For example, the recommended maximum delay for VoIP is 200 ms. We recommend 500 ms
if you do not know what delay to use.
=
__________
Queue limit
(# of packets)
Table 49-2 TX Ring Limit Worksheet
Step 1
__________
Outbound
bandwidth
(Mbps or Kbps)
1
1. For example, DSL might have an uplink speed of 768 Kbps.Check with your provider.
Mbps
x
125
=
__________
# of bytes/ms
Kbps
x
0.125
=
__________
# of bytes/ms
Step 2
___________
# of bytes/ms
from Step 1
÷
__________
Maximum packet
size (bytes)
2
2. Typically, the maximum size is 1538 bytes, or 1542 bytes for tagged Ethernet. If you allow jumbo frames (if supported for your
platform), then the packet size might be larger.
x
__________
Delay (ms)
3
3. The delay depends on your application. For example, to control jitter for VoIP, you should use 20 ms.
=
__________
TX ring limit
(# of packets)

 Loading...
Loading...