58 Planning the electrical installation
Transformer requirements
These are the transformer requirements for a transformer connected to the AC main
supply of the inverter. This can be a main transformer that connects the inverter to a MV
(or LV) network or an external auxiliary power transformer that connects to an AC supply
(possible with option +G429 or +G430).
• Suitable for the network and inverter AC voltage, current and power. For transformer
dimensioning, refer to Derating on page 95.
• Suitable for use with IGBT inverters
• Degree of protection, temperature limits and lifetime are appropriate for the
environment
• With galvanically isolated high-voltage and low-voltage windings
• Equipped with a static grounded screen between the high-voltage and low-voltage
windings
• The voltage withstand level of the inverter-side winding is at least 2.0 kV against
ground.
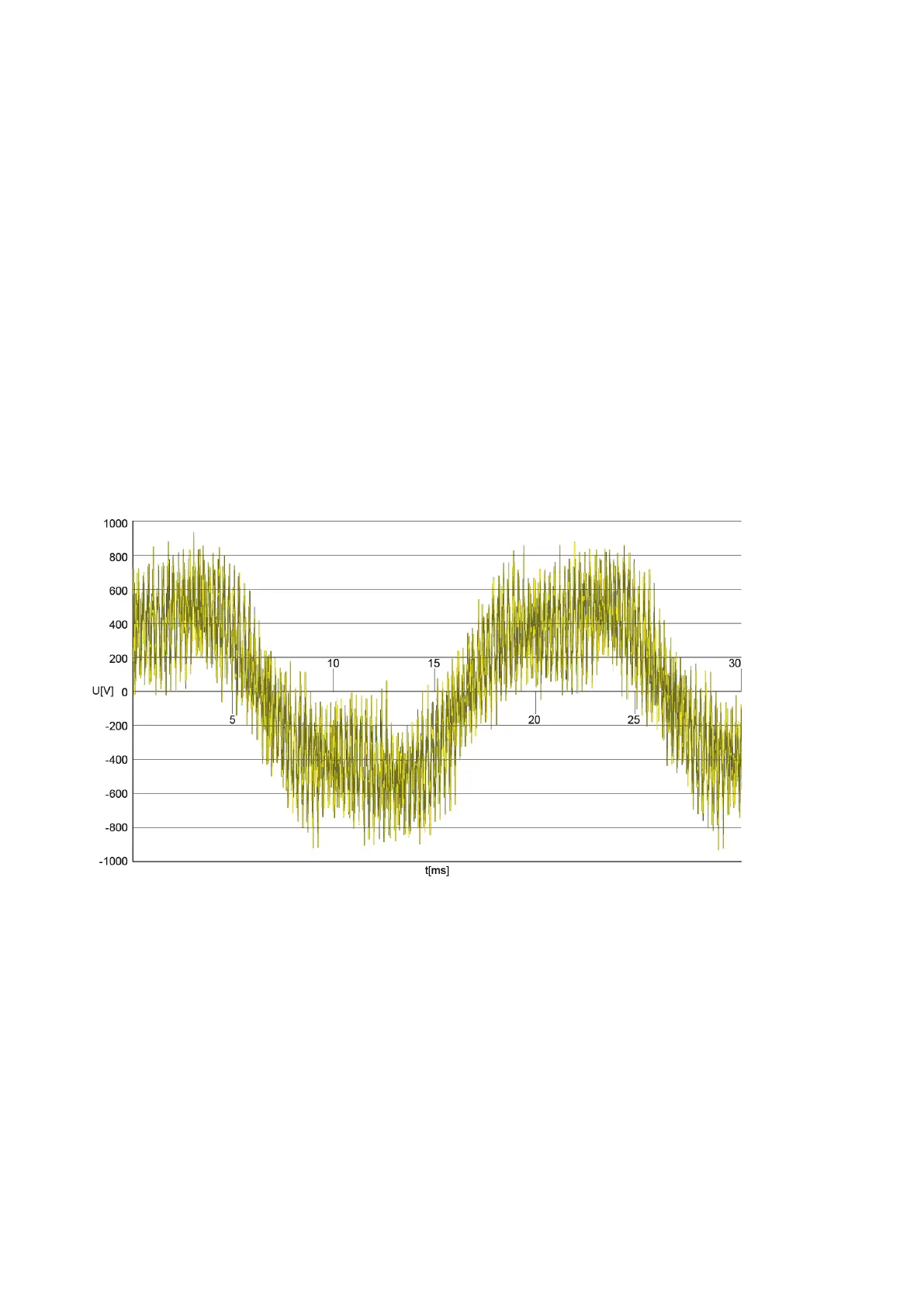
A typical voltage waveform against ground:
• If several inverters are connected to the same transformer:
• Each inverter requires separate galvanically isolated LV windings.
• The impedance between the low-voltage windings must be more than 1.5x the
rated short-circuit impedance.
• Voltage rise time withstand level (du/dt) of the inverter-side winding is at least 1000 V
per microsecond against ground. (In some countries, a 3-winding configuration
corresponds to a 4-winding configuration.)
• Recommended rated short-circuit impedance (X
k
) is 4 to 8%.
• Withstands current DC components of at least 0.5% of the nominal rated current
preferably without using an air gap.
• Withstands the worst case of 3% total harmonic distortion generated by the inverter.
FIMER recommends dimensioning the transformer for at least 5% total harmonic
distortion to withstand possible outside interference from the network.
 Loading...
Loading...