165
IS-IS NSR and IS-IS GR are mutually exclusive. Do not configure them at the same time.
To configure IS-IS NSR:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter IS-IS view.
isis
[ process-id ]
[
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
3. Enable IS-IS NSR.
non-stop-routing
By default, IS-IS NSR is disabled.
IS-IS NSR takes effect on a
per-process basis. As a best
practice, enable NSR for each IS-IS
process.
Configuring BFD for IS-IS
BFD provides a single mechanism to quickly detect and monitor the connectivity of links between
IS-IS neighbors, reducing network convergence time. For more information about BFD, see High
Availability Configuration Guide.
To configure BFD for IS-IS:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
interface
interface-type
interface-number
N/A
3. Enable IS-IS on an interface.
[ process-id ]
N/A
4. Enable BFD on an IS-IS
interface.
isis bfd enable
By default, an IS-IS interface is
not enabled with BFD.
Configuring IS-IS FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and routing loop. IS-IS FRR enables fast
rerouting to minimize the failover time.
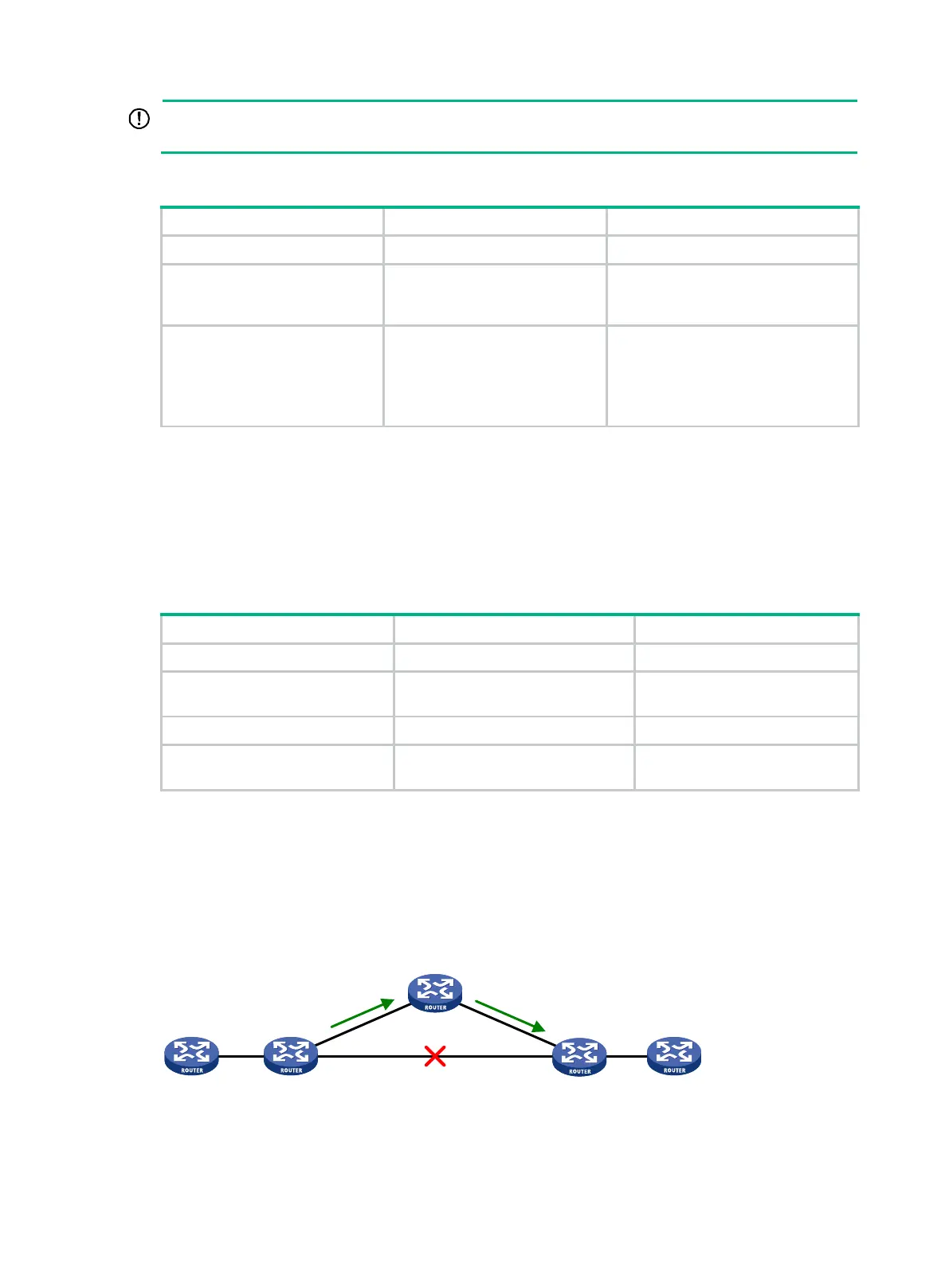
Figure 42 Network diagram for IS-IS FRR
In Figure 42, after you enable FRR on Router B, IS-IS automatically calculates or designates a
backup next hop when a link failure is detected. In this way, packets are directed to the backup next
Router A Router B
Router E
Backup nexthop
: Router C
Nexthop: Router D

 Loading...
Loading...











