Announces the reachability of one or more flowspec NLRI. When a
BGP speaker receives an UPDATE message with the redirect-to- IP
extended community it is expected to create a traffic filtering rule
for every flow-spec NLRI in the message that has this path as its best
path. The filter entry matches the IP packets described in the NLRI
field and redirects them or copies them towards the IPv4 address
specified in the 'Network Address of Next- Hop' field of the associated
MP_REACH_NLRI.
The redirect-to-IP extended community is valid with any
other set of flow-spec extended communities except if that
set includes a redirect-to-VRF extended community (type
0x8008) and in that case the redirect-to-IP extended
community should be ignored.
Note
Command syntax
redirect {ipv4} next-hop <ipv4 address> {ipv4 address}
Redirect
IPv4
Nexthop
Redirect IP NH0x0800
Define Class, on page 214 explains how you can configure specific match criteria for a class map.
BGP Flowspec Client-Server (Controller) Model and Configuration
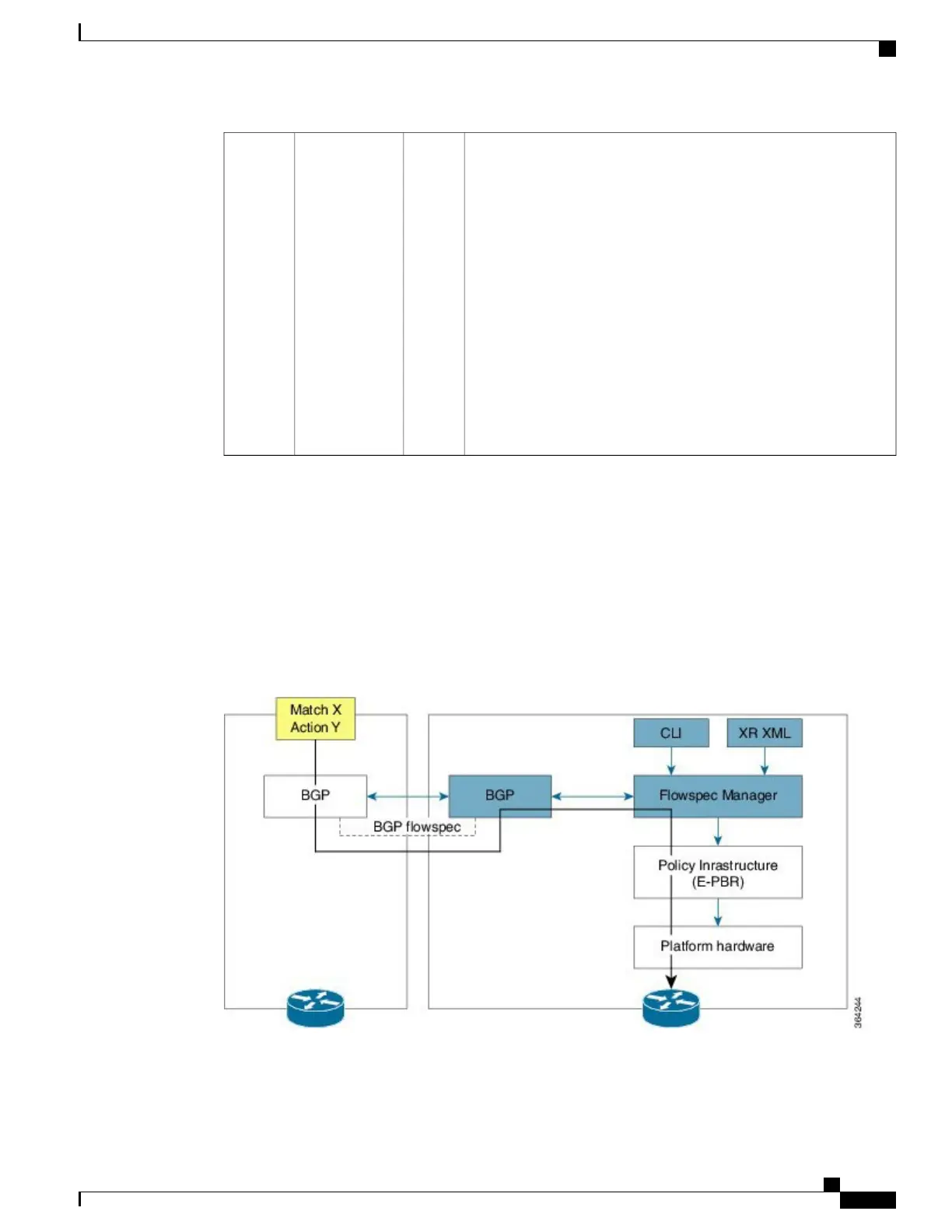
The BGP Flowspec model comprises of a Client and a Server (Controller). The Controller is responsible for
sending or injecting the flowspec NRLI entry. The client (acting as a BGP speaker) receives that NRLI and
programs the hardware forwarding to act on the instruction from the Controller. An illustration of this model
is provided below.
BGP Flowspec Client
Here, the Controller on the left-hand side injects the flowspec NRLI, and the client on the right-hand side
receives the information, sends it to the flowspec manager, configures the ePBR (Enhance Policy-based
Routing) infrastructure, which in turn programs the hardware from the underlaying platform in use.
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Routing Configuration Guide, Release 5.3.x
211
Implementing BGP Flowspec
BGP Flowspec Client-Server (Controller) Model and Configuration

 Loading...
Loading...











